Lu mapping compared to emulation type, Figure 13 example of external lus <= 2 tb, 13 example of external lus <= 2 tb – HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console Software User Manual
Page 26
26
External Storage XP for the XP10000/XP12000
When the amount of I/Os from the host to the external volume exceeds the maximum amount of I/Os
the external disk array can accept, commands from the host to the local disk array might time out. As
you configure the system using external volumes, consider the external disk array’s I/O capacity.
•
When executing Command View XP or XP Remote Web Console commands to the mapped external
volume and, therefore, too many I/Os are issued for the external disk array to process, commands
might time out and errors might occur.
When the amount of I/Os from Command View XP or XP Remote Web Console to the external volume
exceeds the maximum amount of I/Os the external disk array can accept, commands might time out
and errors might occur. As you configure the system using external volumes, consider the external disk
array’s I/O capacity.
•
When using an external volume from the host, note the external volume’s Path Blockade Watch time. If
the Path Blockade Watch time is longer than the host command’s timeout period, commands from the
host might time out when the power supply is off or errors occur for the external disk array. If host I/O
is a significant concern, ensure that the external volume’s Path Blockade Watch time is the same as or
shorter than the host command’s timeout period.
LU mapping compared to emulation type
•
Do not access any external storage volume that is mapped as an External Storage XP volume from a
host connected directly to the external disk array. Also, do not access an External Storage XP mapped
external array volume using the external disk array’s functions (for example, local replication). After
mapping an external disk volume as a local XP10000/XP12000 volume, access the mapped external
disk volume only via the local XP10000/XP12000 disk array.
•
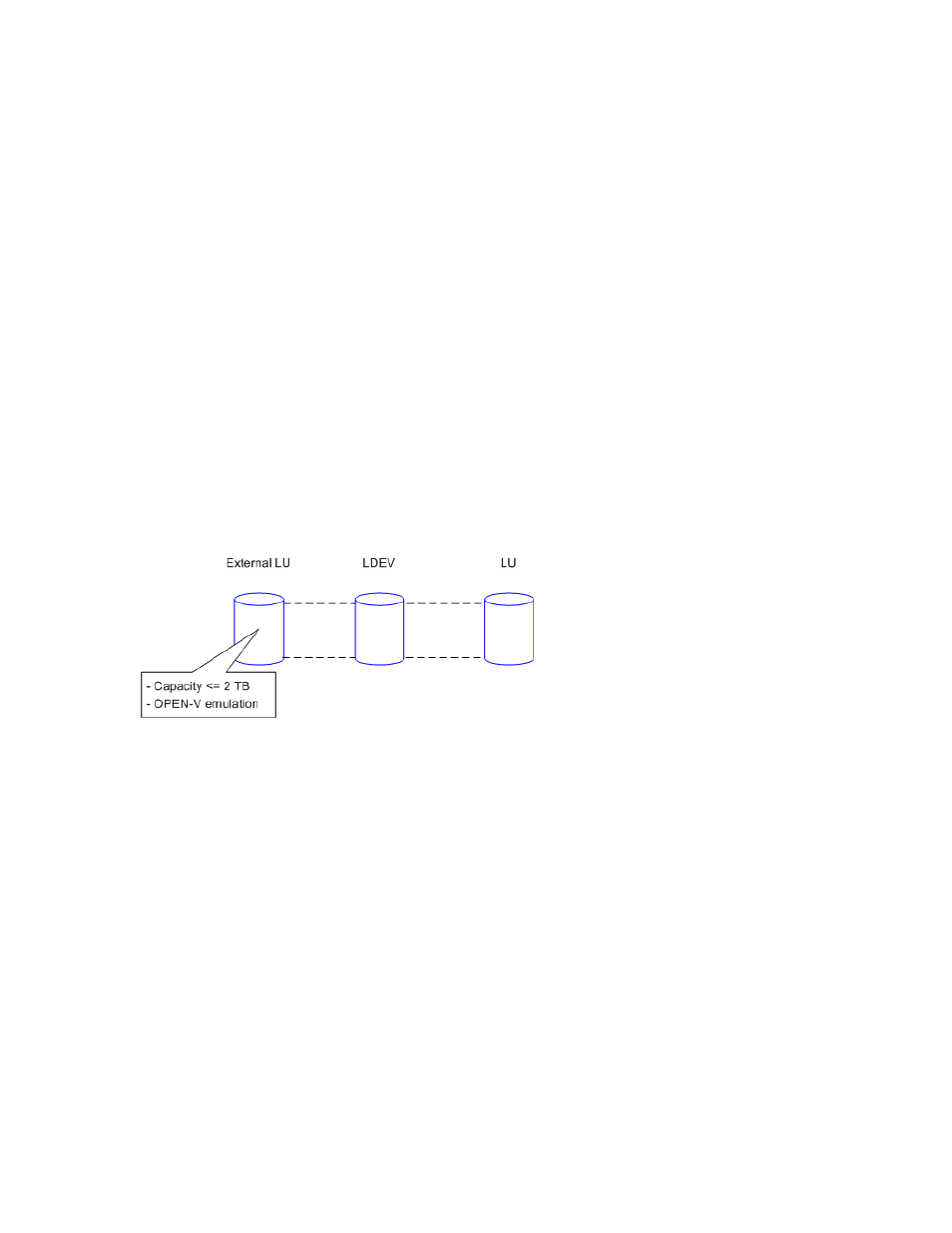
When you map an external disk and specify OPEN-V emulation, the LU is defined as an internal XP
LDEV with the same capacity as the mapped external LU. That is, no space is forfeited for management
space, and no formatting of that data occurs. Therefore, Open-V is recommended.
Figure 13
Example of external LUs <= 2 TB
•
When you map an external LU as internal XP LDEVs and use emulation types other than OPEN-V, the
number of volumes and the volume capacity of the mapped internal XP LDEVs depends on the capacity
of the original external LU and normal size of each emulation type. When an external LU is mapped
using emulation types other than OPEN-V, an XP array management information area is required in the
mapped LU. This means that the capacity available after mapping is slightly smaller than the actual
external LU capacity. Available capacity decreases by the size of the XP array management information
area, and all prior data must be considered lost. For further information, see the HP StorageWorks Flex
Copy XP User Guide.
shows an example where capacity of the external LU is larger than (or a multiple of) the
normal size of the XP10000/XP12000 emulation type (OPEN-3 in this example). Therefore, in this
