Measurement Computing eZ-TOMAS rev.11.0 User Manual
Page 34
XY
Pair
associates 2 probes on a bearing. Typically, probe pairs are located 90 degrees apart.
Orbit displays require a Channel Pair.
Brg Clear
Bearing Clearance is measured in the instrument’s engineering units. You can
optionally overlay the bearing clearance circle onto an orbit display or shaft centerline.
Brg Start
Bearing Start is the location of the shaft relative to the bearing when the machine is at
mechanical rest. Three possible locations are taken into consideration: Bottom, Center,
and Top. For horizontal shafts, a bearing start of bottom is typical, due to gravity;
However, in some situations mechanical linkage can result in a bearing start with the shaft
at the top. For shafts that are oriented vertically, a bearing start of center is likely.
Default
Tach
The "Default Tach" column allows you to define the Tach Preference for each channel.
Thus, on Gauge Display and Plot Display eZ-TOMAS can show 1x values relative to the
preferred tach. When two or more tachs are defined eZ-TOMAS computes spectral data
relative to each. For example, with two tachs: If Tach 1 measures 3000 rpm and Tach 2
measures 4500 rpm eZ-TOMAS computes 1xA values for each. With the RPMs given,
the resulting 1x Frequency values are 50 Hz for Tach 1 and 75 Hz for Tach2.
Clicking the Default Tach column brings up a pull-down list which indicates the
tachometer channels available for use as reference [for the currently displayed data].
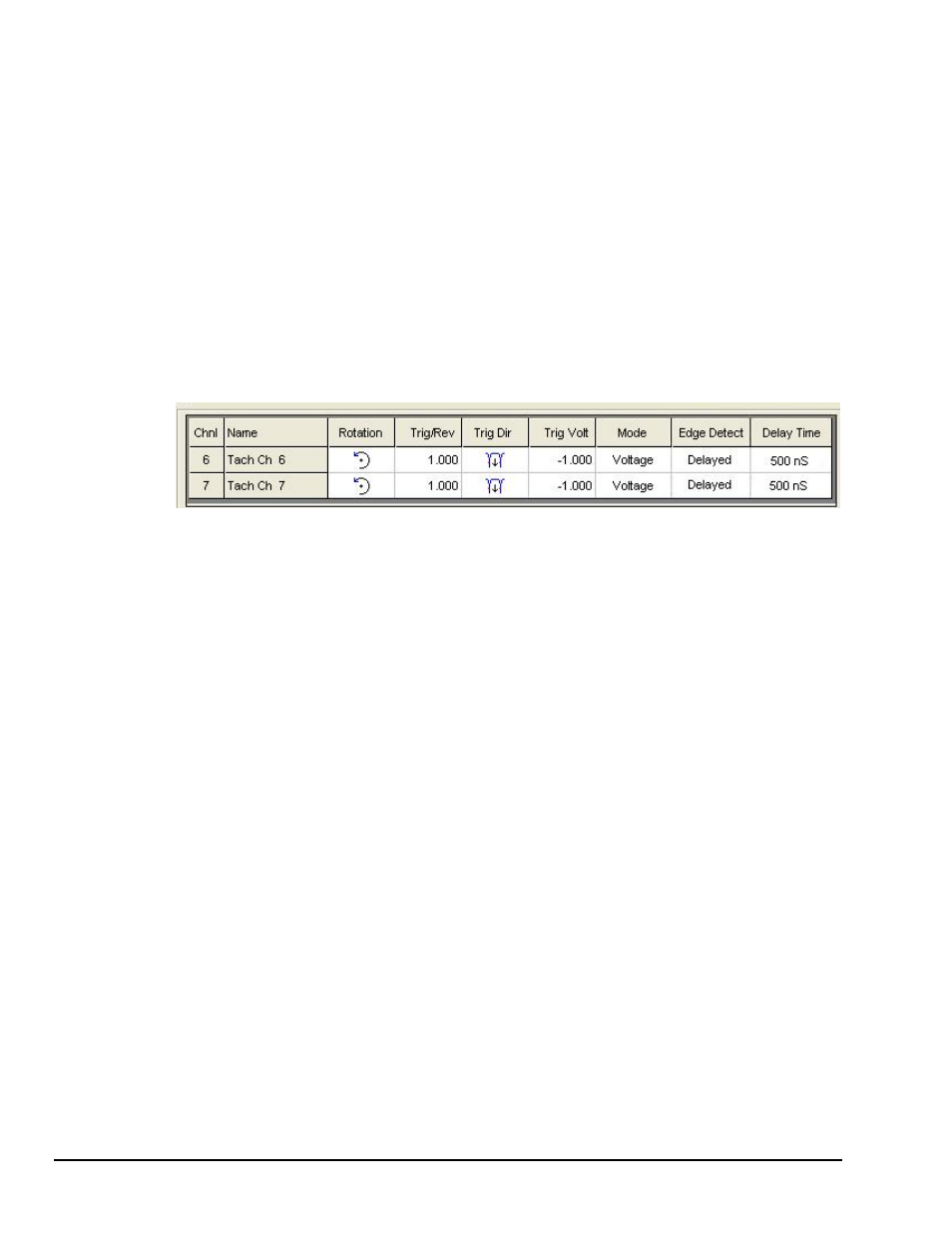
Tach Section of the Input Channels Tab
Rotation
is the shaft’s rotation direction, either clockwise or counter-clockwise. The direction
indicated is as viewed from the driver end of the machine train.
Trig/Rev
is the number of pulses per 360 degree revolution. (Default: 1)
Trig Dir
is the “negative’ [down arrow] or “positive” [up arrow] direction of the moving shaft.
Trig Volt
defines the Tach pulse for tach signals. A keyway will generate a Negative Tach pulse.
Typical Tach signals will generate at least a 1 V pulse. You can check the voltage value
using a Time display.
Mode
Used to select one of three available modes: Voltage, Counter, or Period.
Edge Detect
Edge Detect
– Edge Detect is short for “Tach Pulse Edge Detection.” The term
pertains to detecting the rising or falling edge of a tachometer pulse using either an
“Immediate” or “Delayed” mode.
Immediate Edge Detection
(“Before Stable”)
– “Immediate” is one of two Edge
Detect modes. The term is synonymous with “Before Stable.” If “Immediate” edge
detection is selected a tach pulse will be recognized on any instantaneous measurement
that meets the trigger level criteria. In this setup the “Delay Value” is the amount of time
before the next tach pulse can be recognized. If a keyway is being used as a tach trigger
you must calculate the minimum pulse width, based on the maximum RPM rate
expected.
Delayed Edge Detection
(“After Stable”)
– “Delayed” is one of two Edge Detect
modes. The term is synonymous with “After Stable.” If “Delayed” edge detection is
selected a tach pulse will be recognized when the measurement meets the trigger criteria
for the specified duration. In this setup the “Delay Value” defines the length of time that
the trigger criteria must be stable before the tach pulse will be recognized.
Delay Time:
One of several time settings between 500 ns and 25.5 ms. The delay time is used in
conjunction with edge detect and is used to optimize noise reduction.
4-6 Edit Menu
947394
eZ-TOMAS
