5 ipsec vpn technical reference, Diffie-hellman (dh) key exchange – ZyXEL Communications NBG420N User Manual
Page 185
Chapter 15 IPSec VPN
NBG420N User’s Guide
185
15.5 IPSec VPN Technical Reference
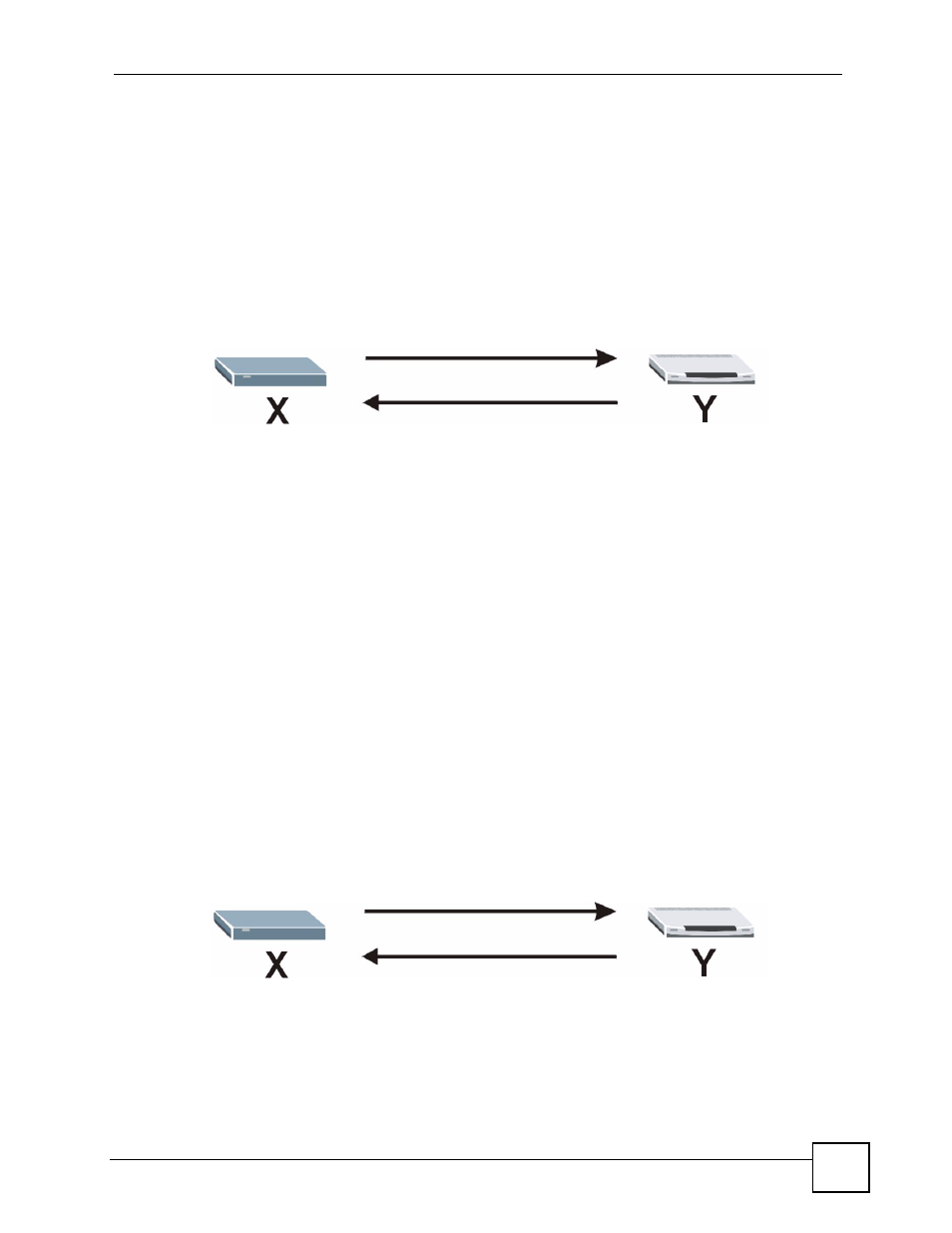
IKE SA Proposal
The IKE SA proposal is used to identify the encryption algorithm, authentication algorithm,
and Diffie-Hellman (DH) key group that the NBG420N and remote IPSec router use in the
IKE SA. In main mode, this is done in steps 1 and 2, as illustrated below.
Figure 111 IKE SA: Main Negotiation Mode, Steps 1 - 2: IKE SA Proposal
The NBG420N sends a proposal to the remote IPSec router. Each proposal consists of an
encryption algorithm, authentication algorithm, and DH key group that the NBG420N wants
to use in the IKE SA. The remote IPSec router sends the accepted proposal back to the
NBG420N. If the remote IPSec router rejects the proposal (for example, if the VPN tunnel is
not configured correctly), the NBG420N and remote IPSec router cannot establish an IKE SA.
Note: Both routers must use the same encryption algorithm, authentication algorithm,
and DH key group.
See the field descriptions for information about specific encryption algorithms, authentication
algorithms, and DH key groups. See
Diffie-Hellman (DH) Key Exchange on page 185
for
more information about DH key groups.
Diffie-Hellman (DH) Key Exchange
The NBG420N and the remote IPSec router use a DH key exchange to establish a shared
secret, which is used to generate encryption keys for IKE SA and IPSec SA. In main mode, the
DH key exchange is done in steps 3 and 4, as illustrated below.
Figure 112 IKE SA: Main Negotiation Mode, Steps 3 - 4: DH Key Exchange
The DH key exchange is based on DH key groups. Each key group is a fixed number of bits
long. The longer the key, the more secure the encryption keys, but also the longer it takes to
encrypt and decrypt information. For example, DH2 keys (1024 bits) are more secure than
DH1 keys (768 bits), but DH2 encryption keys take longer to encrypt and decrypt.
1
2
3
4
