Hyundai HI4 User Manual
Page 369
11. Robot Language Explanation
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
11 - 4
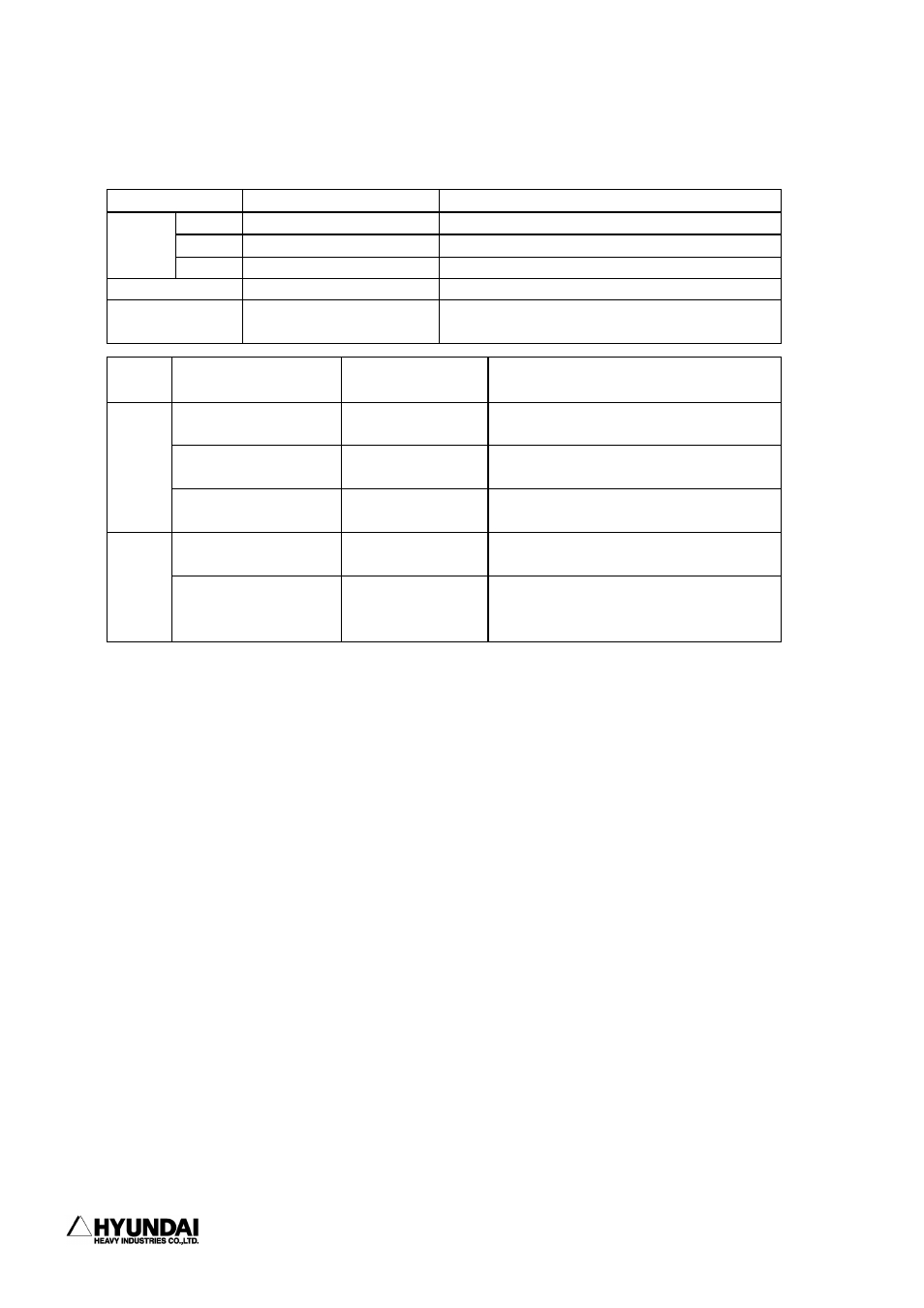
11.1.4 Constant
Reference
(1) Suffix is not added in basic coordinate system, but suffix is added in robot coordinate
system.
(2) In case of basic coordinate system or robot coordinate system, each elements are (X,
Y, Z, RX, RY, RZ, cfg.). If there is an additional axis, it is continued after RZ. X,
Y, Z are coordinate(unit: mm), RX, RY, RZ are each rotational angle of x axis, y axis,
axis(unit: degree).
cfg.(configuration) is consists of 8bit (0∼255) robot type information.
(3) In case that there is not additional axis, it is the same whether R is added or not.
(4) In case of encoder type, suffix is added.
(5) Each elements of encoder type is (S, H, V, R2, B, R1), and there is not cfg. If there
is an additional axis, it is continued after R1.
(6) In case that T is added, only tool coordinate system is applied, so even though user
coordinate system is set, it is ignored.
constant type
range
example
dec.
-32768∼32767
2150, -440
bin.
&B0∼B1111111111111111
&B01101011, &B1000
constant
hex.
&H0∼&HFFFF
&H3F77, &H2A
real number
-3.4E+38∼3.4E+38
55.6, 0.5E-2
string
enable with 35 char.
"INPUT WORK NUMBER:",
"INVALID DATA"
constant
type
coordinate type
range
example
basic coordinate
system
real number range
(204.5, 3719.35, 277.94, 0, 50, 0, 24)
(P* is present pose of robot)
robot coordinate
system
real number range (204.5, 3719.35, 277.94, 0, 50, 0, 24)R
pose
encoder type
0∼&HFFFFFFFF
(&H400000,&H400000,&H400000,
&H400000,&H400000,&H400000)E
basic coordinate
system
real number range (0, 50, 0, 0, 0, 0)
shift
tool coordinate
system
real number range
(0, 50, 0, 0, 0, 0)T
(if T, tool coordinate system
reference)
