Configuration procedure – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 174
10
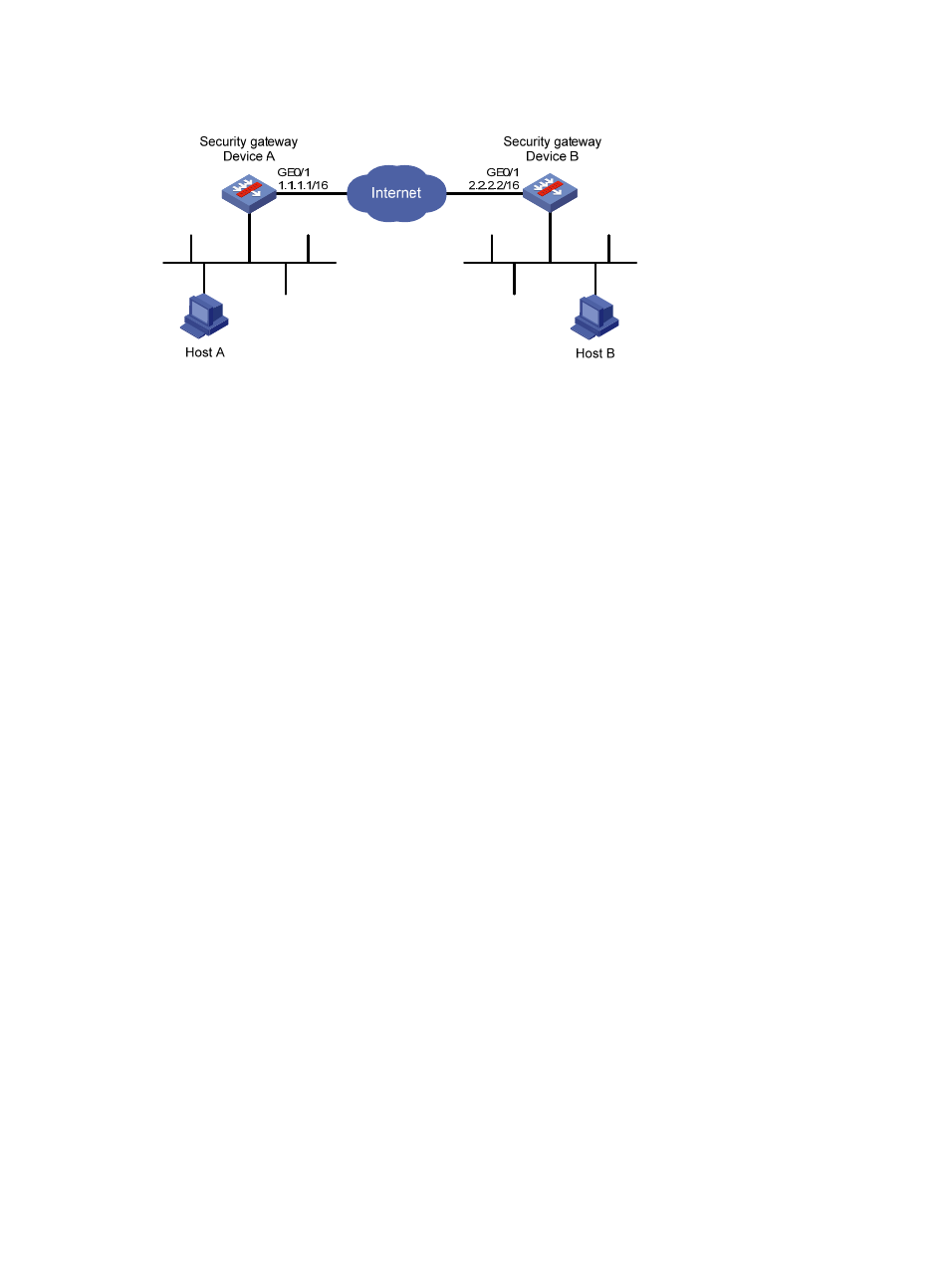
Figure 11 Network diagram for IKE configuration
Configuration procedure
1.
Configure Device A
# Configure an IKE peer.
[DeviceA] ike peer peer
[DeviceA-ike-peer-peer] pre-shared-key abcde
[DeviceA-ike-peer-peer] remote-address 2.2.2.2
[DeviceA-ike-peer-peer] quit
# Create an IKE proposal numbered 10.
[DeviceA] ike proposal 10
# Set the authentication algorithm to MD5.
[DeviceA-ike-proposal-10] authentication-algorithm md5
# Set the authentication method to pre-shared key.
[DeviceA-ike-proposal-10] authentication-method pre-share
# Set the ISAKMP SA lifetime to 5,000 seconds.
[DeviceA-ike-proposal-10] sa duration 5000
2.
Configure Device B
# Configure an IKE peer.
[DeviceB] ike peer peer
[DeviceB-ike-peer-peer] pre-shared-key abcde
[DeviceB-ike-peer-peer] remote-address 1.1.1.1
With the configuration, Device A and Device B should be able to perform IKE negotiation. Device A is
configured with proposal 10, which uses the authentication algorithm of MD5; Device B has only a
default IKE proposal, which uses the authentication algorithm of SHA. Therefore, Device B has no
proposal matching proposal 10 of Device A, and the two devices have only one pair of matching
proposals, namely the default IKE proposals. In addition, the two devices are not required to have the
same ISAKMP SA lifetime; they will negotiate one.
