Raid 0—no fault tolerance, Raid 1+0—drive mirroring, 3 raid 0 features – HP StorageWorks 1510i Modular Smart Array User Manual
Page 147
that was originally on the failed drive to the online spare. The system is quickly restored to full RAID-level
data protection. (In the unlikely event that another drive in the array fails while data is being rewritten to
the spare, the logical drive will still fail.)
A spare is assigned to an array and is automatically assigned to all logical drives in the same array.
You do not need to assign a separate spare to each array; you can configure one hard drive to be
the spare for several arrays.
RAID 0—no fault tolerance
This configuration (
) provides no protection against data loss when a drive fails. However, it is
useful for rapid storage of large amounts of non-critical data (for printing or image editing, for example),
or when cost is the most important consideration.
Table 3 RAID 0 features
Advantages
Disadvantages
Highest performance method for writes.
All data on the logical drive is lost if a physical drive
fails.
Lowest cost per unit of stored data.
Cannot use a spare.
All drive capacity is used to store data (none needed
for fault tolerance).
Can only preserve data by backing it up to external
storage media.
RAID 1+0—drive mirroring
In this configuration, data on a physical hard drive is duplicated to a second hard drive.
NOTE:
When only 2 hard drives are included in the array, this fault-tolerance method is called RAID 1. When
more than two hard drives are included in the array, this fault-tolerance method is called RAID 1+0.
(RAID_1 is not supported on the MSA1510i storage system.)
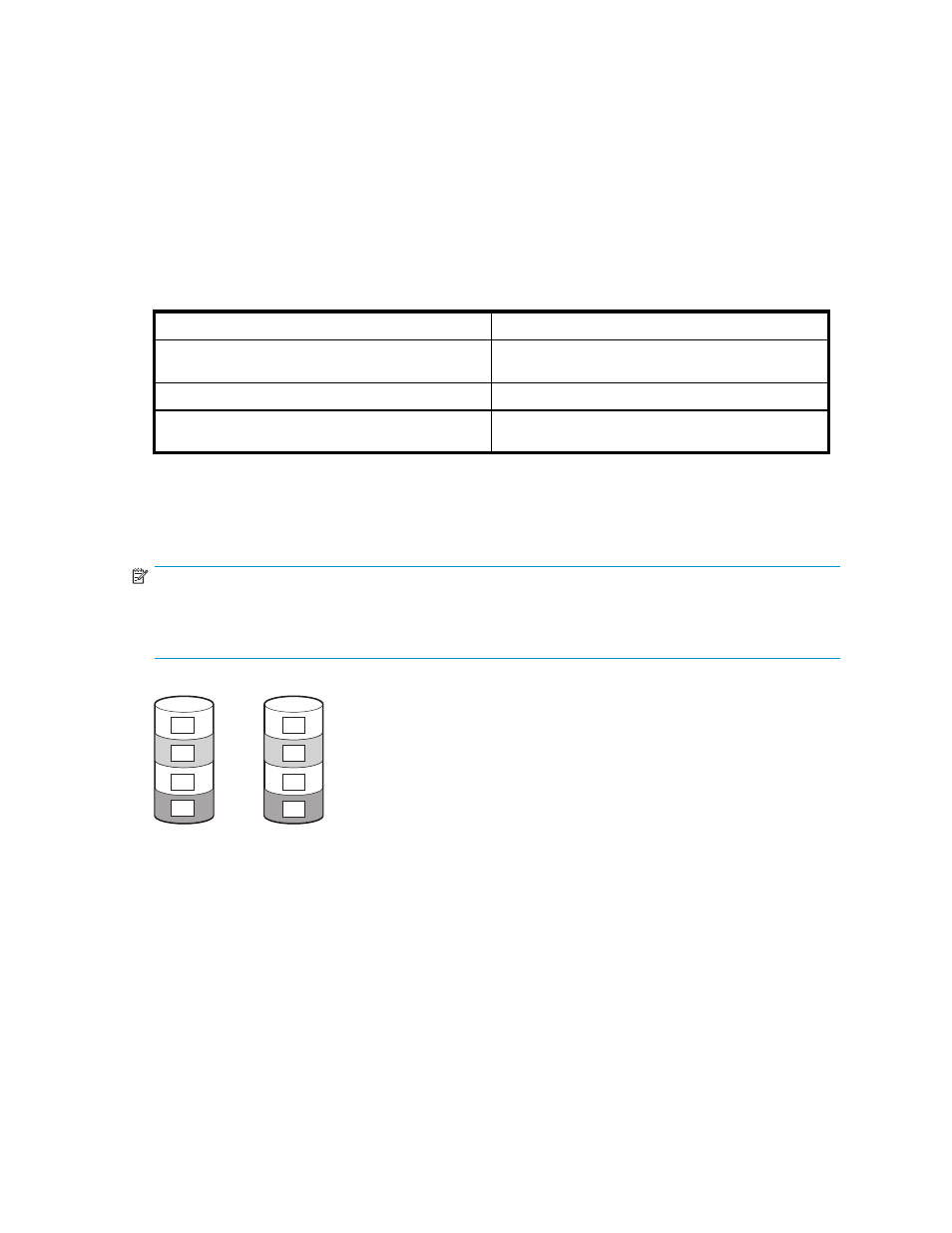
D1
D2
B1
B2
B3
B4
B1
B2
B3
B4
15314
Figure 5 RAID 1 array, with two physical hard drives (D1, D2)
When the array has more than two physical drives, drives are mirrored in pairs (
).
1510i Modular Smart Array Command Line Interface user guide
147
