Layer 3 portal authentication process – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 5
4
•
Direct authentication
Before authentication, a user manually configures a public IP address or directly obtains a public IP
address through DHCP, and can access only the portal server and predefined free websites. After
passing authentication, the user can access the network resources. The process of direct authentication
is simpler than that of re-DHCP authentication.
•
Re-DHCP authentication
Before authentication, a user gets a private IP address through DHCP and can access only the portal
server and predefined free websites. After passing authentication, the user is allocated a public IP
address and can access the network resources. No public IP address is allocated to those who fail
authentication. This solves the problem about IP address planning and allocation and proves to be useful.
For example, a service provider can allocate public IP addresses to broadband users only when they
access networks beyond the residential community network.
•
Cross-subnet authentication
Cross-subnet authentication is similar to direct authentication, but it allows Layer 3 forwarding devices to
be present between the authentication client and the access device.
In direct authentication, re-DHCP authentication, and cross-subnet authentication, the IP address of a
client is used for identification of the client. To control packet forwarding, the access device uses ACLs
assigned to clients based on the IP addresses of the clients. Because no Layer 3 devices are present
between the authentication clients and the access device in direct authentication and re-DHCP
authentication, the access device can directly learn the MAC addresses of the clients, and thus can
control the forwarding of packets from clients in a more granular way by also using the learnt MAC
addresses.
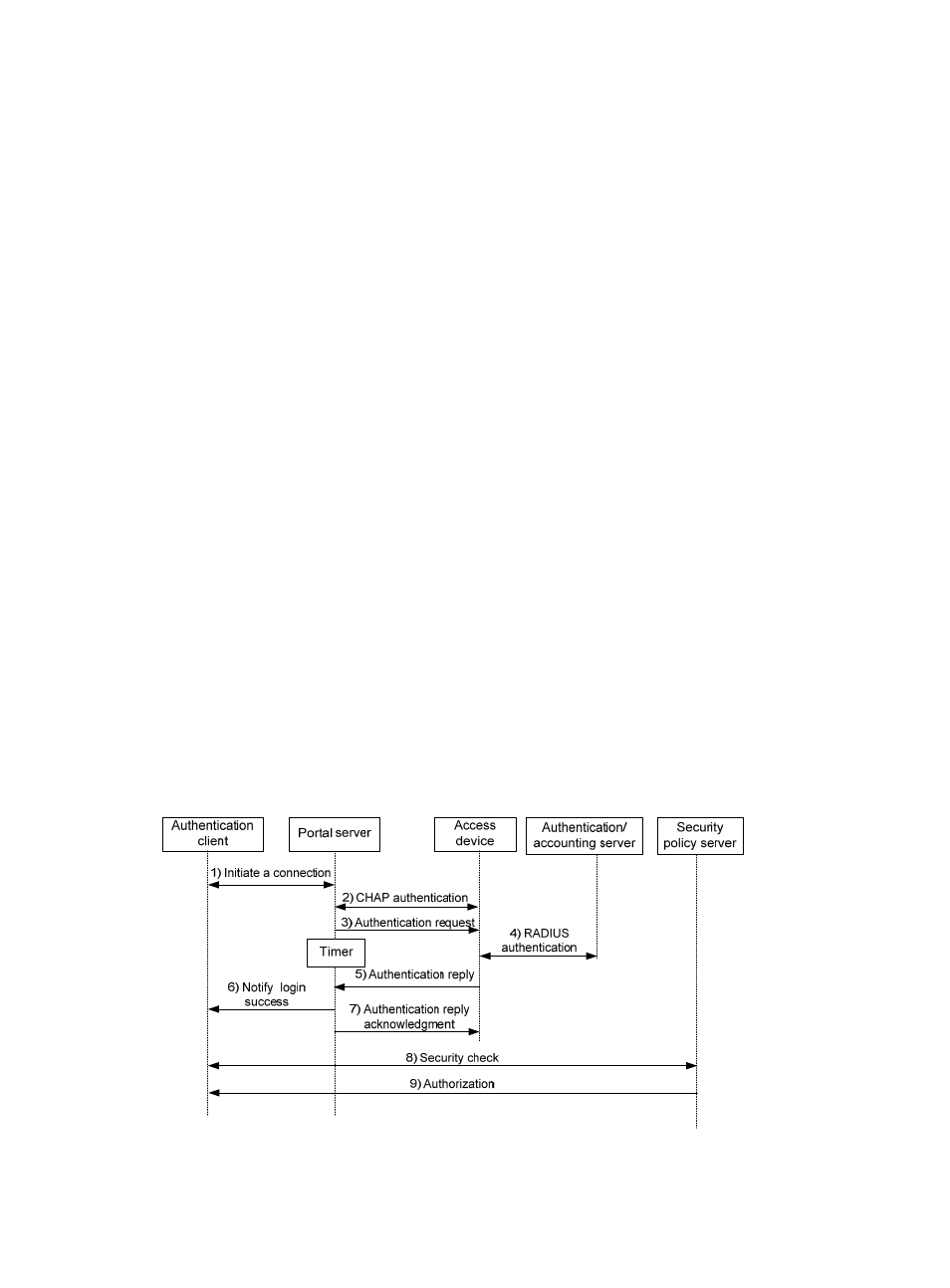
Layer 3 Portal Authentication Process
Direct authentication and cross-subnet authentication share the same authentication process, while
re-DHCP authentication has a different process because of the presence of two address allocation
procedures.
Direct authentication/cross-subnet authentication process
Figure 2 Direct authentication/cross-subnet authentication process
