JLG 450A_AJ Series II Service Manual User Manual
Page 154
SECTION 3 - CHASSIS & TURNTABLE
3-104
– JLG Lift –
3121180
FUEL METERING SYSTEM PURPOSE
The basic function of the air/fuel metering system is to
control air/fuel delivery to the engine. Fuel is delivered to
the engine by individual fuel injectors mounted in the
intake manifold near each intake valve.
The main control sensor is the heated oxygen sensor
(H02S) located in the exhaust system. The H02S tells the
ECM how much oxygen is in the exhaust gas. The ECM
changes air/fuel ratio to the engine by controlling the
amount of time the fuel injector is “ON.” The best mixture
to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7 parts of air to 1 part
of gasoline by weight, which provides the most efficient
combustion. Because of constant measuring and adjust-
ing of the air/fuel ratio, the fuel injection system is called a
“closed loop” system.
The ECM monitors signals from several sensors in order
to determine the fuel needs of the engine. Fuel is deliv-
ered under one of several conditions called “modes.” All
modes are controlled by the ECM. Refer to “Open Loop
and Closed Loop Operation” for more information.
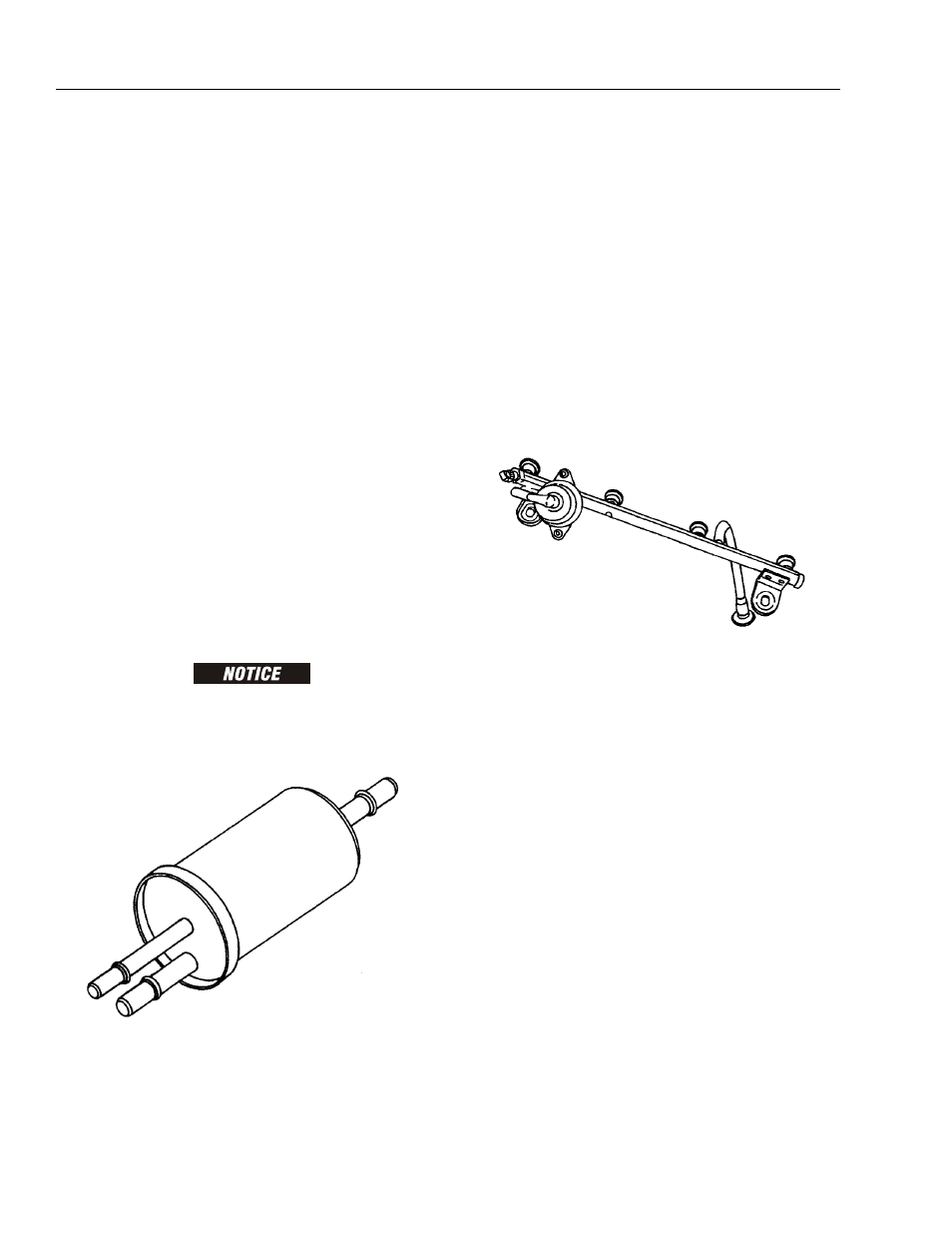
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
The fuel pressure regulator is a relief valve mounted in the
fuel filter. It provides a constant fuel pressure of 441 kPa
(64 psi).
If pressure is too low, poor performance and a DTC 32 will
set. If pressure is too high, excessive odor and/or a DTC
42 will result.
USE AN IDENTICAL FILTER/REGULATOR ASSEMBLY WHEN
REPLACING THE FUEL FILTER. A STANDARD FUEL FILTER
DOES NOT REGULATE PRESSURE AND COULD CAUSE ENGINE
PROBLEMS OR COMPONENT DAMAGE.
FUEL PUMP ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT
When key is first turned “ON,” the ECM energizes the fuel
pump relay for two seconds to build up fuel pressure
quickly. If engine is not started within two seconds, the
ECM shuts the fuel pump off and waits until engine is
cranked. When engine is cranked and crankshaft position
signal has been detected by the SECM, the ECM supplies
12 volts to the fuel pump relay to energize the electric fuel
pump.
An inoperative fuel pump will cause a “no-start” condition.
A fuel pump which does not provide enough pressure
causes poor performance.
FUEL RAIL
The fuel rail is mounted to top of engine and distributes
fuel to individual injectors. Fuel is delivered to fuel inlet
tube of fuel rail by fuel lines.
