Rockwell Automation AutoMax Enhanced Ladder Editor User Manual
Page 78
CĆ2
Using the PreĆDefined Error Handling Variables
Use the following Boolean variables to help you handle error conditions. Use
error_eno and no_error_log for output (read and write) parameters. You can use
task_error as either an input (readĆonly) or output (read and write) parameter:
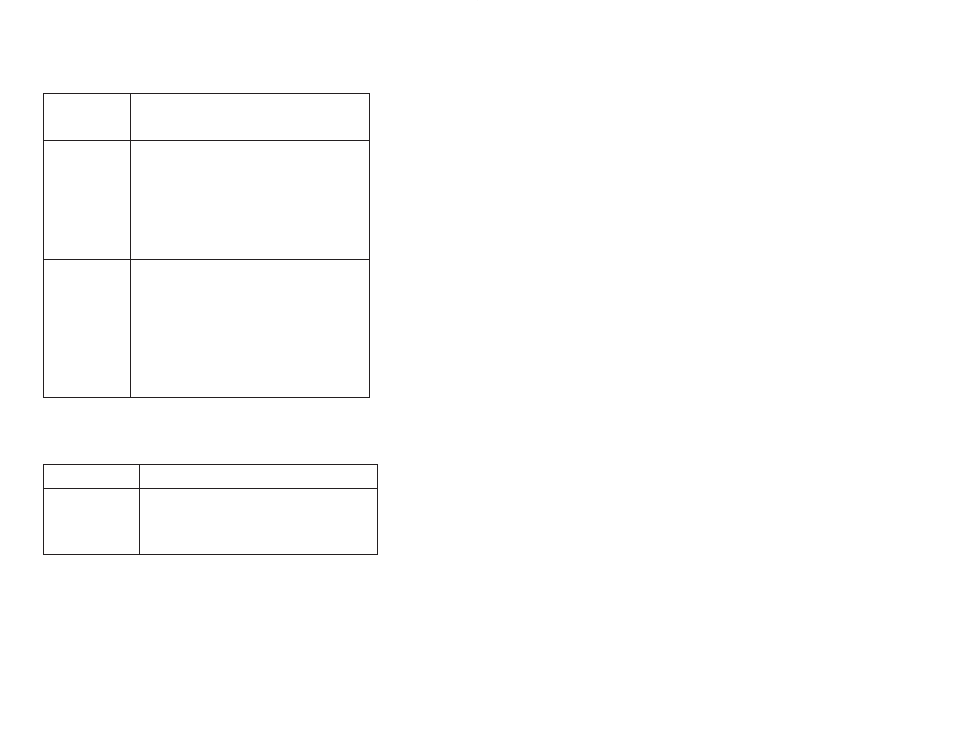
D task_error
This variable is set true whenever an error is found.
Monitor the bit to see if an error occurs during execuĆ
tion and clear it by using the ladder logic. This bit is
set true even if errors are not being logged.
D error_eno
Use this bit to determine the value ENO outputs will
have if the instruction has an error. The default value
is false, which disables any instructions that are conĆ
nected to the ENO output, possibly making math
expressions incomplete. When you set error_eno
true, you can continue the execution of the logic conĆ
nected to the ENO output even if the instruction
block had an error.
This variable can be changed during ladder logic
program execution.
D no_error_log
Set this variable true to prevent errors from being
entered into the program error log or being seen by
the rung monitor. Only one error is logged for each
instruction per program scan; however, you may
want to prevent the errors encountered on certain
instructions from being entered into the error log.
The default state for the no_error_log is false. You
can suppress error messages for a group of rungs
by changing this variable during program execution.
STOP ALL errors and parameter limit errors for AR1,
AR2, and ARC instructions are still inserted into the
error log when the no_error_log variable is true.
Using the PreĆDefined Ladder Execution Time Variables
Use the following double integer variables to help you check and monitor the
program's execution time. Only use these variables as input parameters.
D task_usec_max
Use this variable to monitor the maximum execution
time (in
µ
s) for the current program.
D task_usec_now
Use this variable to monitor the latest execution time
(in
µ
s) of the current program. The execution time is
the real clock" time it took the program to run from
start to finish. It includes the execution time for higher
priority programs and interrupt service routines if
they run while your program is running.
To reset these times, write a value of 0 into the variable.
