14 firmware application information, 1 sag detection, 2 temperature measurement – Maxim Integrated 71M6521BE Energy Meter IC Family Software User Manual
Page 79: Firmware application information, Sag detection, Temperature measurement, Dip sag
71M652X Software User’s Guide
Revision 1.7
TERIDIAN Proprietary
79 of 138
© Copyright 2005-2007 TERIDIAN Semiconductor Corporation
5.14 FIRMWARE APPLICATION INFORMATION
5.14.1
Sag Detection
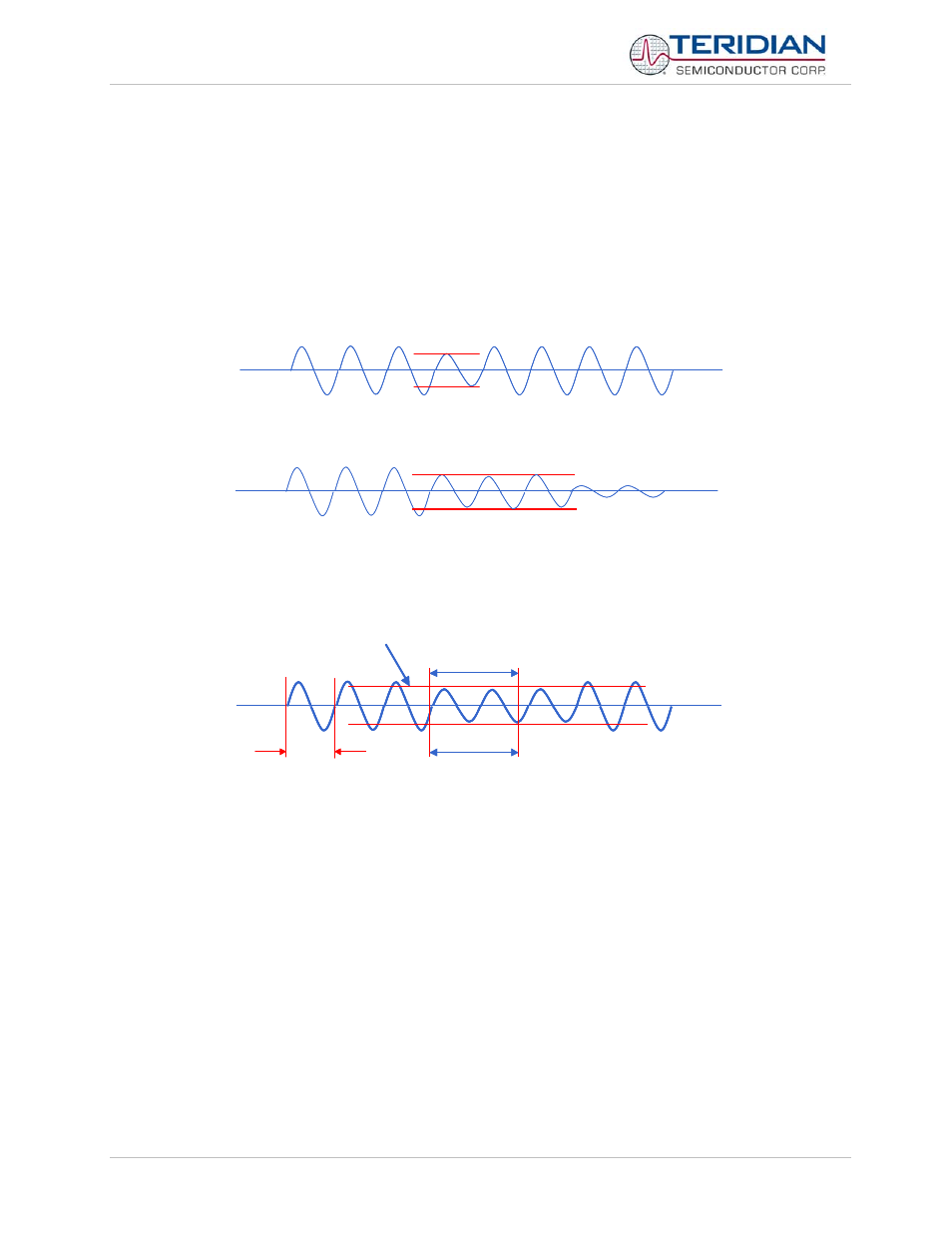
A sag is defined as an undervoltage condition that persists for more than one period. A shorter undervoltage condition
is called a dip (see Figure Figure 5-22). The occurrence of sags can announce an impending loss of power. Since
accumulated energy values etc. in the meter will have to be saved to non-volatile memory in the case of loss of power,
a sag can be used to initiate data saving operations. Some applications may instead save or count the sag event for
the purpose of recording power quality data.
dip
sag
Figure 5-22: Sag and Dip Conditions
Sag detection is performed by the CE, based on the CE DRAM registers SAG_THR and SAG_CNT. SAG_THR defines
the threshold which the input voltage has to be continuously below, and SAG_CNT defines the number of samples
required to trigger the sag bit (see Figure 5-23).
16.67ms
SAG_THR
SAG_CNT
84 samples
16.67ms
16.67ms
SAG_THR
SAG_CNT
84 samples
Figure 5-23: Sag Event
When the CE detects a sag that meets the sag conditions specified in SAG_THR and SAG_CNT on one of the input
voltage channels, it will reflect this in the corresponding bit (SAG for single-phase, or SAG_A, SAG_B, SAG_C for poly-
phase) of the CE STATUS Word. See the CE Interface section in the 652X Data Sheet for details.
It is up to the MPU firmware to decide what is to be done in case a sag is detected. The Demo Code does not have any
provisions for actions due to sags detected by the CE.
5.14.2
Temperature Measurement
The temperature output of the on-chip temperature sensor (TEMP_RAW) is provided by the CE in CE DRAM location
0x7B. The relative chip temperature deltaT (MPU location 0x20) is derived by subtracting the raw temperature from the
nominal temperature (TEMP_NOM) and multiplying it with a constant factor. Thus, once the raw temperature obtained
at a known environmental temperature is stored in TEMP_NOM, deltaT will always reflect the deviation from nominal
temperature. The scaling is in tenths of Centigrades, i.e. a reading of 75 means that the measured temperature is
7.5°C higher than the reference temperature.
