Analog triggers, Analog triggers …… 6-11, Ranges and resolutions – Measurement Computing ZonicBook 618E rev.3.4 User Manual
Page 59: Hysteresis effect on a rising-edge trigger
Analog Triggers
The analog triggers discussed in this section make use of the analog channel
input BNCs labeled CH1 through CH8.
Reference Note:
Your software documentation contains information regarding how to select
trigger types and how to set trigger values.
Chapter 8 includes information regarding TTL compatible triggers, which
make use of the Trigger Input BNC connector.
Ranges and Resolutions
The low-latency analog trigger compares the analog signal with a programmable voltage source.
Analog-Trigger Comparator, Ranges and Resolutions
Input Range
Trigger Threshold Range
Resolution (mV)
0-10 or ±5
-5.0 to 9.996
0.299
0-5 or ±2.5
-2.5 to 4.998
0.114
0-2 or ±1
-1.0 to 1.999
0.0458
0-1 or ±0.5
-0.5 to 0.9996
0.0229
0-0.5 or ±0.25
-0.25 to 0.4998
0.0114
0-0.2 or ±0.1
-0.10 to 0.1999
0.00458
0-0.1 or ±0.05
-0.05 to 0.09996
0.00229
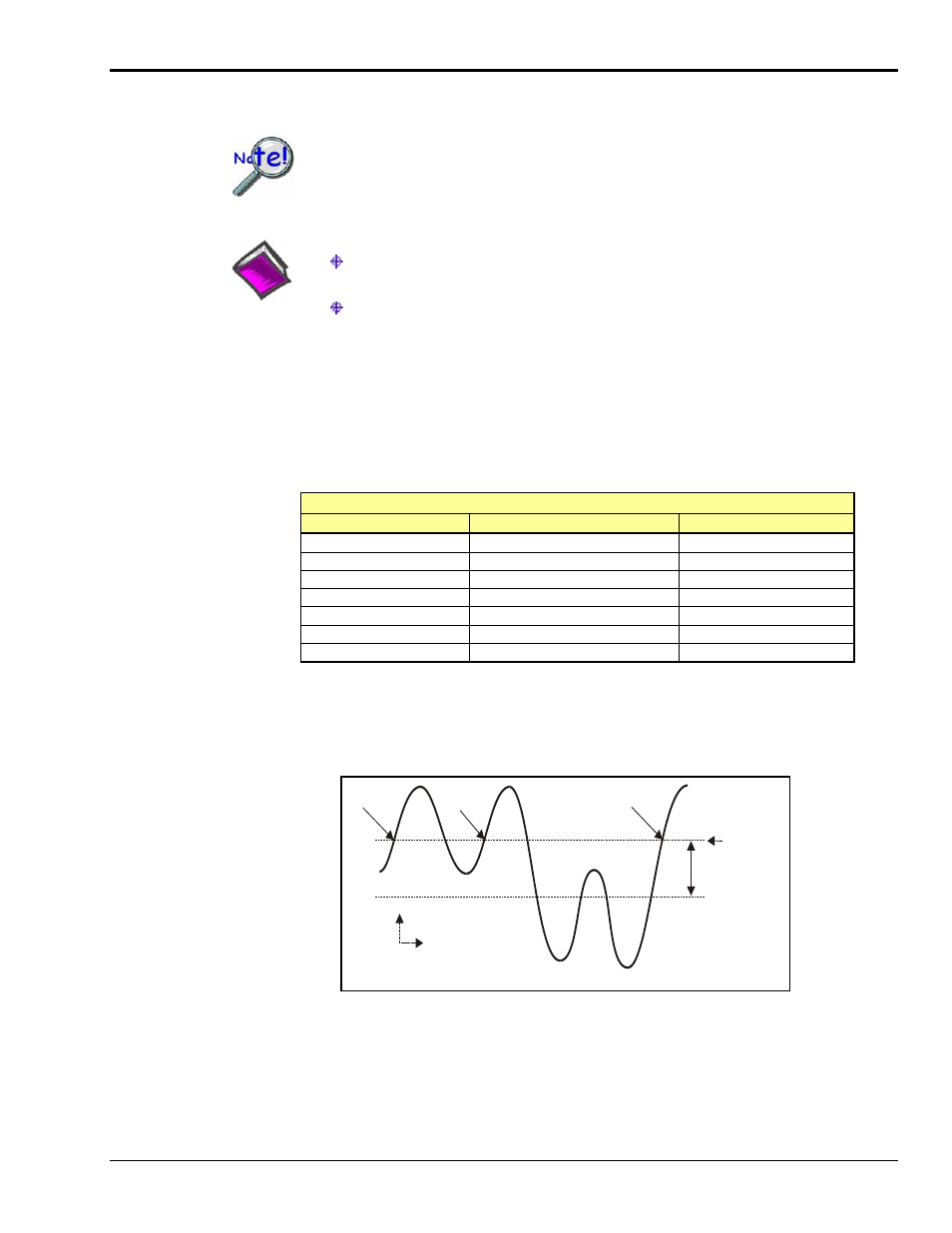
The analog trigger circuit has hysteresis that reduces the occurrence of re-triggering due to input noise.
The hysteresis is 1/600 of the comparator range. The following figure shows the hysteresis effect for a
rising-edge trigger.
Trigger
Trigger
No
Trigger
Trigger Level
Hysteresis Range
Hysteresis Effect on a Rising-Edge Trigger
Amplitude
Time
A trigger will occur when the analog input rises above the trigger level, but only after the input level has
been below the hysteresis range. If the level momentarily drops just below the trigger level (perhaps due to
noise) and then rises above it again, no extra triggers will be generated because the signal did not drop
below the hysteresis range. After the level drops below hysteresis, it can then again produce a trigger by
rising above the trigger level.
ZonicBook/618E
878595
Analog Signals 6-11
