39 isochronous transmit context control register – Texas Instruments TSB12LV26 User Manual
Page 75
4–37
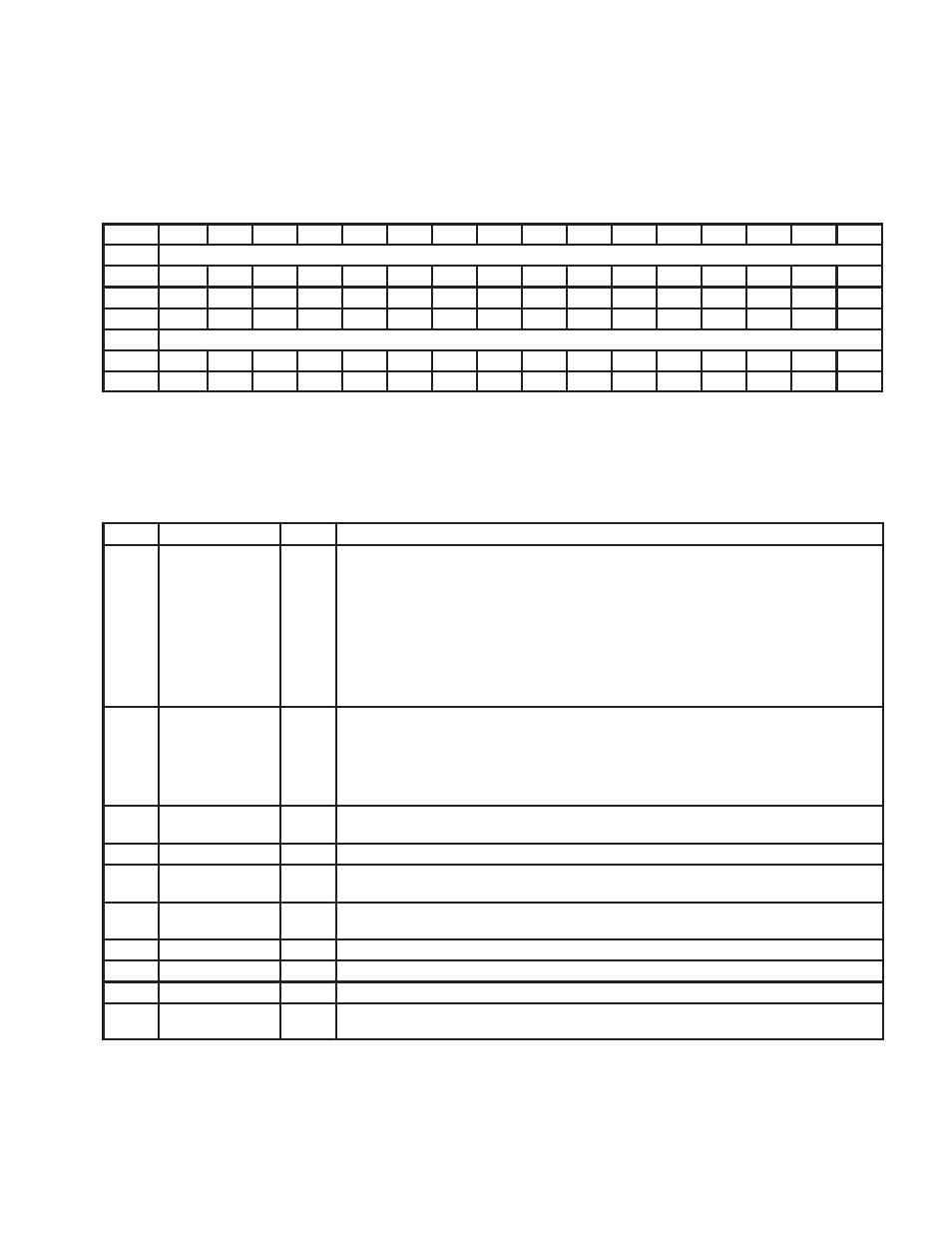
4.39 Isochronous Transmit Context Control Register
The isochronous transmit context control set/clear register controls options, state, and status for the isochronous
transmit DMA contexts. The n value in the following register addresses indicates the context number (n = 0, 1, 2, 3,
…
,
7). See Table 4–29 for a complete description of the register contents.
Bit
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
Name
Isochronous transmit context control
Type
RSCU
RSC
RSC
RSC
RSC
RSC
RSC
RSC
RSC
RSC
RSC
RSC
RSC
RSC
RSC
RSC
Default
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Bit
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Name
Isochronous transmit context control
Type
RSC
R
R
RSU
RU
RU
R
R
RU
RU
RU
RU
RU
RU
RU
RU
Default
0
0
0
X
0
0
0
0
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Register:
Isochronous transmit context control
Type:
Read/Set/Clear/Update, Read/Set/Clear, Read/Update, Read-only
Offset:
200h + (16 * n)
set register
204h + (16 * n)
clear register
Default:
XXXX X0XXh
Table 4–29. Isochronous Transmit Context Control Register Description
BIT
FIELD NAME
TYPE
DESCRIPTION
31
cycleMatchEnable
RSCU
When this bit is set to 1, processing occurs such that the packet described by the context first
descriptor block is transmitted in the cycle whose number is specified in the cycleMatch field
(bits 30–16). The cycleMatch field (bits 30–16) must match the low-order two bits of cycleSeconds
and the 13-bit cycleCount field in the cycle start packet that is sent or received immediately before
isochronous transmission begins. Since the isochronous transmit DMA controller may work ahead,
the processing of the first descriptor block may begin slightly in advance of the actual cycle in which
the first packet is transmitted.
The effects of this bit, however, are impacted by the values of other bits in this register and are
explained in the
1394 Open Host Controller Interface Specification. Once the context has become
active, hardware clears this bit.
30–16
cycleMatch
RSC
Contains a 15-bit value, corresponding to the low-order two bits of the bus isochronous cycle timer
register (OHCI offset F0h, see Section 4.31) cycleSeconds field (bits 31–25) and the cycleCount field
(bits 24–12). If bit 31 (cycleMatchEnable) is set, then this isochronous transmit DMA context
becomes enabled for transmits when the low-order two bits of the bus isochronous cycle timer
register cycleSeconds field (bits 31–25) and the cycleCount field (bits 24–12) value equal this field
(cycleMatch) value.
15
run
RSC
This bit is set by software to enable descriptor processing for the context and cleared by software to
stop descriptor processing. The TSB12LV26 changes this bit only on a hardware or software reset.
14–13
RSVD
R
Reserved. Bits 14–13 return 0s when read.
12
wake
RSU
Software sets this bit to cause the TSB12LV26 to continue or resume descriptor processing. The
TSB12LV26 clears this bit on every descriptor fetch.
11
dead
RU
The TSB12LV26 sets this bit when it encounters a fatal error and clears the bit when software resets
bit 15 (run).
10
active
RU
The TSB12LV26 sets this bit to 1 when it is processing descriptors.
9–8
RSVD
R
Reserved. Bits 9–8 return 0s when read.
7–5
spd
RU
This field is not meaningful for isochronous transmit contexts.
4–0
event code
RU
Following an OUTPUT_LAST* command, the error code is indicated in this field. Possible values are:
ack_complete, evt_descriptor_read, evt_data_read, and evt_unknown.
