Measurement Computing eZ-TOMAS version 7.1.x User Manual
Page 29
eZ-TOMAS & eZ-TOMAS Remote
887591
Edit Menu 3-3
Panels of the Acquisition Tab
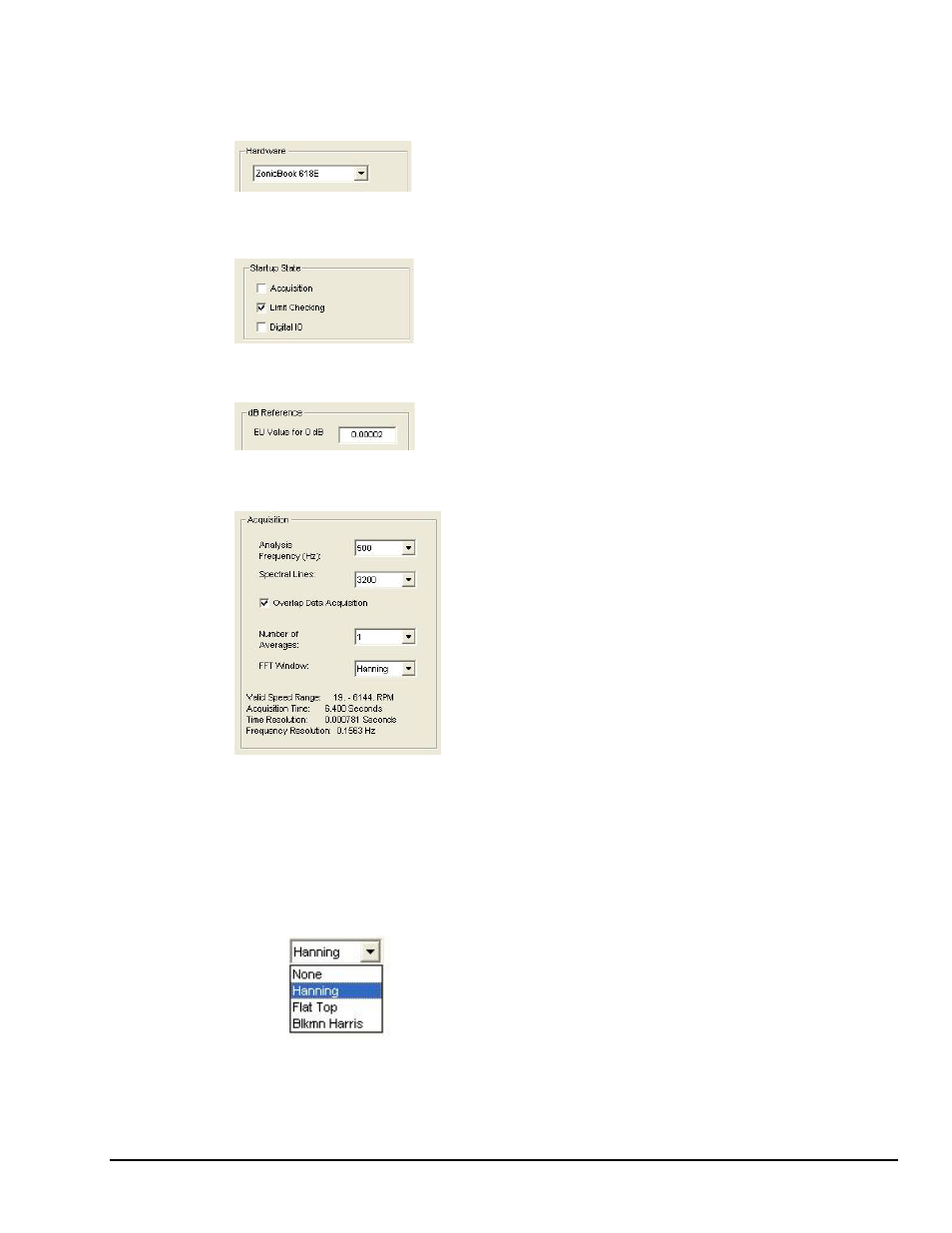
Hardware
The Hardware Panel has a pull-down list from which the applicable
data acquisition device must be selected.
Startup State
Used to set the default startup state for the Project's Acquisition, Limit
Checking, and Digital IO processes. eZ-TOMAS will turn on the
selected processes when the project is opened.
dB Reference
This panel is used to set the 0 dB reference point in Engineering Units
(EU). The EU value for 0 dB reference is used with microphone input
channel types. The default setting is 20 micro-Pascals (0.000020 pa).
Acquisition
Analysis Frequency (Hz) The maximum frequency of interest. The
sampling rate will be 2.56 times the analysis frequency. Verify the
maximum frequency response of your probes. For a Tach signal,
your Analysis Frequency should be a higher multiple of the maximum
rotating speed. Typically, this multiple is at least 10 times the rotating
frequency.
Spectral Lines The number of lines per spectrum and the number of
data samples used in the FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) process. The
more spectral lines, the greater the data resolution. As the number of
spectral lines increases, so does the time that it takes to collect the
data and the amount of disk space.
Overlap Data Acquisition For slow speed data acquisition
applications, you have the option to select overlap data processing to
speed up real time data displays. This option is enabled when the
Acquisition Time is greater than 2 seconds.
If you select Overlap Data Acquisition, eZ-TOMAS will automatically
determine the overlap percentage needed to achieve a 1 to 2 second
display update rate. For example, if your analysis frequency is
500 Hz and you have 3200 spectral lines, the acquisition time is 6.4
seconds. With Overlap Data Acquisition, the overlap percentage will
be 75% and the update rate will be 1.6 seconds. (6.4 sec / 4). The
divisor is a power of 2.
Number of Averages The number of data blocks averaged before a
block of data is accepted and displayed. Typically, the value is “1”
indicating no averaging.
FFT Window Fast Fourier Transform. FFT is an efficient technique
for calculating the frequency of components in a time-domain
waveform based on digitized voltage measurements. The result is a
display of amplitude versus frequency and phase versus frequency.
The FFT Window is a weighting window, typically either Hanning or
Flat Top. Hanning provides better frequency resolution. Flat Top
provides better amplitude resolution.
