Performing neuron c input/output – Echelon Mini FX User Manual
Page 83
70 Developing
Device
Applications
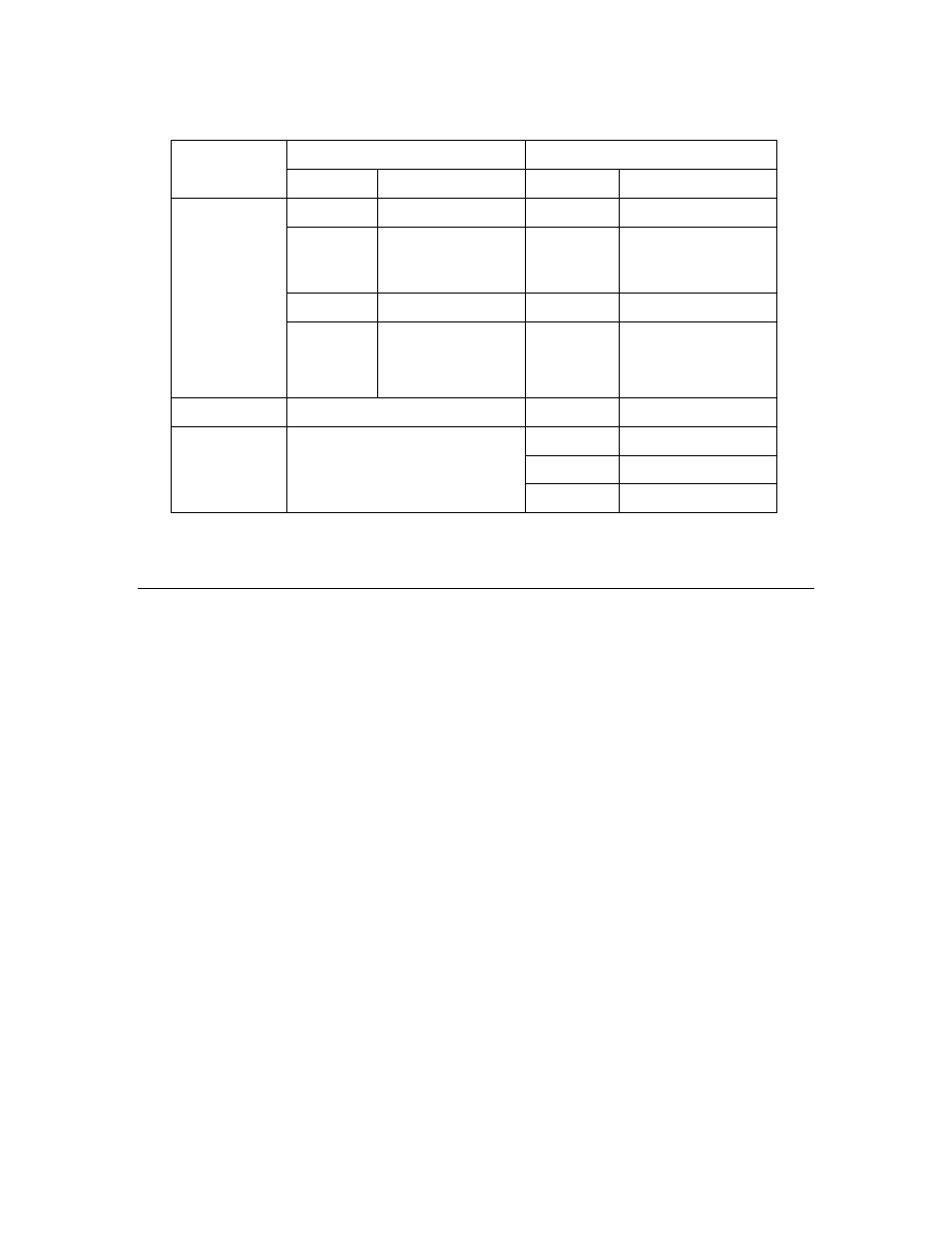
Table 5.3 Required EVB Jumper Configurations
Required Connections
Required Disconnections
Board
Jumper Pin
Jumper Pin
JP31
all
JP21
all
JP32 1-2
(SWSH)
3-4 (TEMP)
7-8 (SW1)
JP32 11-12
(3PD)
13-14 (1PD)
15-16 (9PD)
JP33 LCD
5V
JP201 all
FT 5000 EVB
P201
7-8 (10 T1IN)
JP203
1-2 (SPD)
3-4 (6PD)
5-6 (T2IN)
7-8 (FON PD)
PL 3150 EVB Mini Gizmo I/O Board (P201)
—
—
JP201 all
JP203 IO5
PL 3170 EVB Mini Gizmo I/O Board (P201)
JP204 IO6
Note: You can use other Series 3100 EVBs to run the examples applications. To do this,
connect the Mini Gizmo I/O Board to the P201 connector on the EVB, connect the IO10
jumper, and remove the IO5, IO6, IO0, IO8, IO4, and IO1 jumpers.
Performing Neuron C Input/Output
A Neuron Chip or Smart Transceiver may be connected to one or more physical I/O
devices via up to 12 versatile I/O pins. Examples of simple I/O devices include
temperature, light, and position sensors; valves; switches; LEDs; and LCDs. Neuron
Chips and Smart Transceivers can also be connected to other microprocessors. The
Neuron firmware implements numerous I/O objects that manage the interface to these
devices for a Neuron C application. For more details on I/O objects, see the Neuron C
Programmer’s Guide and the Neuron C Reference Guide.
To set up I/O devices in your Neuron C code, you declare the I/O objects that monitor and
control the Neuron Chip or Smart Transceiver I/O pins, named IO_0 – IO_10 or IO_11
(depending on the Neuron Chip or Smart Transceiver model). To perform I/O, you use
the built in I/O events and functions in the Neuron C programming language.
You can then use the built in I/O events and functions to debug your device application.
For example, you can use the LED outputs on your EVBs to signal events from within
your application.
You can also perform application level debugging using the serial ports on your EVBs, or
exchange other data to any other computer using a serial connection. To do this, you
insert code in your device application that sends output to the serial ports, enable serial
communication on your EVB, and connect your EVB to your development computer via a
serial interface. You can then monitor the serial output with Windows HyperTerminal,
, or another terminal emulation program on your computer.
• You can connect an FT 5000 EVB to your development computer via a USB or EIA
232 interface For more information on connecting the serial interface on an FT 5000
EVB, see Chapter 2 of the FT 5000 EVB Hardware Guide. The examples in this
