5 trigger events and timing, Trigger events and timing -9, Simpliq – ElmoMC SimplIQ Software Manual User Manual
Page 105
SimplIQ
Software Manual
Development Aids
MAN-SIMSW (Ver. 1.4)
7-9
Note that RG specifies only the recorder sampling rate, not the trigger sampling rate. A
trigger event will cause the recorder to start within one time quantum (TS).
RL defines the maximum number of data items to collect. For example, if RL=11, TS=70,
RG=1 and RP[0]=0, then the 11 samples will be taken at the rate of 280 microseconds, lasting
(11-1) x 280 microseconds = 2,800 microseconds.
The recorder memory is limited to a total of 4096 long variables. When more signals are
recorded, less memory is available for each recorded signal.
If RL > (recorder memory) / (number of signals), the recorder will fail to record the
specified RL samples and instead, will record up to its data volume.
The actual amount of recorded data can be polled using the WI[21] command.
7.4.5
Trigger Events and Timing
The recorder is started by a trigger event, which is one of the following:
Immediate: The recorder starts immediately after the recording request has been issued.
Begin motion: The recorder is triggered by the execution of a software BG command, by
a timed BG command, or by a hardware command.
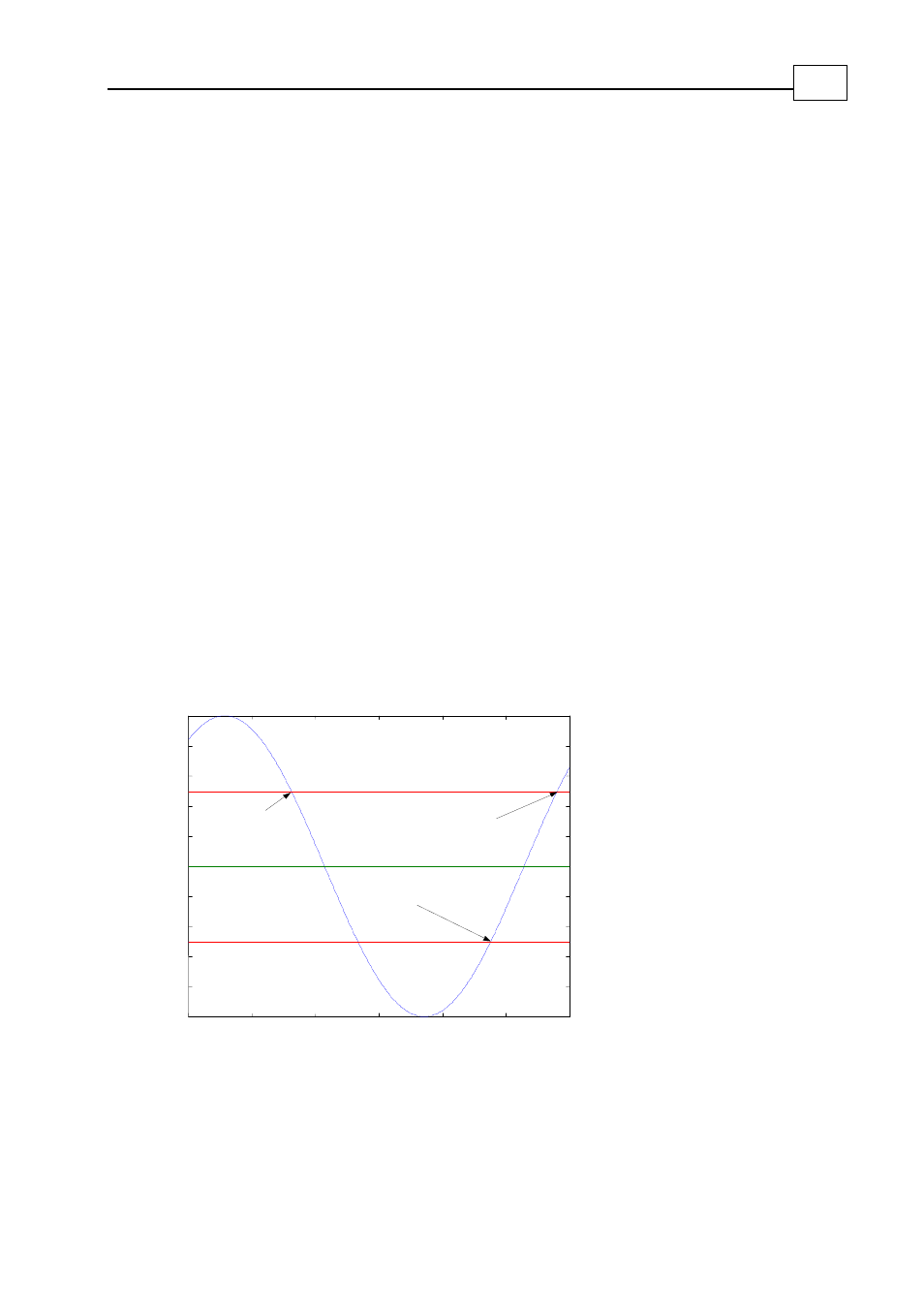
Analog signal: The recorder starts upon one of the following:
Positive slope: The signal crosses a prescribed level with a positive slope.
Negative slope: The signal crosses a prescribed level with a negative slope.
Window: The signal exits a window of two prescribed signal levels.
The following graph depicts the analog signal trigger types:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
-1
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Trigger signal (not necessarily recorded)
Level 1
The trigger
occurs here if set
for negative slope
The trigger
occurs here if set
for positive slope
Level 2
The trigger
occurs here if set
for window
Figure
7-1: Slope and Window Trigger Types
Digital signal: The
SimplIQ
drives will support this trigger option in the future.
