HP TopTools for Hubs and Switches User Manual
Page 43
Alerts
Interpreting the Alert Log - Automatic Fault Finding
5-3
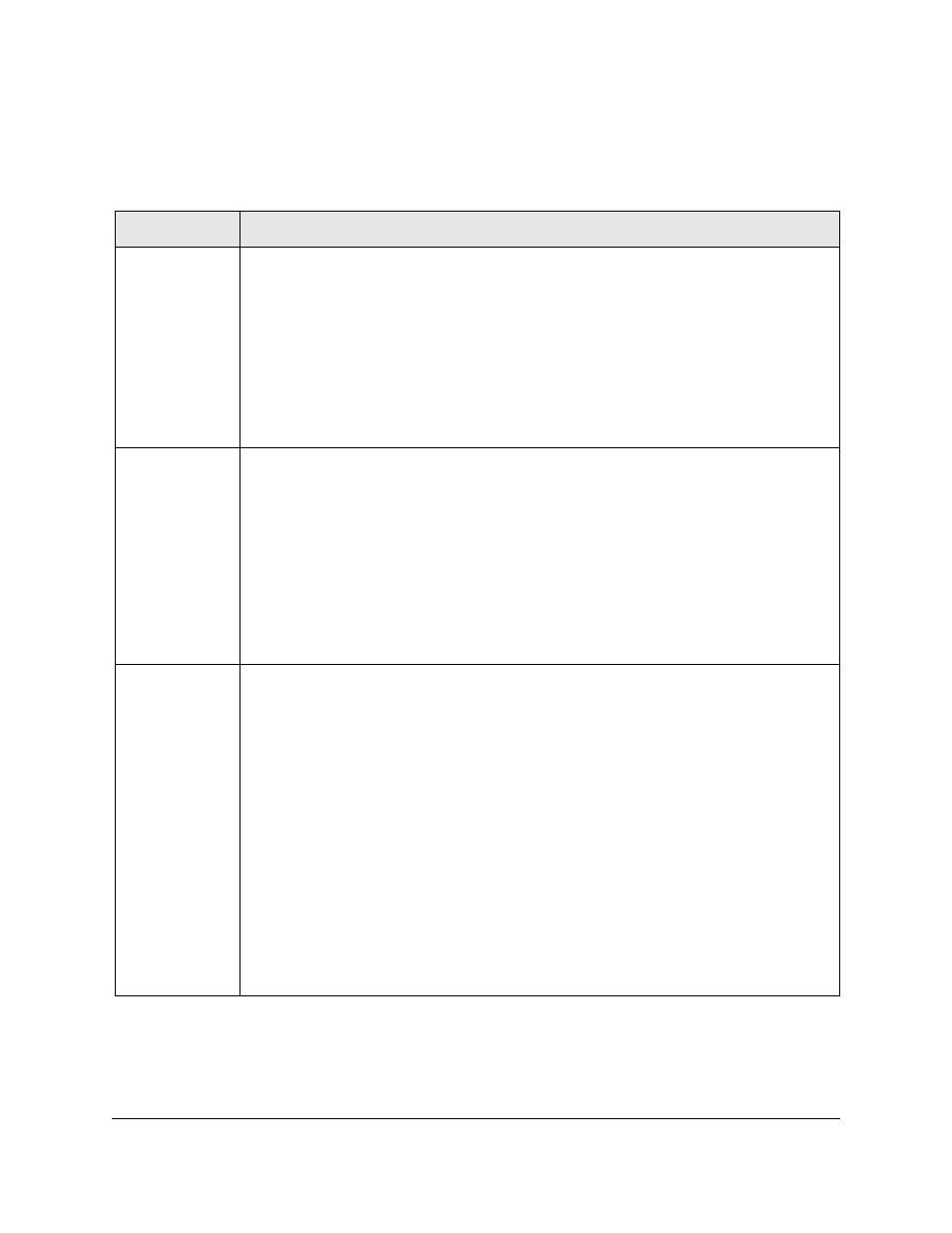
Table 5-1.
Common Faults
Fault
Description, Cause and Actions
Too many
undersized/giant
packets
Description: A device on this port is transmitting packets shorter than 64 bytes or longer than 1518 bytes
(longer than 1522 bytes if tagged), with valid CRCs.
Possible Causes: a misconfigured NIC or a malfunctioning NIC, NIC driver, or transceiver
Actions:
1. Check the NIC for a misconfiguration.
2. Update the NIC driver software.
3. Replace the malfunctioning NIC or transceiver.
4. Check for a short-circuit in the cable patch connected to this port.
Excessive
jabbering
Description: A device on this port is continually transmitting packets (jabbering). This is detected as
oversize packets with CRC errors.
Possible causes: A misconfigured NIC, or a malfunctioning NIC or transceiver. It could also be caused by
a short-circuit in the network cable path.
Actions:
1. Check NIC for a misconfiguration.
2. Update the NIC driver software.
3. Replace the NIC or transceiver.
4. Check for a short-circuit in the cable path connected to this port.
Excessive CRC/
alignment errors
Description: A high percentage of data errors was detected on this port.
Possible Causes:
• Faulty cabling or topology
• Half/full duplex mismatch
• Misconfigured NIC
• Malfunctioning NIC, NIC driver or transceiver
Actions:
1. If the port is 100Base-T, make sure the cable, connectors, punch-down blocks, and patch panels
connecting to the port are Category 5 or better. Verify the installation with a Category 5 test device.
2. Check the directly-connected device for mismatches in half/full duplex operation (half duplex on the
switch and full duplex on the connected device, or the reverse).
3. Update the NIC driver software.
4. Verify that the network topology conforms to IEEE 802.3 standards.
5. Replace or relocate the cable.
6. Check the wiring closet components, transceivers, and NICs for proper operation.
