2 list of servo adjustment functions, 1) autotuning functions, 2) positioning time reduction functions – Yaskawa Sigma II Series DC Power Input SGMAJ User Manual
Page 254
9.1 Autotuning
9-3
9
9.1.2 List of Servo Adjustment Functions
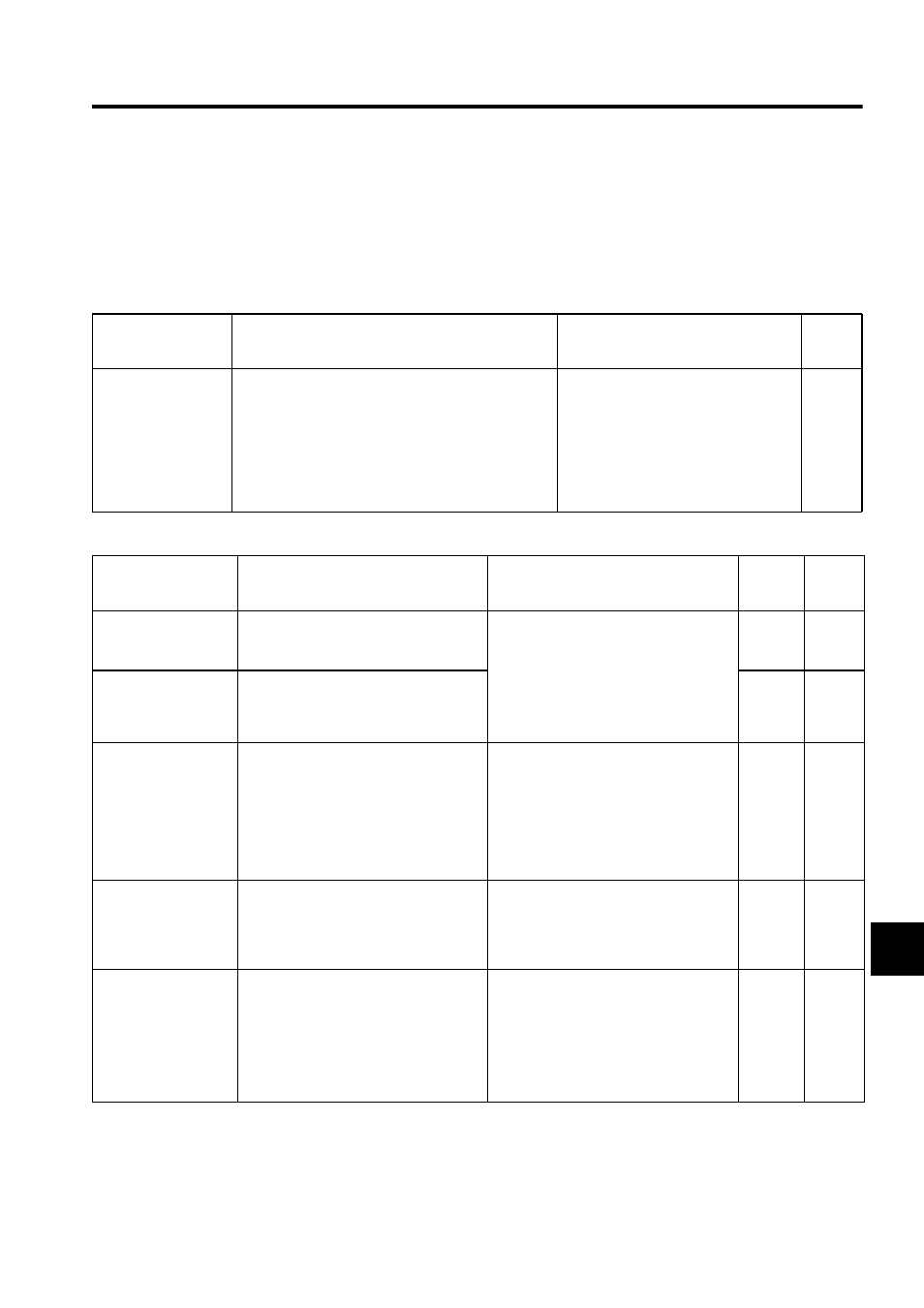
(1) Autotuning Functions
Autotuning calculates the load moment of inertia, which determines the servo responsiveness, and automatically
adjusts parameters, such as the Speed Loop Gain Kv (Pn100), Speed Loop Integral Time Constant Ti (Pn101),
Position Loop Gain Kp (Pn102), and Torque Reference Filter Time Constant Tf (Pn401). Refer to the following
table to select the appropriate autotuning function for your desired purpose and adjust the servo gains.
(2) Positioning Time Reduction Functions
Function Name and
Related Parameters
Description
Guidelines for Selection
Refer-
ence
Section
Online Autotuning
Pn110.0
Fn001
Fn007
This function automatically measures the machine char-
acteristics and sets the required servo gains accordingly.
This function allows beginners to adjust the servo gains
easily.
The load moment of inertia is calculated during opera-
tion for a user reference, and the servo gains (Kv, Ti,
Kp, and Tf) are set according to the Machine Rigidity
Setting (Fn001).
Only the minimum number of parameters
must be set for autotuning using a normal
operation reference.
9.2
Function Name and
Related Parameters
Description
Features
Valid
Control
Modes
Refer-
ence
Section
Feed-forward
Pn109
Pn10A
Feed-forward compensation for the posi-
tion reference is added to the speed refer-
ence.
Adjustment is easy.
The system will be unstable if a large
value is set, possibly resulting in over-
shooting or vibration.
Position
9.4.1
Torque feed-forward
Pn002
Pn400
Inputs torque feed-forward to the torque
reference input terminal and adds to the
internal torque reference at the speed con-
trol.
Speed
9.4.2
Mode Switch
(P/PI Switching)
Pn10B
Pn10C
Pn10D
Pn10E
Pn10F
Switches from PI control to P control
using the value of an internal servo vari-
able in a parameter (torque, speed, accel-
eration, or position error) as a threshold
value.
The setting for automatic switching
between PI and P control is easy.
Position
Speed
9.4.4
Speed Feedback
Compensation
Pn110
Pn111
Compensates the motor speed using an
observer.
Adjustment is easy because the compensa-
tion can be set as a percentage. If the
speed loop gain increases, the position
loop gain also increases, however some-
times the servo rigidity decreases.
Position
Speed
9.4.7
Gain Switching
Pn100
Pn101
Pn102
Pn104
Pn105
Pn106
Uses the external signals to change each
parameter for speed loop gain (Kv), speed
loop integral time constant (Ti), and posi-
tion loop gain (Kp.)
−
Position
Speed
9.4.8
