Network properties, Figure 32 network properties dialog boxes, Network ip configuration – HP 8.20q Fibre Channel Switch User Manual
Page 65: 32 network properties dialog boxes
HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide
65
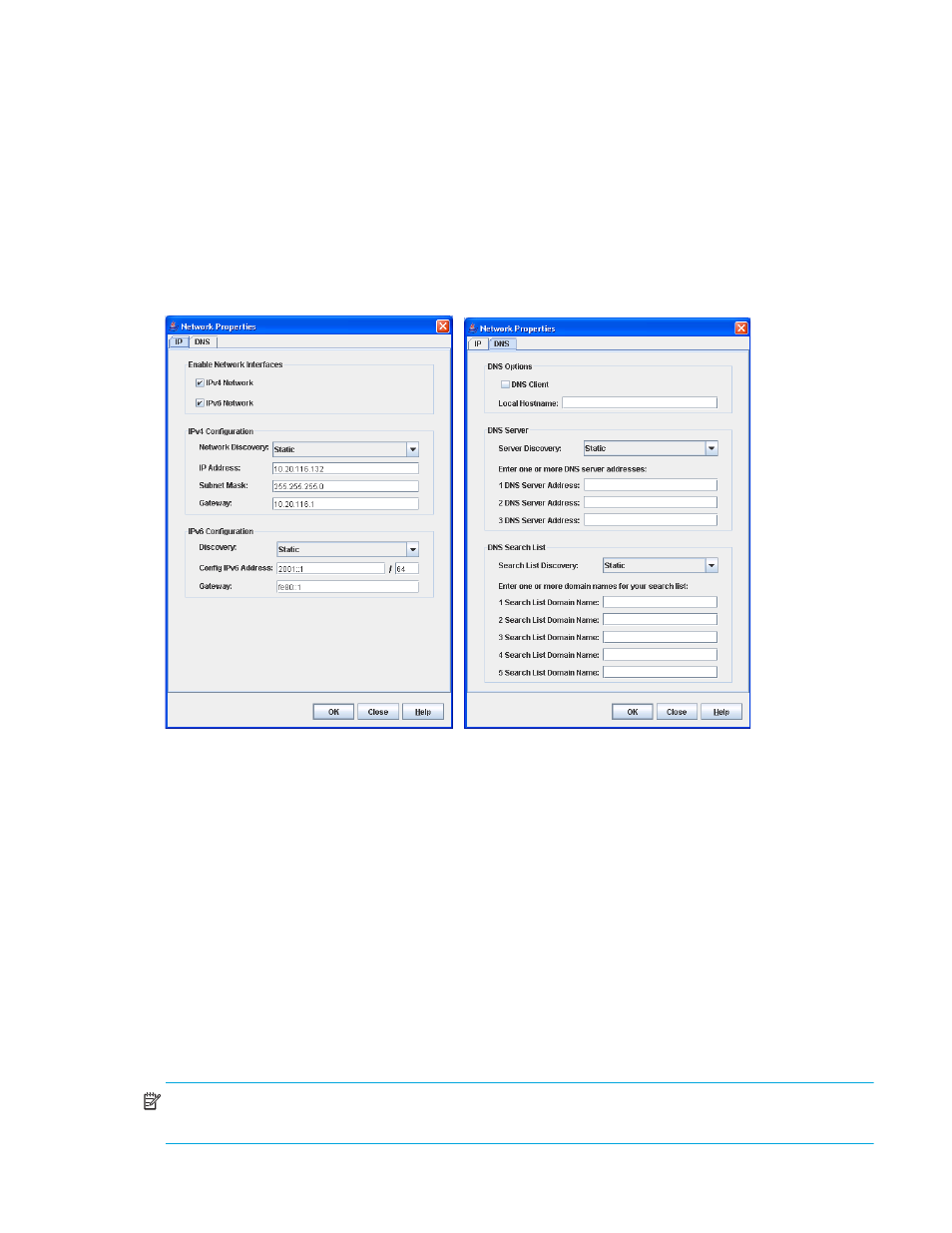
Network properties
Use the Network Properties dialog boxes (
) to configure IP and DNS parameters.
1.
Open the Network Properties dialog box, using one of the following methods:
• Open the faceplate display for the switch you are configuring, and then select Switch > Network
Properties, or
• Right-click a switch graphic in the faceplate display, and then select Network Properties from the
popup menu.
2.
Click the IP tab to open the Network Properties IP dialog box or the DNS tab to open the Network
Properties DNS dialog box, as appropriate for your network setup.
3.
Make the desired changes to the network properties.
4.
After making changes, click OK to put the new values into effect.
Figure 32
Network Properties dialog boxes
Network IP configuration
The IP configuration identifies the switch on the Ethernet network, determines which network discovery
method to use, and enables/disables the IPv4 and IPv6 network addressing.
An IPv4 address is 32 bits and consists of four blocks of decimal numbers, with each block separated by a
period. Each block can have up to three numbers. A single zero character displayed in a block indicates
that the block consists of all zeroes. An example of an IPv4 address is 10.20.30.40. All four blocks
contain numbers.
describes the IPv4 and IPv6 configuration parameters.
An IPv6 address provides a much wider range of IP addresses than an IPv4 address. An IPv6 address is
128 bits, and consists of eight blocks of hexadecimal numbers, with each block separated by a colon. The
maximum number of numerals in each block is four. One or more blocks with all zeroes are represented by
two colon characters. The total number of blocks always adds up to eight. To determine how many
contiguous blocks contain only zeroes, subtract the number of populated blocks from eight. For example,
the IPv6 address 2eee::49:24:7a:54:3434 is equivalent to 2eee:0000:0000:49:24:7a:54:3434. The
number of blocks containing zeroes in this example is two (8-6=2).
NOTE:
Switches without IPv6 addressing enabled can not communicate over Ethernet with hosts or
switches using the IPv6 addressing.
