Measurement Computing ZonicBook 618E rev.3.4 User Manual
Page 72
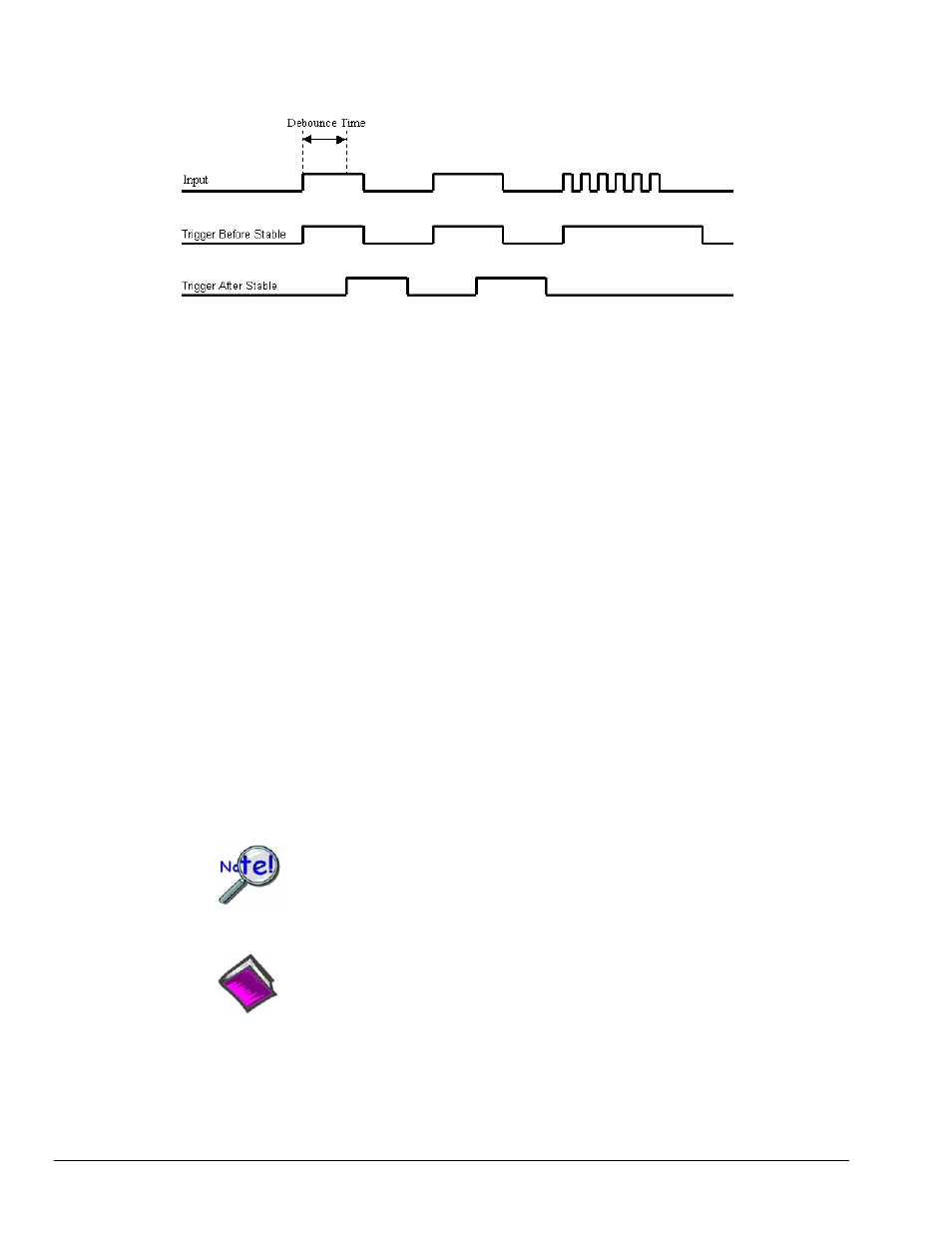
the desired input pulse but longer than the period of the undesired disturbance as shown in the diagram
below.
To make an optimal noise rejection setting in software . . .
1. Setup the input for Voltage Mode (Select AC or DC Coupling).
2. Take a measurement.
3. View the Tach Signal on a TimeWaveform plot.
4. Set the Trigger Slope [Trig Slope] to Positive (POS) or Negative (NEG).
5. Set the Trigger Level [Trig Level] to a value between 50 and 75 % of the maximum excursion.
6. Set Edge Detect to “Immediate” or “Delayed.” An illustrated example making use of a
500 ns delay follows shortly.
You may need to experiment with Edge Detect settings to determine whether “Immediate” or
“Delayed” works best for your application. Optimum settings will vary, depending upon the noise
present on the Tach input.
7. Set the Delay Time to a pre-set value between 500 ns and 25.5 ms. To have no delay time select
“none.”
The debounce time should initially be set as low as possible, i.e., to 500 ns or to “none.”
If the velocity readings are jumping around, that is, they are either too high [as if there was an extra
tach pulse] or too low [as if there was a missing pulse] increase the debounce value to higher than
500 ns. Some experimentation is to be expected.
Increasing the debounce value too high will reject the tachometer pulse altogether, particularly at
high RPM.
Do not set the debounce value to higher than one-half of the minimum tach pulse
period. The minimum tach pulse period is that which exists during the highest
RPM.
Reference Notes:
For details you will need to refer to eZ-Analyst or eZ-TOMAS documentation, as
applicable.
A PDF version of each is included on the installation CD.
¾
eZ-Analyst Series Software Reference Manual
¾
eZ-TOMAS User’s Manual
7-8 Tach Channels
917695
ZonicBook/618E
