Functions of ike, Relationship between ike and ipsec, Protocols and standards – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 167: Ike configuration task list
3
Functions of IKE
•
IKE automatically negotiates IPsec parameters such as the keys, reducing the manual configuration
complexity greatly.
•
IKE always performs DH exchange when establishing an SA, ensuring that each SA has a key with
no relation with any other key.
•
IPsec uses the sequence number, a 32-bit value in the AH or ESP header, for anti-replay. If the value
overflows, a new SA needs to be established for anti-replay, in which procedure IKE is required.
•
IKE allows for end-to-end dynamic authentication.
•
Identity authentication and management of peers influence IPsec deployment. A large-scale IPsec
deployment needs the support of certificate authorities (CAs) or other institutes which manage
identity data centrally.
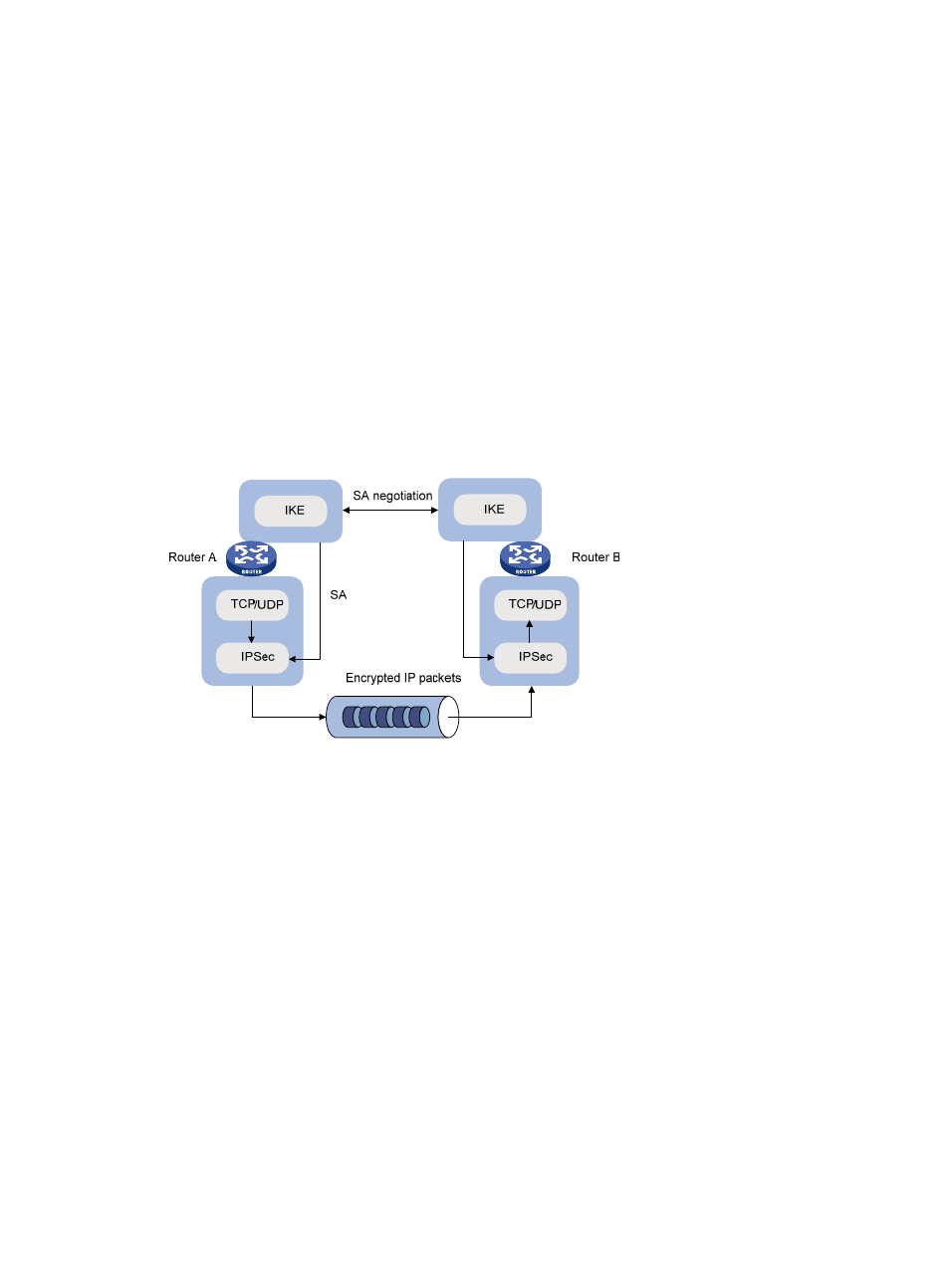
Relationship Between IKE and IPsec
Figure 10 Relationship between IKE and IPsec
illustrates the relationship between IKE and IPsec:
•
IKE is an application layer protocol using UDP and functions as the signaling protocol of IPsec.
•
IKE negotiates SAs for IPsec and delivers negotiated parameters and generated keys to IPsec.
•
IPsec uses the SAs set up through IKE negotiation for encryption and/or authentication of IP
packets.
Protocols and Standards
These protocols and standards are relevant to IKE:
•
RFC 2408: Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP)
•
RFC 2409: The Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
•
RFC 2412: The OAKLEY Key Determination Protocol
IKE Configuration Task List
Prior to IKE configuration, you need to:
