Deleting wlan profiles, Wlan clients” menu, System features” menu – AASTRA SIP-DECT (Release 2.1)- OM System Manual - Installation, Administration and Maintenance EN User Manual
Page 70: Digit treatment” menu, Ystem features, Ter 5.9, Chapter 5.8.1.2), 2). note, that some device-specif, 2 deleting wlan profiles, 2 “wlan clients” menu
SIP – DECT OM System Manual Release 2.1
5 OMM Web Service
depl-1230/1.3
Page: 70 (196)
3 Enter at least a new
SSID
. Also enter a currently unused
VLAN tag
number.
4 You can specify different authentication/encryption settings for each SSID section. For
example, you can use
WPA/Pre-shared key
with different passwords.
Note, that some configuration combinations are incompatible with multiple SSIDs. For
example, the wireless hardware only manages a single WEP encryption key. Also, some
features apply to all defined SSIDs, this includes the
MAC access filters
list and the
BSS
isolation
option.
5.8.1.2 Deleting WLAN Profiles
To delete an existing WLAN profile:
1 You cannot remove WLAN profile that is in use. To remove a currently used WLAN profile,
you need to select another WLAN profile for all assigned RFPs first (see chapter 5.6.3.
2 On the
WLAN profiles
page click on the icon next to the profile entry.
The
Delete WLAN profile?
dialog opens showing a summary of the WLAN profile’s
configuration.
3 Press the
Delete
button.
5.8.2
“WLAN clients” Menu
The
WLAN clients
page shows the status of all WLAN clients currently connected to the
WLAN. This can be used for example for troubleshooting purposes. The display shows the
total number of connected WLAN clients and a list of RFPs that are part of the WLAN. For
each RFP, the WLAN client connected to the RFP are listed. You can view the
MAC
address
and the current
Status
of each WLAN client.
5.9
“System features” Menu
The
System features
menu allows administration of system features concerning call number
handling and directory access.
5.9.1
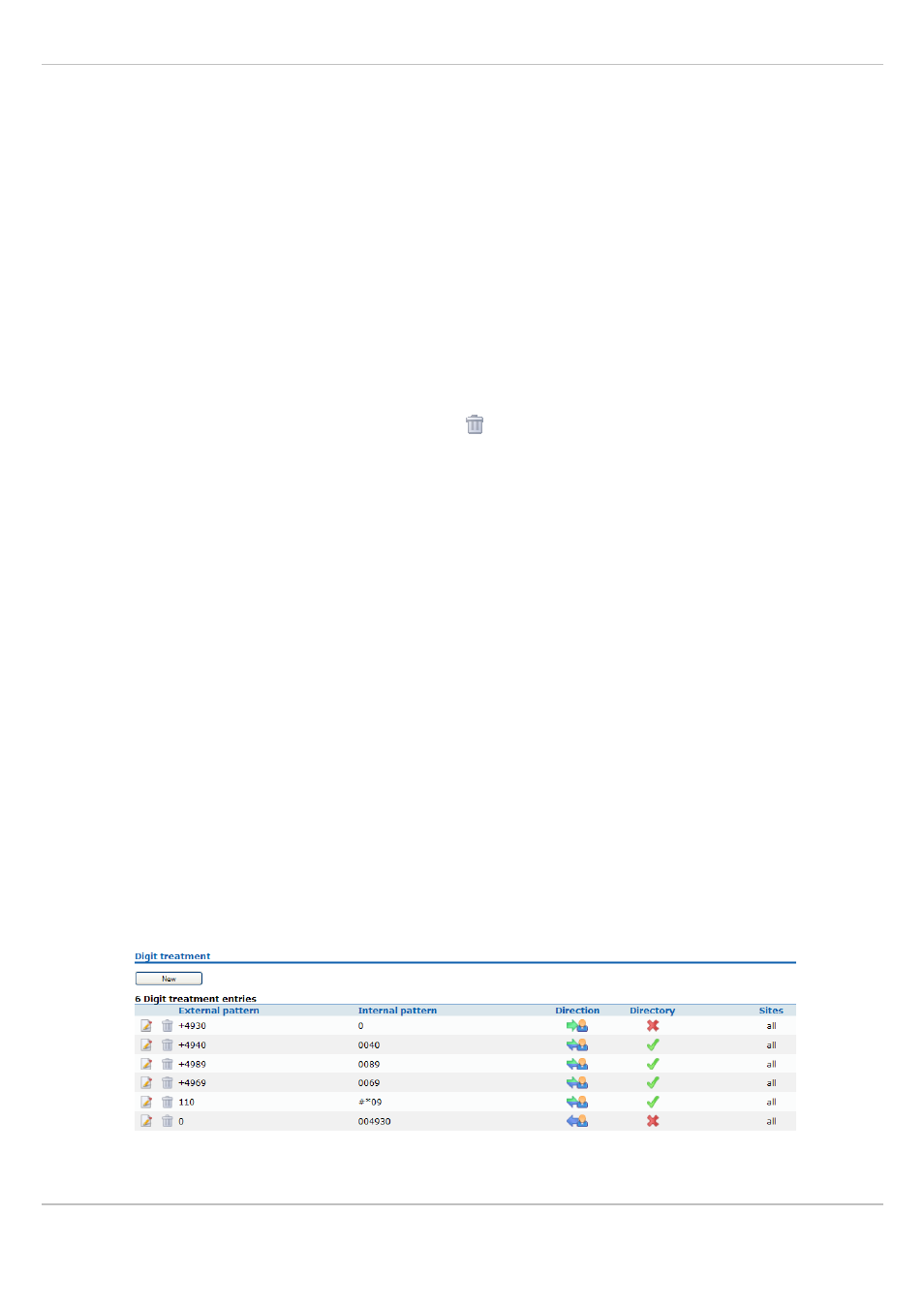
“Digit treatment” Menu
A number manipulation is provided by the digit treatment feature for LDAP corporate
directories, that handles both incoming and outgoing calls (see chapter 5.9.2).
