Re-dhcp authentication process – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 6
5
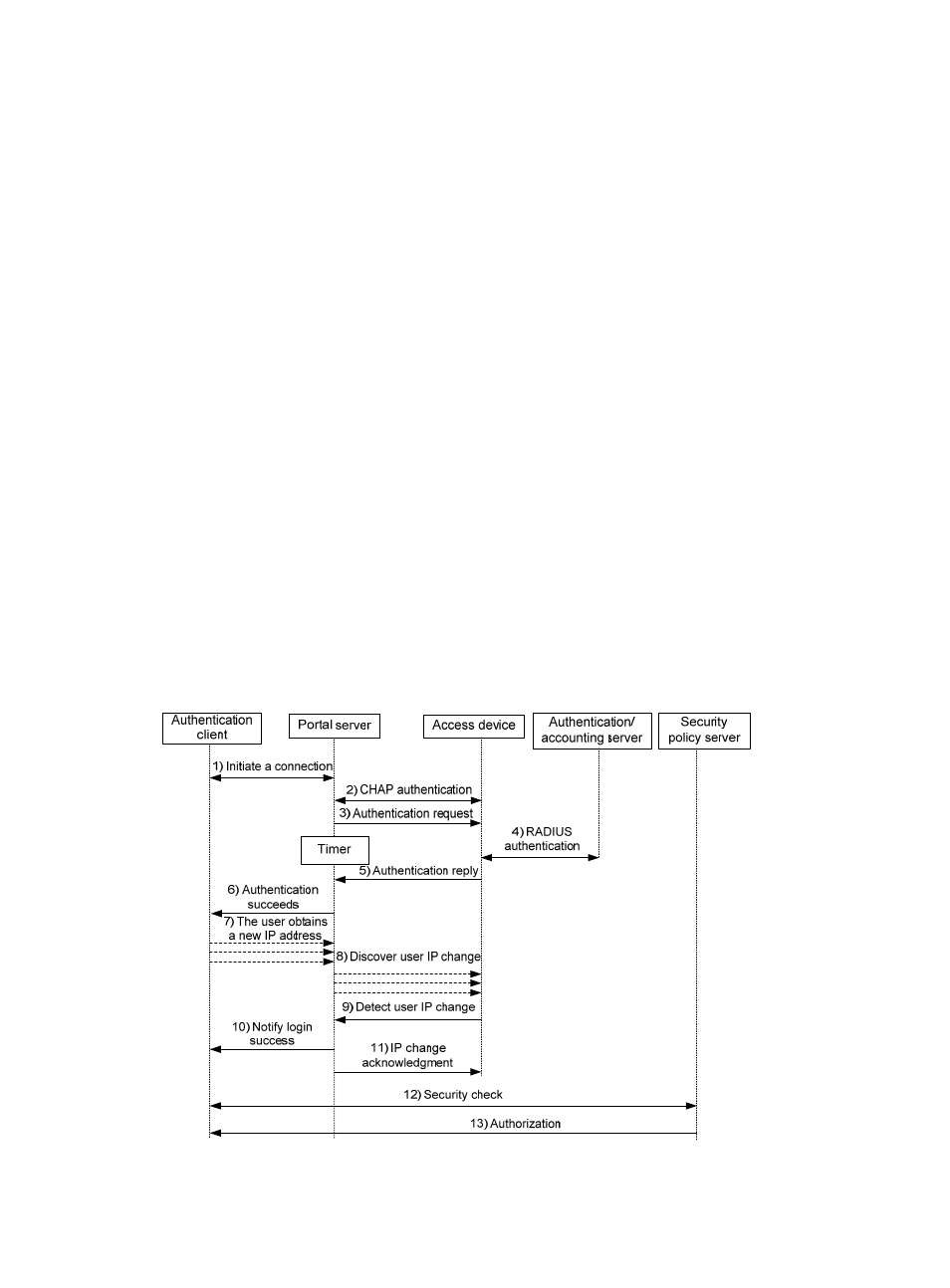
The direct authentication/cross-subnet authentication process is as follows:
Step1
An authentication client initiates authentication by sending an HTTP request. When the HTTP packet
arrives at the access device, the access device allows it to pass if it is destined for the portal server or a
predefined free website, or redirects it to the portal server if it is destined for other websites. The portal
server pushes a web authentication page to the user and the user enters the username and password.
Step2
The portal server and the access device exchange Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP)
messages. For Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) authentication, this step is skipped.
Step3
The portal server assembles the username and password into an authentication request message and
sends it to the access device. Meanwhile, the portal server starts a timer to wait for an authentication
acknowledgment message.
Step4
The access device and the RADIUS server exchange RADIUS packets to authenticate the user.
Step5
The access device sends an authentication reply to the portal server.
Step6
The portal server sends an authentication success message to the authentication client to notify it of
logon success.
Step7
The portal server sends an authentication reply acknowledgment message to the access device.
With extended portal functions, the process includes two additional steps:
Step8
The security policy server exchanges security check information with the client to check whether the
authentication client meets the security requirements.
Step9
Based on the security check result, the security policy server authorizes the user to access certain
resources, and sends the authorization information to the access device. The access device then controls
accesses of the user based on the authorization information.
Re-DHCP authentication process
Figure 3 Re-DHCP authentication process
