Pi controltype: controller definition, Pid control type: controller definition, Pi control – Pyromation Series 610 1_16 DIN User Manual
Page 153: Type: controller definition, Pid control, Figure 43. overlap/deadband pi control, Din controllers & indicators - product manual
1
/
4
-DIN,
1
/
8
-DIN &
1
/
16
- DIN Controllers & Indicators - Product Manual
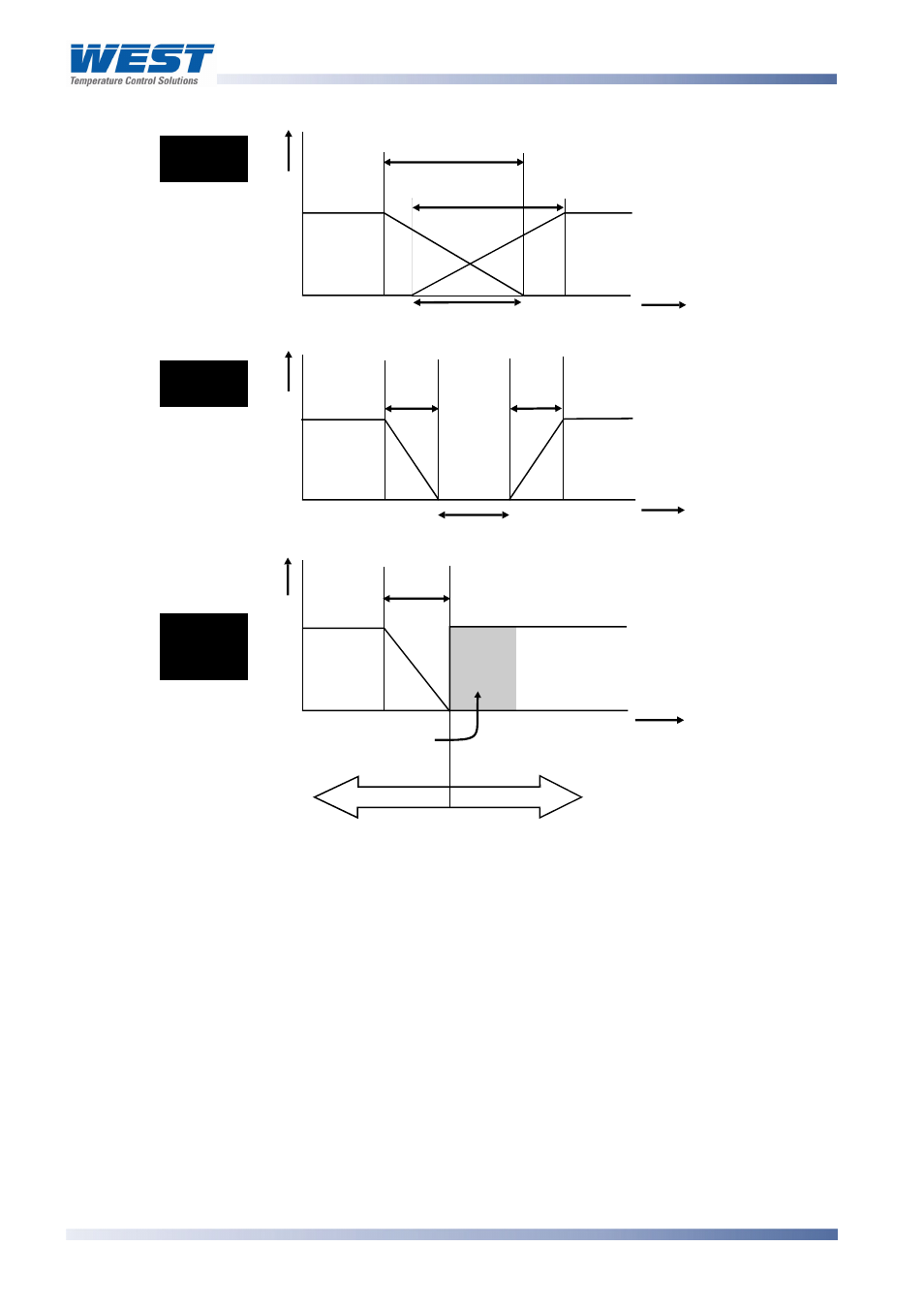
Overlap/Dead
Output 1
Output 1
Output 2
Output 2
Output 2
Process Variable
Process Variable
Process Variable
Proportional Band 1
Proportional
Band 1
Proportional
Band 1
Proportional
Band 2
Proportional Band 2 = 0
Output 1
Output 1
Output 1
Output 1
Output 2
Output 2
Output 2
Overlap
(positive value)
Deadband
(negative value)
Negative values
Positive values
O
WIT
VERLAP
H PID
DEA
WIT
DBAND
H PID
OVERL
DEA
WITH O
AP &
DBAND
N/OFF
Ou
tpu
t P
o
wer
(
%
)
Ou
tpu
t P
o
wer
(
%
)
Ou
tpu
t P
o
wer
(
%
)
Ou
tpu
t 2
ON
Ou
tpu
t 2
OF
F
ON/OFF Differential
Proportional Band 2
Figure 43.
Overlap/Deadband
PI Control
Type: Controller Definition
Proportional and Integral (PI) Control is used to control Modulating Valves. It is similar to PID
Control, but without Derivative (Rate) action that causes excessive valve movement.
Also refer to Modulating Valve, PID Control, Rate, Tuning and Valve Motor Drive Control.
PID Control
Type: Controller Definition
Proportional Integral and Derivative control maintains accurate and stable levels in a process
(e.g. temperature control). It avoids the oscillation characteristic of On-Off control by
continuously adjusting the output to keep the process variable stable at the desired setpoint.
Also refer to Control Action, Control Type, Automatic Reset, Controller, Manual Mode, On-Off
Control, PI Control, Primary Proportional Band, Process Variable, Rate, Secondary
Proportional Band, Setpoint, Tuning and Valve Motor Drive Control.
Page 148
Glossary
59305, Issue 6 – March 2006
