1 six-step commutation, Six-step commutation -11 – ElmoMC SimplIQ Software Manual User Manual
Page 121
SimplIQ
Software Manual
Commutation
MAN-SIMSW (Ver. 1.4)
8-11
To optimize the torque, it is necessary to maintain
o
90
r
F
≈
θ
−
θ
.
The commutation error can be defined as follows:
(
)
r
F
90
θ
−
θ
−
=
ε
θ
o
. Ideally,
.
0
=
ε
θ
The torque production is not very sensitive to
ε
θ
. Writing equation (1) as:
T = KT * I cos (
ε
θ
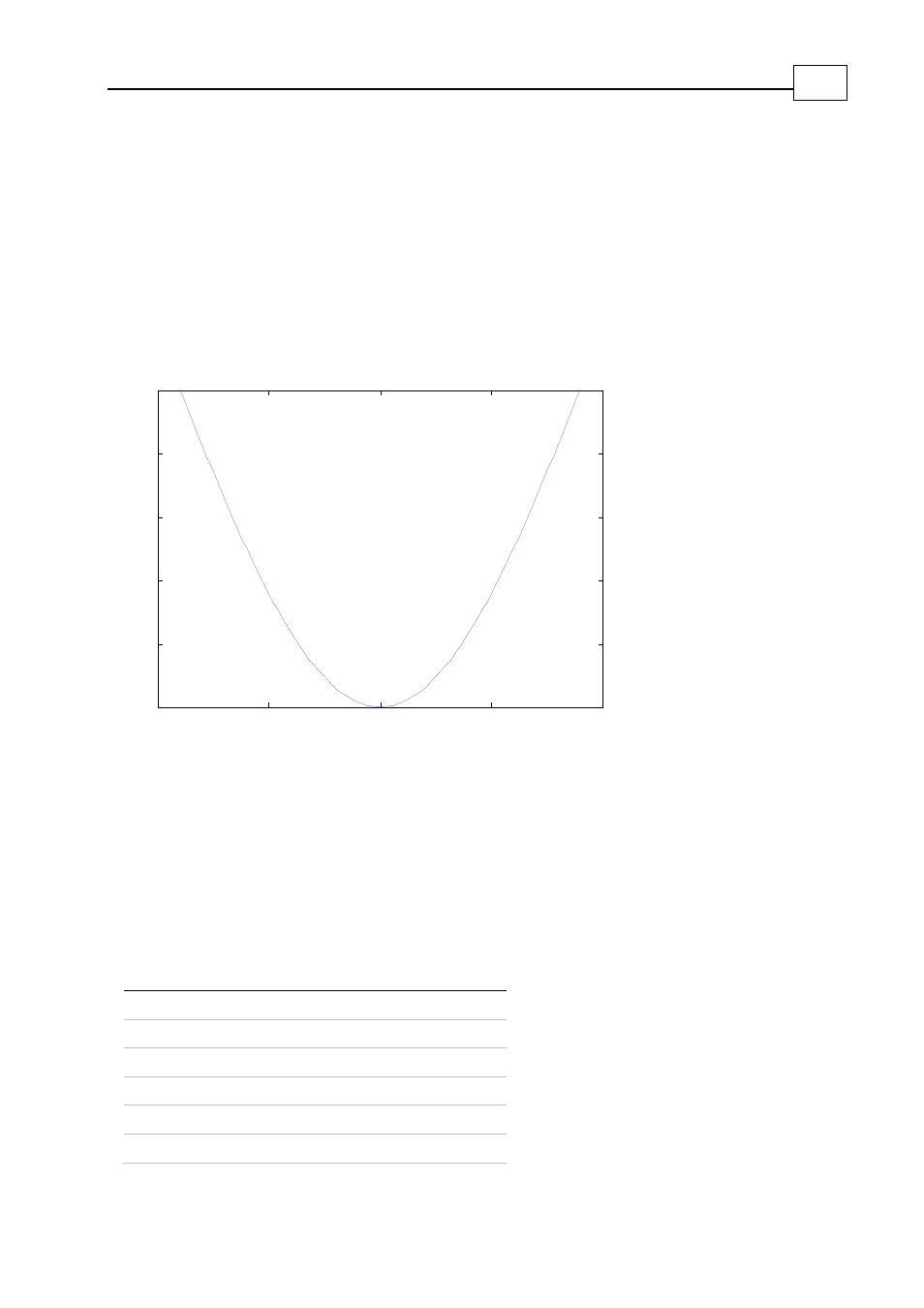
), it can be seen that a discrepancy of 5° can result in a loss of about 0.4% of
the torque. With a miss of 30°, 13.4% of the torque is lost, as illustrated in the following
figure:
-100
-50
0
50
100
0
20
40
60
80
100
Commutation miss angle, degrees
Lost torque, %
Figure
8-2: Loss of Torque due to Commutation Miss
Two main methods — six-step commutation and continuous commutation — are used to
keep
ε
θ
near zero.
8.5.1
Six-step Commutation
With six-step commutation, only two motor terminals are energized at each time instance.
The third motor phase is open-circuited. Six field angles are possible:
Current flows:
Field Direction (degrees)
C → A, B open
30
C → B, A open
90
A → B, C open
150
A → C, B open
210
B → C, A open
270
B → A, C open
330
Table
8-4: Six-step Commutation
