Piping, 1 piping for system 1, Piping -1 – Yokogawa Integral Oxygen Analyzer ZR202 User Manual
Page 50: Piping for system 1 -1, Caution
<4. Piping>
4-1
IM 11M12A01-04E
4. Piping
This chapter describes piping procedures in the three typical system configurations for EXAxt ZR
Integrated type Zirconia Oxygen Analyzer.
• Ensure that each check valve, stop valve and joints used for piping are not leaking.
Especially, when there is any leakage at piping and joints for the calibration gas, it may cause
clogging of the piping or incorrect calibration.
• Be sure to conduct leakage test after setting the piping.
• Basically, apply instrument air (dehumidified to the dew point -20°C or lower, removed any dust,
oil mist and the like) for the reference gas when piping.
• When the instrument applies natural convection for reference gas (Model ZR202G-----
C), ambient air near the probe is used for reference gas; therefore the accuracy of analysis will
be affected by ambient humidity changes or the like. If more accurate analysis is necessary, use
instrument air (dehumidified to the dew point -20°C or lower, removed any dust, oil mist and the
like) for reference gas.
Stable analyzing can be conducted when using instrument air.
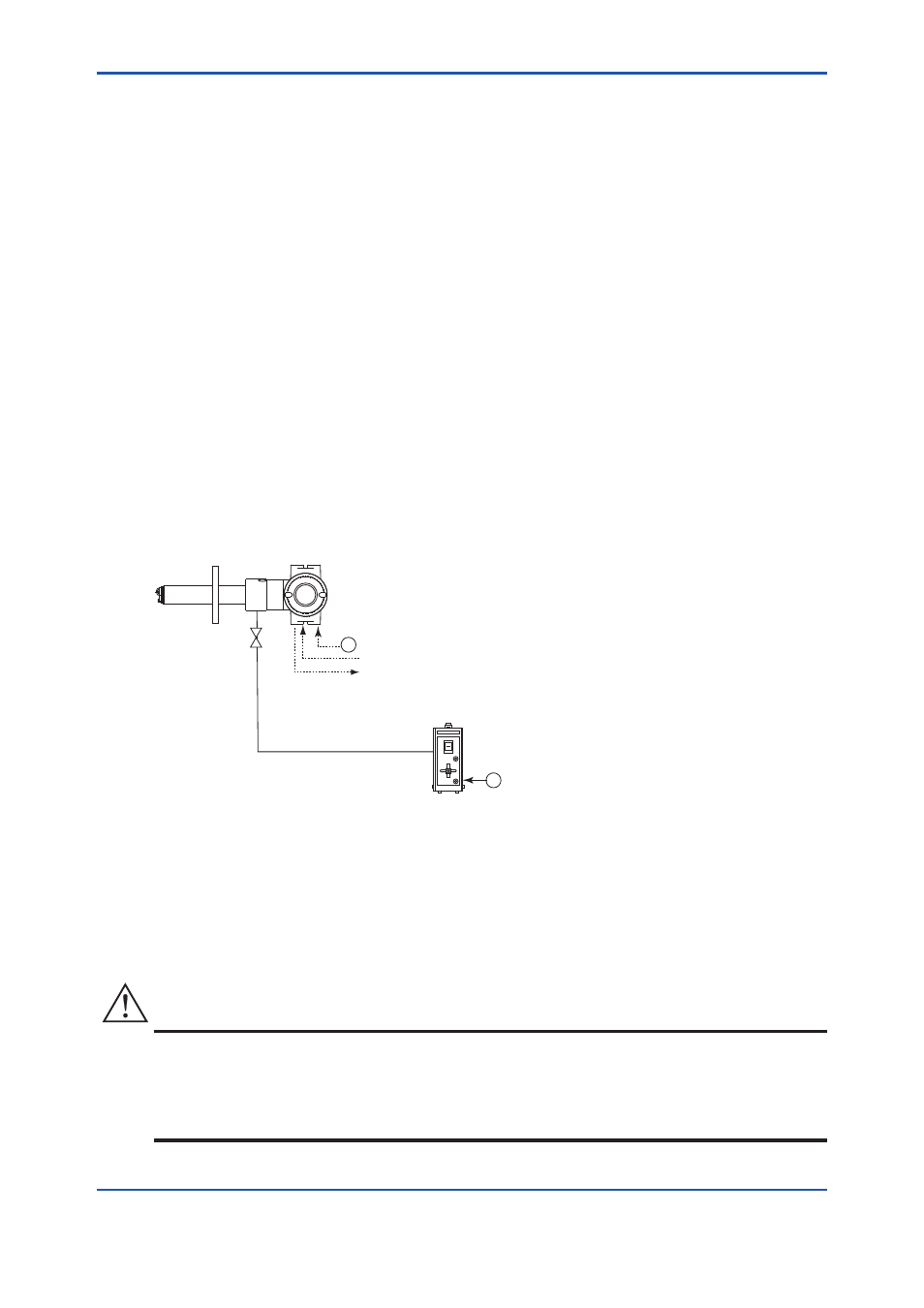
4.1 Piping for System 1
The piping in System 1 is illustrated in Figure 4.1
~
ZR202G Integrated type Zirconia Oxygen Analyzer
ZO21S Standard gas unit
Stop valve
Calibration gas
F1.1E.ai
~
100 to 240 V AC
100/110/115/200/220/240 V AC
Contact input
Analog output, contact output
Digital output (HART)
Figure 4.1
Piping for System 1
Piping in System 1 is as follows:
• Place a stop valve through the nipple at the calibration gas inlet of the equipment.
Then mount a joint for a 6 mm (O.D.) x 4 mm (I.D.) soft tube at the stop valve connection hole of
the inlet side (see Section 4.1.2). The tube is to be connected to this joint only during calibration.
CAUTION
• The stop valve should be connected directly to the equipment. If any piping is present between
the analyzer and the stop valve, condensed water may be produced in the pipe, which may
cause damage to the sensor by rapid cooling when the calibration gas is introduced.
• The reference gas should have an oxygen concentration identical to that of fresh air (21%).
