1 what is an alarm, What is an alarm? -4 – Yokogawa Integral Oxygen Analyzer ZR202 User Manual
Page 143
<12. Troubleshooting>
12-4
IM 11M12A01-04E
12.2 Displays and Measures to Take When Alarms are
Generated
12.2.1 What is an Alarm?
When an alarm is generated, the alarm indication blinks in the display to notify of the alarm (Figure 12.3).
Pressing the alarm indication displays a description of the alarm. Alarms include those shown in Table 12.2.
Displayed alternately
AL-06
21.0%
F12.4E.ai
Figure 12.4
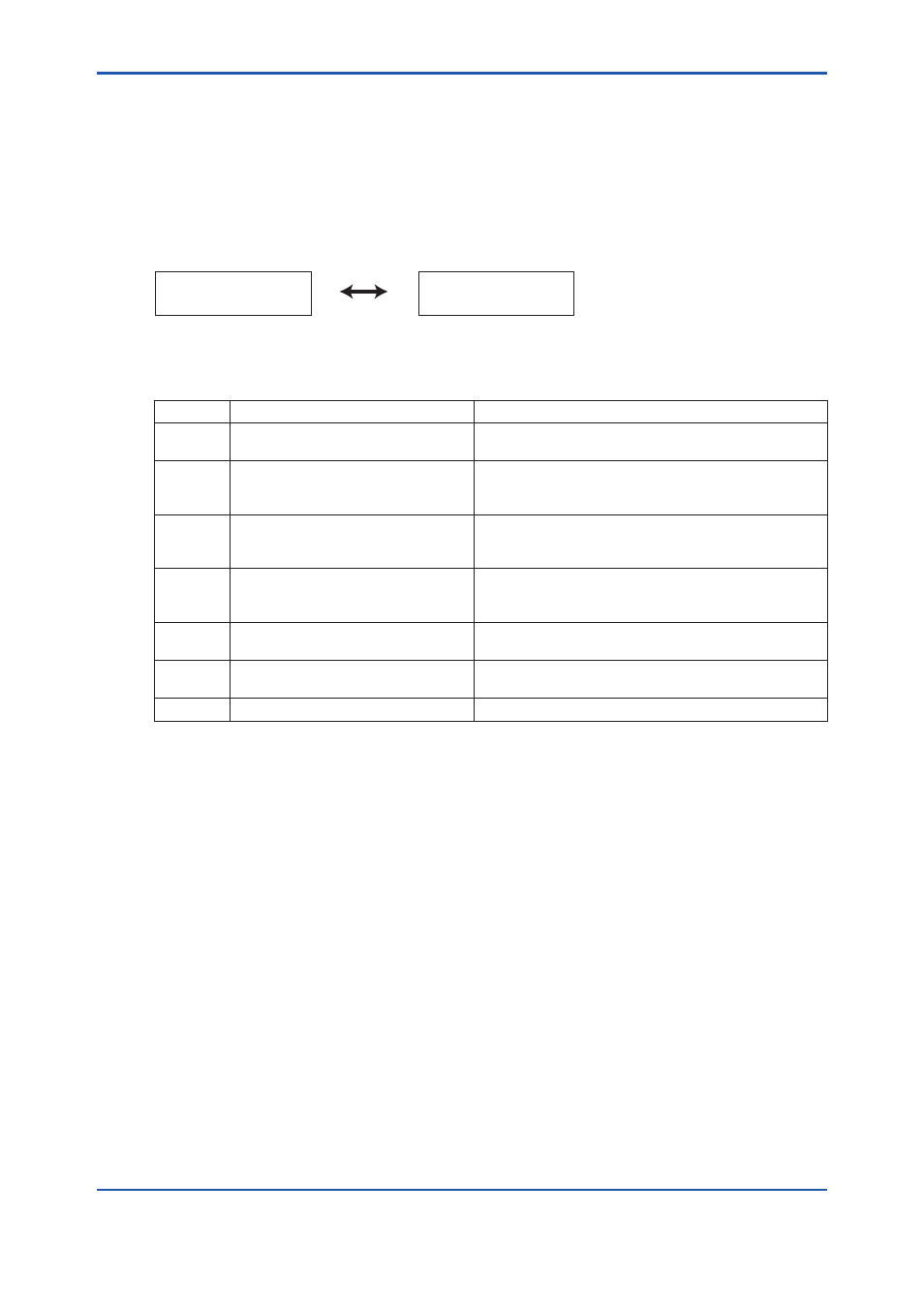
Table 12.2
Types of Alarms and Reasons for Occurrence
Alarm
Type of alarm
Reason for occurrence
Alarm 1
Oxygen concentration alarm
concentration alarm
Occurs when a measured value exceed or falls below
the set alarm value (refer to Section 8.4, "Alarm Setting").
Alarm 6 Zero calibration coefficient alarm
Generated when the zero correction ratio is out of the
range of 100 ± 30% in automatic and semi-automatic
calibration (refer to Section 9.1.3, Compensation).
Alarm 7 Span calibration coefficient alarm
Generated when the span correction ratio is out of the
range of 0 ± 18% in automatic and semi-automatic
calibration (refer to Section 9.1.3, "Compensation").
Alarm 8 EMF stabilization time-up
Generated when the cell (sensor) voltage is not stabilized
even after the calibration time is up in automatic and
semi-automatic calibration.
Alarm 10 Cold junction temperature alarm
Occurs when an equipment internal temperature
exceeds 85°C.
Alarm 11 Thermocouple voltage alarm
Generated when thermocouple voltage exceeds 42.1 mV
(about 1020°C ) or falls below -5 mV (about -170°C).
Alarm 13 Battery low alarm
Internal battery needs replacement
If an alarm is generated, such measures as turning off the heater power are not carried out. The alarm is
released when the cause for the alarm is eliminated.
However, Alarm 10 and/or Alarm 11 may be generated at the same time as Error-2 (heater temperature error).
In such a case, the measure taken for this error has priority.
If the converter power is turned off after an alarm is generated and restarted before the cause of the alarm
has been eliminated, the alarm will be generated again.
However, Alarms 6, 7, and 8 (alarms related to calibration) are not generated unless calibration is executed.
12.2.2
Measures Taken When Alarms are Generated
12.2.2.1
Alarm 1: Oxygen Concentration Alarm
This alarm is generated when a measured value exceeds an alarm set point or falls below it. For
details on the oxygen concentration alarm, see Section 8.4, “Setting Oxygen Concentration Alarms,”
in the chapter on operation.
12.2.2.2
Alarm 6: Zero Calibration Coefficient Alarm
In calibration, this alarm is generated when the zero correction ratio is out of the range of 100 ± 30%
(refer to Section 9.1.3, “Compensation”). The following can be considered the causes for this:
(1) The zero gas oxygen concentration does not agree with the value of the zero gas concentration
set (refer to Section 9.2.1,“Calibration Setup.)” Otherwise, the span gas is used as the zero gas.
(2) The zero gas flow is out of the specified flow (600 ± 60 ml/min).
(3) The sensor assembly is damaged and so cell voltage is not normal.
