Operation of ike – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 166
2
PFS
The Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) feature is a security feature based on the DH algorithm. It guarantees
that decryption of a key makes no impact on the security of other keys because the keys have no
derivative relations. For IPsec, PFS is implemented by adding an additional key exchange at IKE
negotiation phase 2.
Operation of IKE
IKE negotiates keys and establishes SAs for IPsec in two phases:
1.
Phase 1: The two peers establish an ISAKMP SA, a secure, authenticated channel for
communication. In this phase, two modes are available: main mode and aggressive mode.
2.
Phase 2: Using the ISAKMP SA established in phase 1, the two peers negotiate to establish IPsec
SAs.
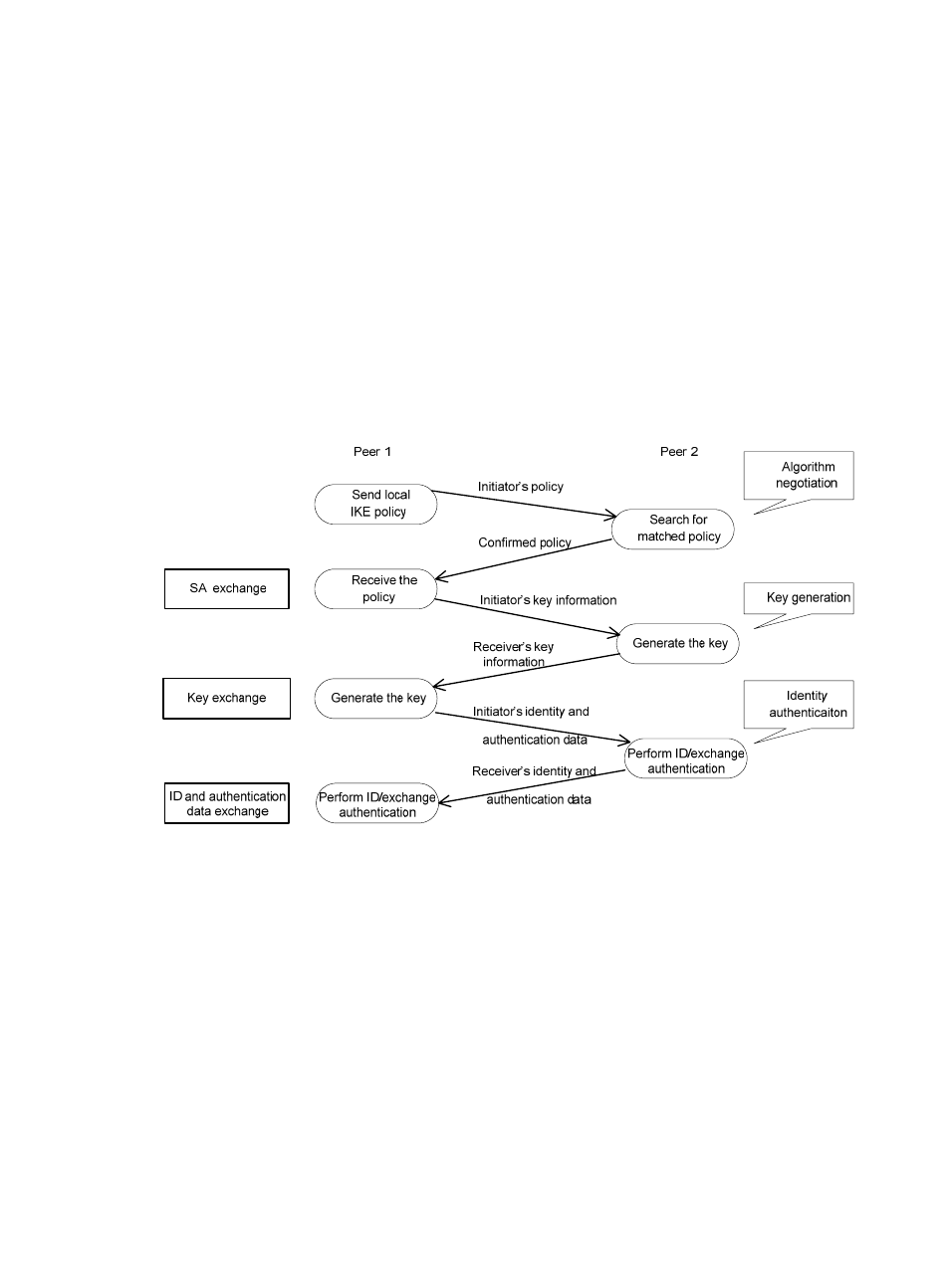
Figure 9 IKE exchange process in main mode
As shown in
, the main mode of IKE negotiation in phase 1 involves three pairs of messages:
•
SA exchange, used for negotiating the security policy.
•
Key exchange, used for exchanging the Diffie-Hellman public value and other values like the
random number. Key data is generated in this stage.
•
ID and authentication data exchange, used for identity authentication and authentication of data
exchanged in phase 1.
The main difference between main mode and aggressive mode is that aggressive mode does not provide
identity protection and only exchanges the above three messages. As aggressive mode exchanges less
information and features higher negotiation speed, it is better for scenarios where the requirement for
identity protection is lower. For scenarios with higher requirement for identity protection, main mode is
recommended.
