Rainbow Electronics AT89C5131 User Manual
Page 108
108
AT89C5131
4136A–USB–03/03
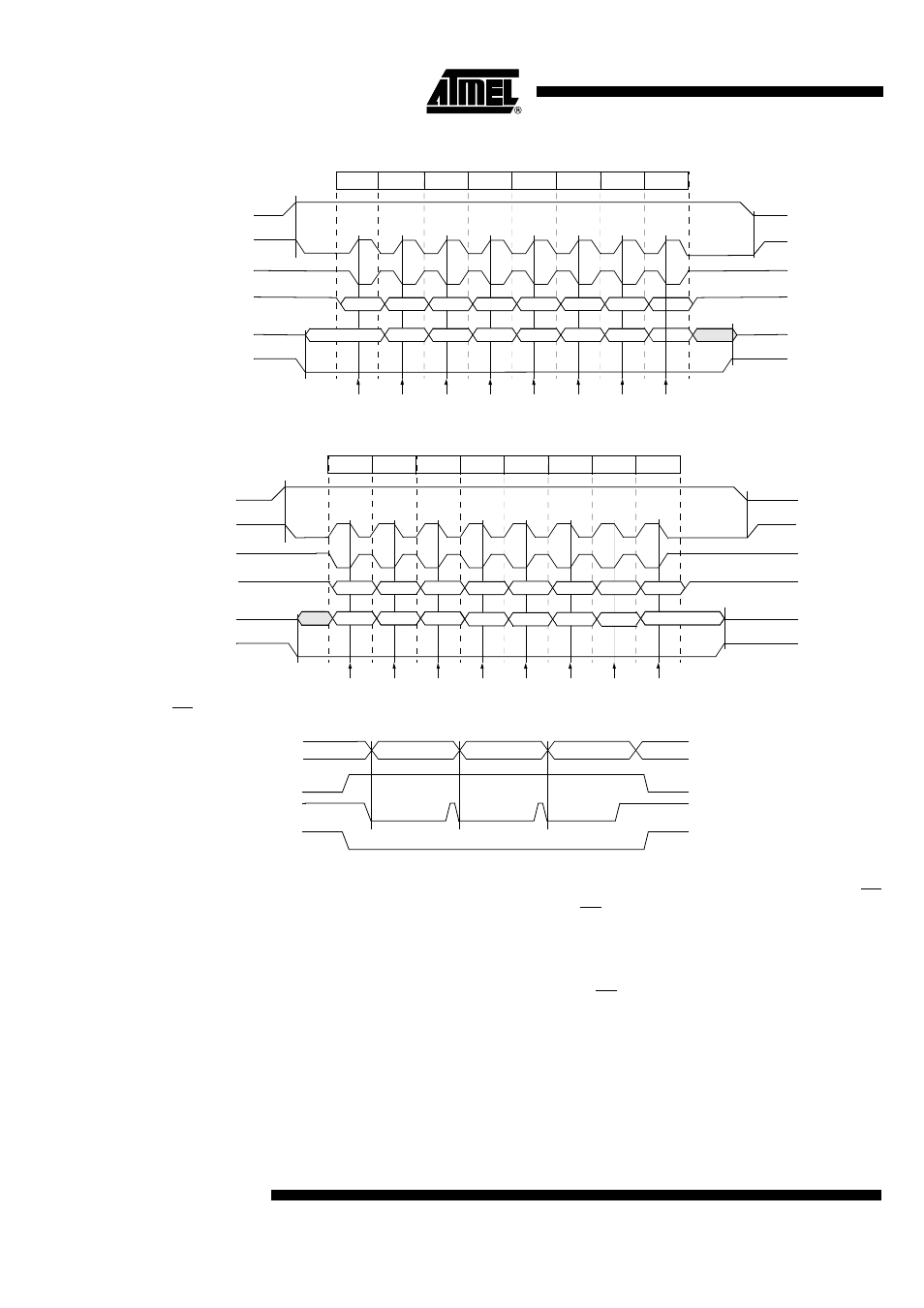
Figure 45. Data Transmission Format (CPHA = 0)
Figure 46. Data Transmission Format (CPHA = 1)
Figure 47. CPHA/SS Timing
As shown in Figure 46, the first SCK edge is the MSB capture strobe. Therefore the
Slave must begin driving its data before the first SCK edge, and a falling edge on the SS
pin is used to start the transmission. The SS pin must be toggled high and then low
between each byte transmitted (Figure 43).
Figure 47 shows an SPI transmission in which CPHA is’1’. In this case, the Master
begins driving its MOSI pin on the first SCK edge. Therefore the Slave uses the first
SCK edge as a start transmission signal. The SS pin can remain low between transmis-
sions (Figure 42). This format may be preferable in systems having only one Master and
only one Slave driving the MISO data line.
MSB
bit6
bit5
bit4
bit3
bit2
bit1
LSB
bit6
bit5
bit4
bit3
bit2
bit1
MSB
LSB
1
3
2
4
5
6
7
8
Capture point
SS (to Slave)
MISO (from Slave)
MOSI (from Master)
SCK (CPOL = 1)
SCK (CPOL = 0)
SPEN (internal)
SCK cycle number
MSB
bit6
bit5
bit4
bit3
bit2
bit1
LSB
bit6
bit5
bit4
bit3
bit2
bit1
MSB
LSB
1
3
2
4
5
6
7
8
Capture point
SS (to Slave)
MISO (from Slave)
MOSI (from Master)
SCK (CPOL = 1)
SCK (CPOL = 0)
SPEN (internal)
SCK cycle number
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
MISO/MOSI
Master SS
Slave SS
(CPHA = 1)
Slave SS
(CPHA = 0)
