Pid m – IDEC MicroSmart Pentra User Manual
Page 28
PID M
ODULE
M
AIN
F
UNCTIONS
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
4-5
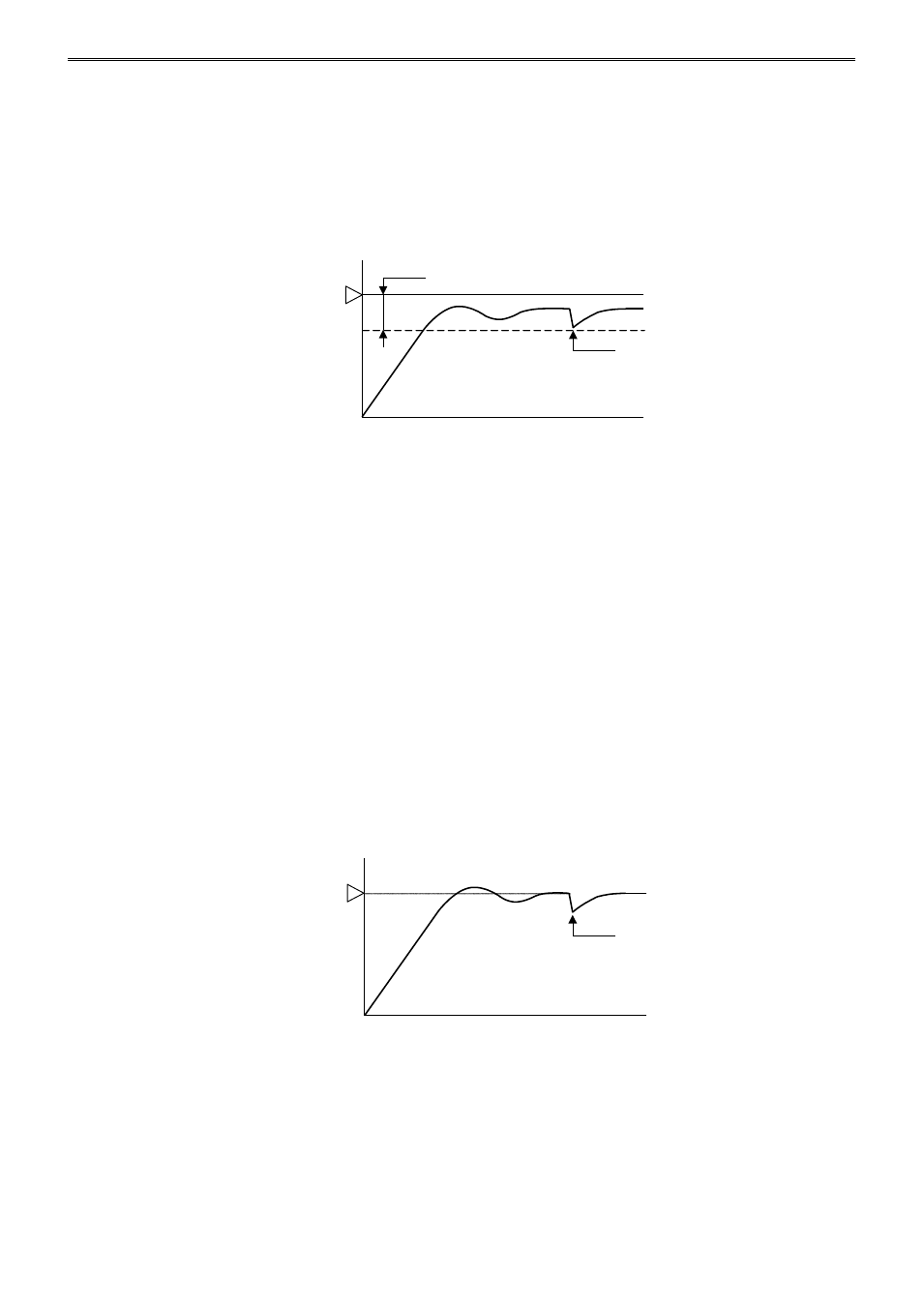
PD Control Action (Proportional + Derivative Action)
Compared with P action, the response to rapid temperature change due to disturbance is faster, the
temperature control can be stabilized in a shorter time, and transitional response characteristic can be
improved in PD control action. PD control action is suitable for the processes in which the temperature
rapidly changes.
If the integral time of the PID module parameter is set to 0, the control action becomes the PD control
action.
• If the derivative time is shortened, the derivative action becomes weak. The response to the rapid
temperature change becomes slower. Because the action to suppress the rapid temperature rises
becomes weaker, the time for the process variable (PV) to reach the set point (SP) is shortened;
however, overshoot can occur.
• If the derivative time is extended, the derivative action becomes strong. The response to the rapid
temperature change becomes faster. Because the action to suppress the rapid temperature rises
becomes strong, the time for the process variable (PV) to reach the set point (SP) is extended; however,
overshoot can be decreased.
The offset caused by the PD control action can be corrected by configuring the reset value. The reset
value can be automatically calculated by the auto-reset function.
PID Control Action (Proportional + Integral + Derivative Action)
P action suppresses the overshoot and the hunting, I action corrects the offset, and D action corrects
rapid temperature change due to disturbance in shorter time. Thus, using PID control action, optimal
temperature control can be performed. The proportional band, integral time, derivative time, and ARW
can be automatically calculated by the auto-tuning (AT).
Set Point (SP)
Temperature
Time
Proportional Band
Disturbance
Set Point (SP)
Temperature
Time
Disturbance
