GE Industrial Solutions MX350 Communications Guide User Manual
Page 49
COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
45
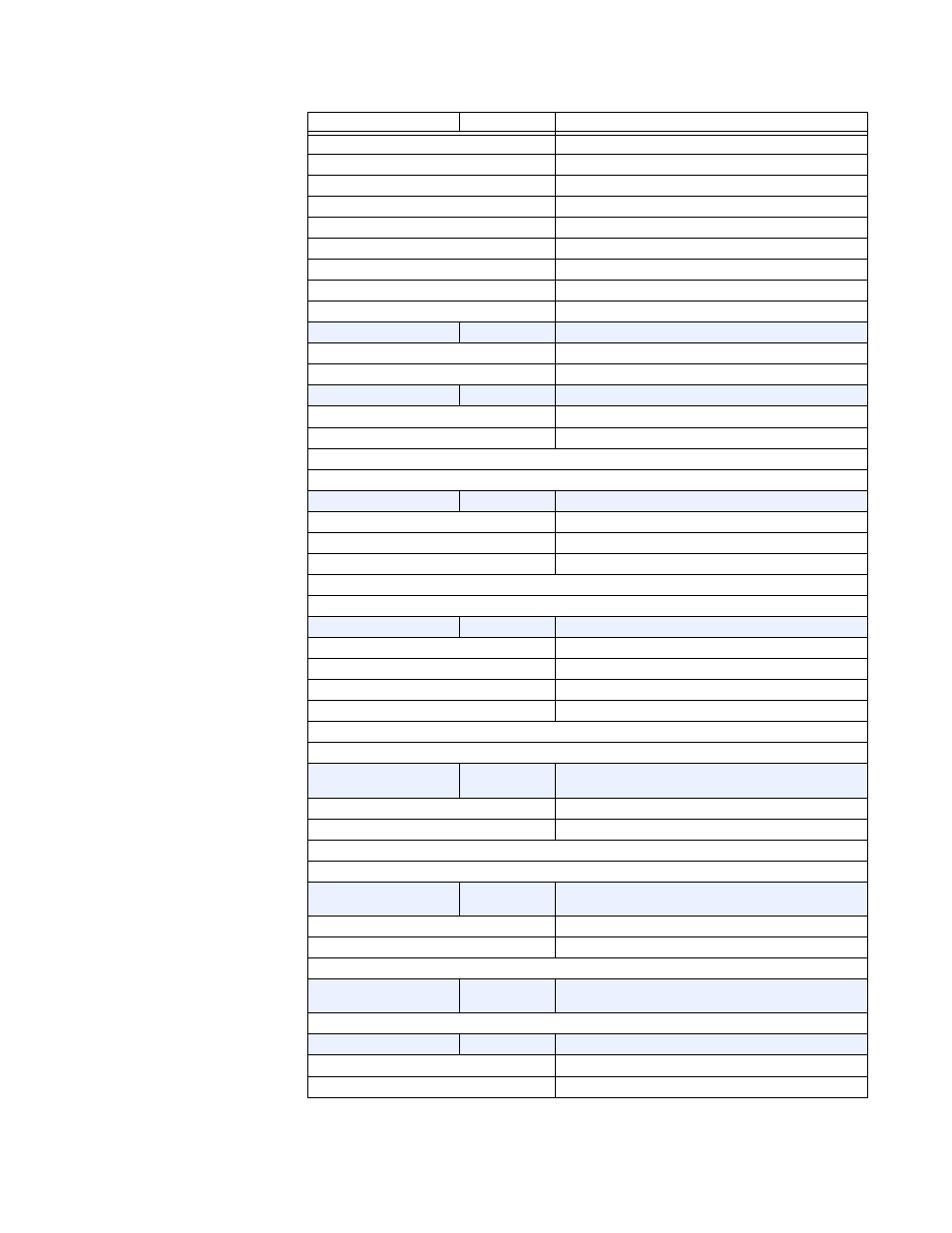
18
R
19
S
20
T
21
U
22
V
23
W
24
X
25
Y
26
Z
F16
16 bits
2’s COMPLEMENT SIGNED VALUE, 1 DECIMAL PLACE
<0
S2 Leads S1
>0
S1 Leads S2
F17
32 bits
UNSIGNED LONG VALUE, 3 DECIMAL PLACES
1st 16 bits
High Order Word of Long Value
2nd 16 bits
Low Order Word of Long Value
Example: 123456 stored as 123456
i.e. 1st word: 0001 hex, 2nd word: E240 hex
F18
32 bits
DATE MM/DD/YYYY
1st byte
Month 1 to 12
2nd byte
Day 1 to 31
3rd and 4th byte
Year 1995 to 2094
Example: Feb 20, 1995 stored as 34867147
i.e. 1st word: 0214, 2nd word 07CB
F19
32 bits
TIME HH:MM:SS:hh
1st byte
Hours 0 to 23
2nd byte
Minutes 0 to 59
3rd byte
Seconds 0 to 59
4th byte
Hundredths of seconds 0 to 99
Example: 2:05pm stored as 235208704
i.e. 1st word: 0E05, 2nd word 0000
F21
16 bits
2’s COMPLEMENT SIGNED VALUE, 2 DECIMAL PLACES
Power Factor
< 0
Leading Power Factor - Negative
> 0
Lagging Power Factor - Positive
Example: Power Factor of 0.87 lag is used as 87
i.e. 0057
F22
16 bits
TWO 8-BIT CHARACTERS PACKED INTO 16-BIT
UNSIGNED
MSB
First Character
LSB
Second Character
Example: String ‘AB’ stored as 4142 hex
F24
16 bits
UNSIGNED VALUE AS SECONDS SHOW AS Duration,
MAX VALUE = OFF
Example: 1234 stored as 1234, and displayed as 20 Mins
F25
16 bits
Trace Memory Channel Data
0
Leading
1
Lagging
Code
Type
Definition
