Kohler Command Pro CV980 User Manual
Page 94
Section 9
Inspection and Reconditioning
9.2
45
°
High Point from
Fillet Intersections
This Fillet Area
Must Be
Completely Smooth
Minimum
The Fillet Must
Blend Smoothly
with the Bearing
Journal Surface
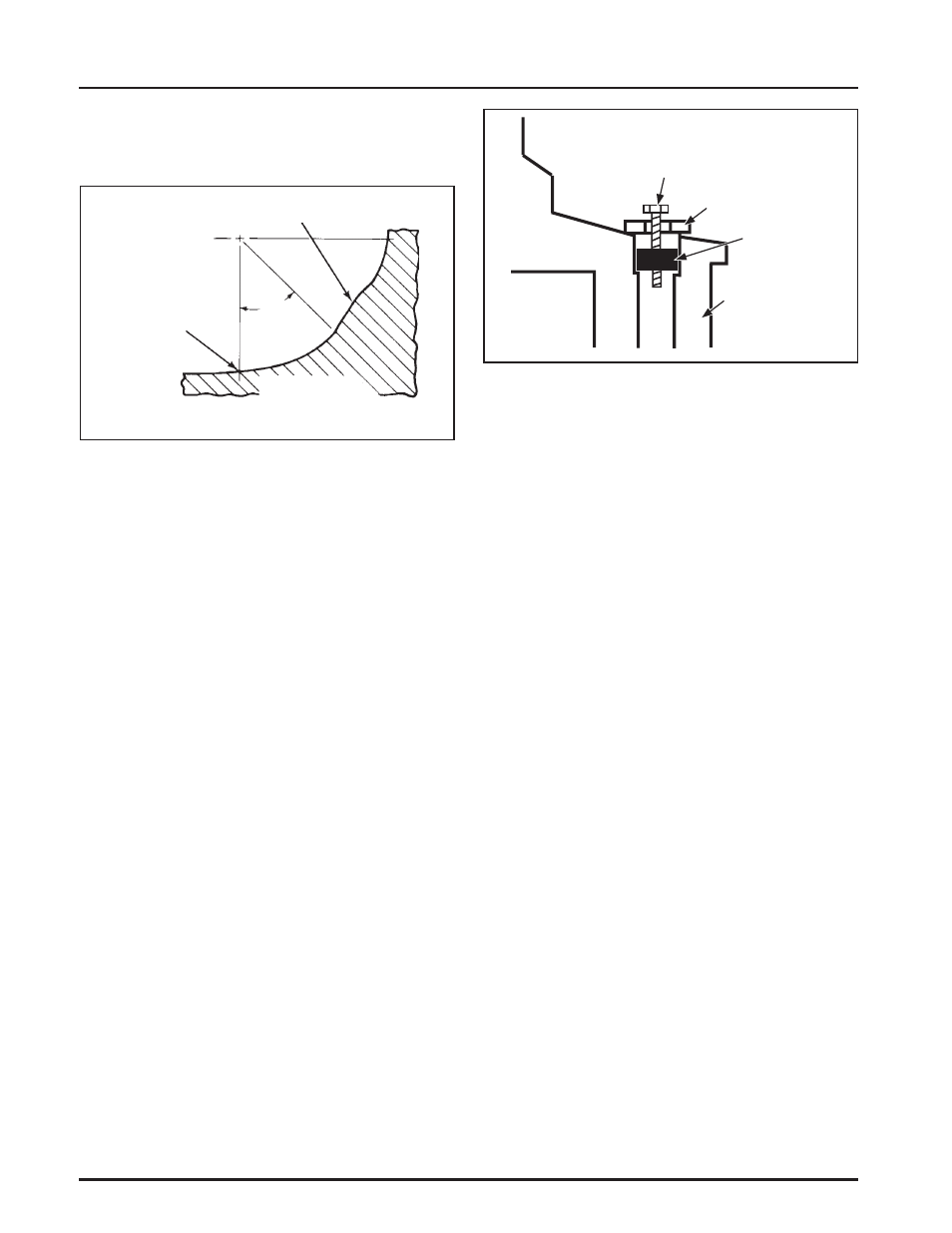
NOTE: If the crankpin is reground, visually check to
ȱȱȱęȱȱ¢ȱ ȱ
the crankpin surface. See Figure 9-1.
Figure 9-1. Crankpin Fillets.
The connecting rod journal can be ground one size
ǯȱȱȱȱĞǰȱȱȱ
deposits can get caught in the oil passages, which
could cause severe engine damage. Removing the
ȱȱ ȱȱĞȱȱȱȱ
easy access for removing any grinding deposits that
may collect in the oil passages.
Use the following procedure to remove and replace
the plug.
Procedure to Remove Crankshaft Plug:
1. Drill a 3/16" hole through the plug in the
Ğǯ
2. Thread a 3/4" or 1" long self-tapping screw with a
Ěȱ ȱȱȱȱǯȱȱĚȱ ȱ
must be large enough to seat against the shoulder
of the plug bore. See Figure 9-2.
3. Tighten the self-tapping screw until it draws the
ȱȱȱȱĞǯ
Procedure to Install New Plug:
ȱ ŗǯȱ ȱȱȱ¢ȱĞȱǰȱ
ȱȱ
No. 47 380 09-S as a driver and tap the plug into
ȱȱȱȱȱȱȱȱĴȱȱȱ
bore. Make sure the plug is tapped in evenly to
prevent leakage.
Figure 9-2. Removing Crankpin Plug.
Crankcase
Inspection and Service
Check all gasket surfaces to make sure they are free of
gasket fragments. Gasket surfaces must also be free of
deep scratches or nicks.
Inspect the main bearing (if so equipped) for wear or
ȱǻȱȱȱŗǰȱȃęǰȱǰȱ
ȱȱȱȄǼǯȱȱȱȱ
or crankcase using a miniblock or short block as
required.
Check the cylinder bore for scoring. In severe cases,
ȱȱȱȱĜȱȱȱȱȱ
cylinder wall. It washes the necessary lubricating
ȱěȱȱȱȱ¢ȱ ǯȱȱ ȱȱ
seeps down the cylinder wall, the piston rings make
metal to metal contact with the wall. Scoring of the
cylinder wall can also be caused by localized hot
ȱȱȱȱȱęȱȱȱ
inadequate or contaminated lubrication.
If the cylinder bore is badly scored, excessively worn,
tapered, or out-of-round, resizing is necessary. Use an
inside micrometer to determine the amount of wear
ǻȱȱȱȃęǰȱǰȱȱȱ
ȱȄǰȱȱȱŗǼǰȱȱȱȱȱ
suitable oversize of either 0.25 mm (0.010 in.) or 0.50
mm (0.020 in.). Resizing to one of these oversizes will
allow usage of the available oversize piston and ring
assemblies. Initially, resize using a boring bar, then
use the following procedures for honing the cylinder.
Honing
While most commercially available cylinder hones
can be used with either portable drills or drill presses,
the use of a low speed drill press is preferred as it
facilitates more accurate alignment of the bore in
ȱȱȱĞȱǯȱȱȱȱ
Flat Washer
Self-Tapping Screw
Plug
Crankshaft
