Addressing dh and dh+ data transfers chapter 5 – Rockwell Automation 1775-S5_SR5,D17756.5.5 User Manual PLC-3 FAMILY I/0 User Manual
Page 90
Addressing DH and DH+ Data Transfers
Chapter 5
5-16
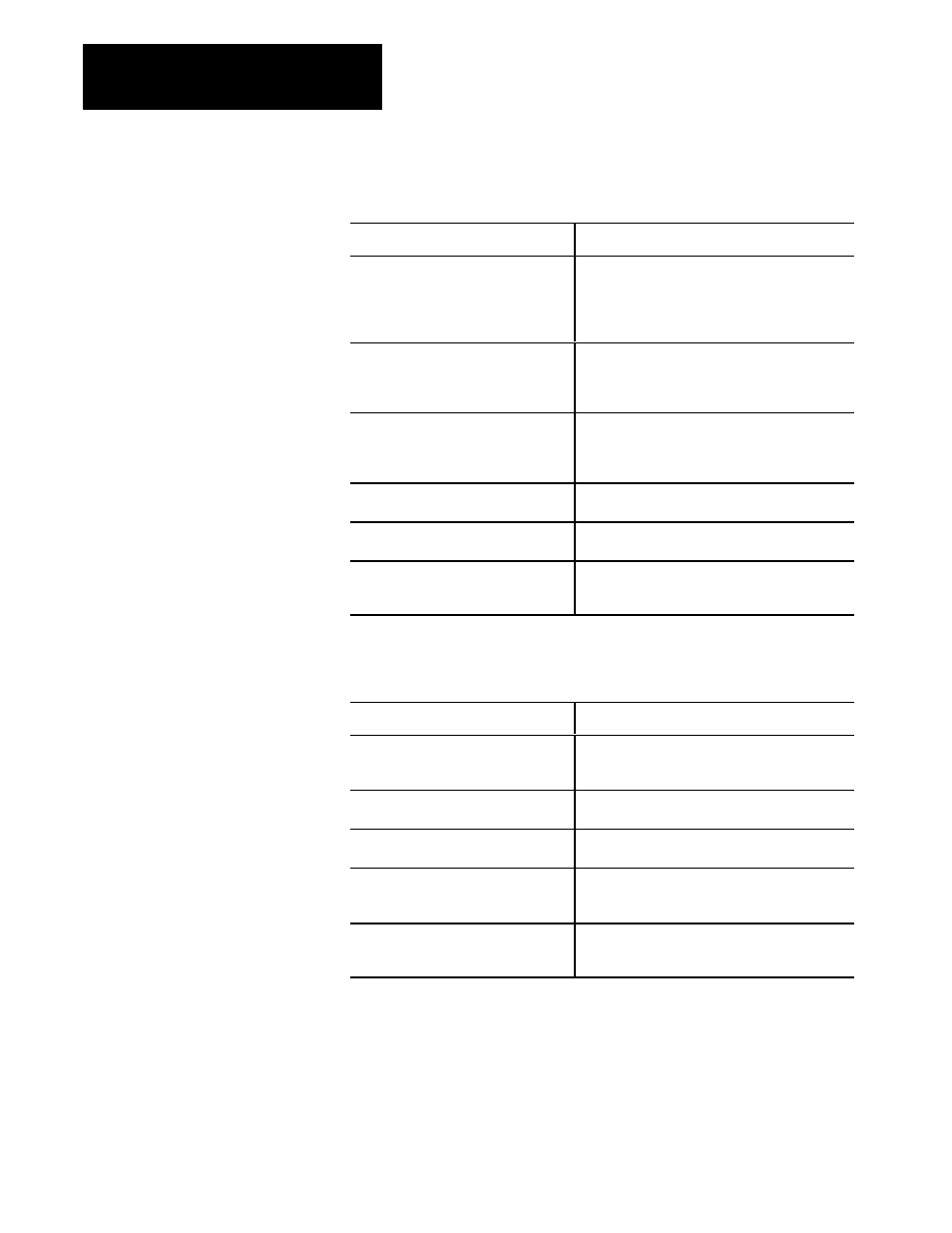
Table 5.C
PLCĆ3 Logical Binary Addressing
Binary Addressing
Description
#H02$F0:0 = $F0:0,6
write 6 contiguous words beginning with floating
point file 0, word 0 to remote station 2 floating point
section file 0 word 0. A total of three complete
floating point words (2 words each) are being
transferred.
$D0:0 = #H054$E0.0.0.14
read the year from the system clock of remote
station 45 and store the data in decimal file 0, word
0. Writes to nonĆdata table addresses are not
allowed.
#H014$T0:5 = $T4,2
write two words beginning with timer four to remote
station 14 timer 5. In this example, the data in
$TCTL:4 and $TPRE:4 is written to $TCTL:5 and
$TPRE:5 respectively in the remote station.
#H046$N0:0 = $N4:1
write integer file 4, word 1 into remote station 46's
integer file 0, word 0.
#H055$N1 = $N0
the entire integer file 0 is written into integer file 1 of
remote station 55. The file sizes must be identical.
#H02$H0:0 = $H0:0,6
high order integers are treated as 32 bits or 2
words. This example writes 6 complete high order
integers to remote station 2.
Table 5.D
Logical ASCII Data Type Addressing
Data Type Addressing
Description
$N0:10 =
#H003$”N55:0”,100
read 100 words from remote station 3 beginning
with integer file 55, word 0 and store the data in
integer file 0, beginning with word 10.
$D0:0 = #H055$”N0:0”
read integer file 0, word 0 from remote station 55
and store data in decimal file 0, word 0.
#H020$”B10:10” = 15
write a decimal value of 15 into binary file 10, word
10 of remote station 20.
#H014$”T5” = $T4,4
write the contents of four complete timers (three
words each) beginning with timer 4 into remote
station 14 beginning with timer 5.
#H02$”F0:0” = $F0:0,6
write the contents of 6 complete floating point
numbers (two words each) into remote station 2
beginning with floating point number 0.
