1 ramp details, Ramp details -24 – KEPCO EL Series Electronic Load Operator Manual P/N 243-1295 Firmware Version 4.00 to 4.xx User Manual
Page 60
3-24
SERIES EL 071414
3.15.1
RAMP DETAILS
NOTE: The following discussion can also apply to the use of SCPI commands via a remote
interface to program the ramps. The front panel POS ramp is programmed using
SYST:RAMP:POS (PAR. B.108), NEG ramp is programmed using SYST:RAMP:NEG
(PAR. B.110), and INPT ramp is programmed using INP:RAMP (PAR. B.15).
POS and NEG ramps establish the time it takes for the load to go from one setpoint to another.
Figure B-1 of Appendix B shows typical timing when POS and NEG ramps are used with tran-
sients to change state (see PAR B.100 for details on transients).
INPT ramp establishes the time it takes to attain the operating mode setpoint value once the
load is engaged. For current and conductance modes, the ramp starts at zero and increases in
even steps over the duration established by the INPT time until the setpoint is reached. For volt-
age and resistance modes the ramp starts at maximum and decreases to the setpoint value.
The INPT ramp does not function in Power mode. Units are shipped from the factory with INPT
set to 0.02 seconds (the recommended minimum).
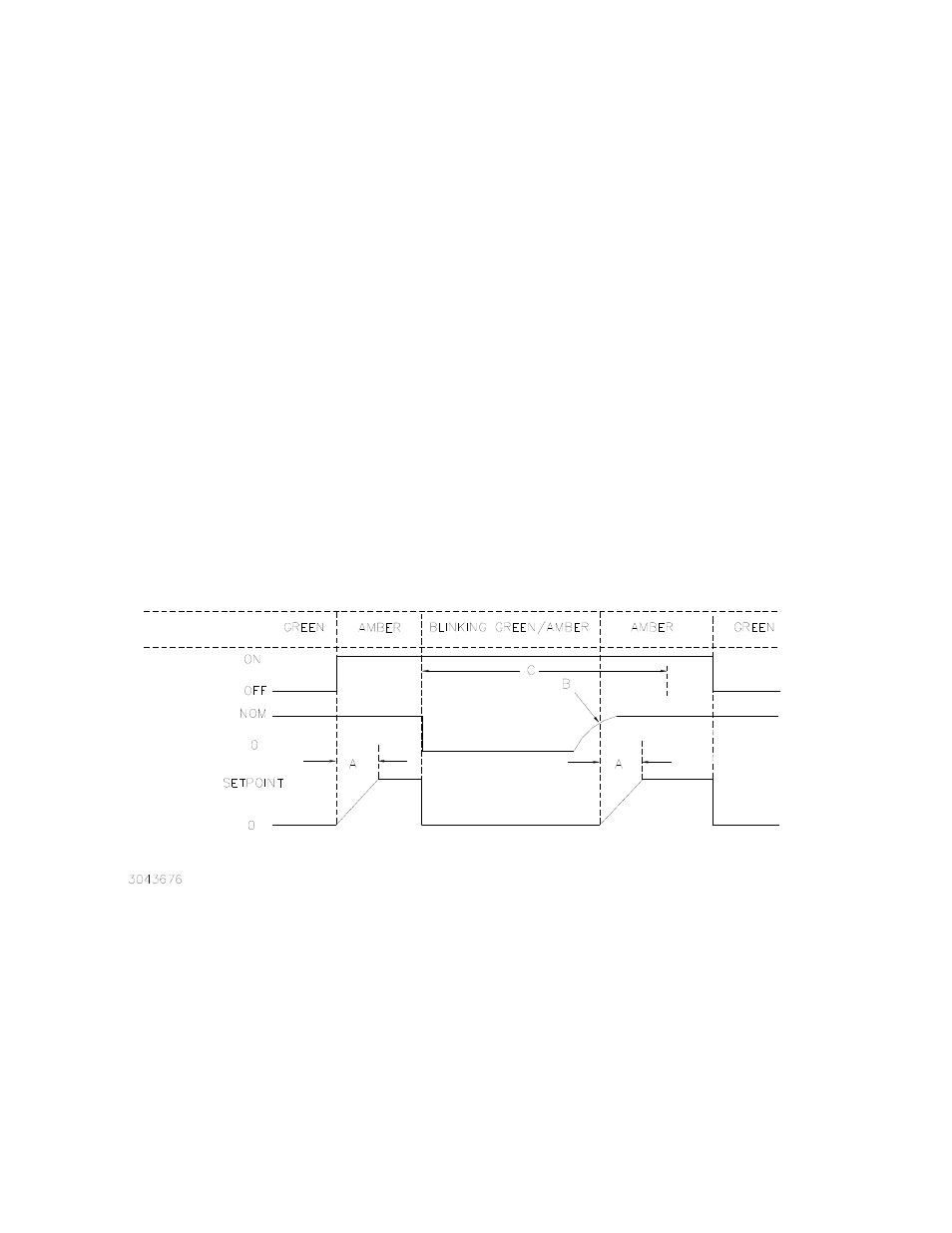
With INPT ramp time set between 0.001 and 2, the INPT ramp occurs when the LOAD switch is
pressed to engage the load. This ramp can also occur if a minimum input voltage and recovery
time has been programmed (see PAR. 3.16). If input voltage is lost, then rises above the cutoff
point within the recovery period, the INPT ramp occurs. Figure 3-7 shows the timing for INPT
ramps.
FIGURE 3-7. TIMING FOR PROGRAMMING INPT RAMP AND MINIMUM VOLTAGE
INPUT STATE
(LOAD SWITCH)
LOAD
INDICATOR
OUTPUT
(CURRENT OR
CONDUCTANCE)
INPUT
VOLTAGE
A = Time determined by INP:RAMP (or RAMP INPT from front panel).
B = Value determined by INP:CUT:VOLT (or INPT VOLT from front panel).
C = Time determined by INP:CUT:TIME or (INPT DELY from front panel).
