Texas Instruments MSP50C614 User Manual
Page 192
Individual Instruction Descriptions
4-100
4.14.18
FIR
FIR Filter Function (Coefficients in RAM)
Syntax
[label]
name
dest, src
Clock,
clk
Word,
w
With RPT,
clk
Class
FIR
A
n, *Rx
2
1
2(n
R
+2)
9a
Execution
With RPT N–2:
(
mask interrupts)
RPT counter = N–2
MR =
h[0] = first filter coefficient
x = sample data pointed at by Rx
even
h[1] = second filter coefficient pointed at Rx
even
+1
y = result stored in three consecutive accumulators (32 bit) pointed by An
{between every accumulation}
IF TAG = 1
R
x
even
= R
x
even
+ R5 {for circular buffering}
ELSE
R
x
even
++
{ if R
x++ is specified in the instruction}
ENDIF
PC
⇐
PC + 1
{final result}
y
+
ȍ
k
+
0..N–1
h[k] · x[N–1–k]
(Execution is detailed in section 4.11)
Flags Affected
None
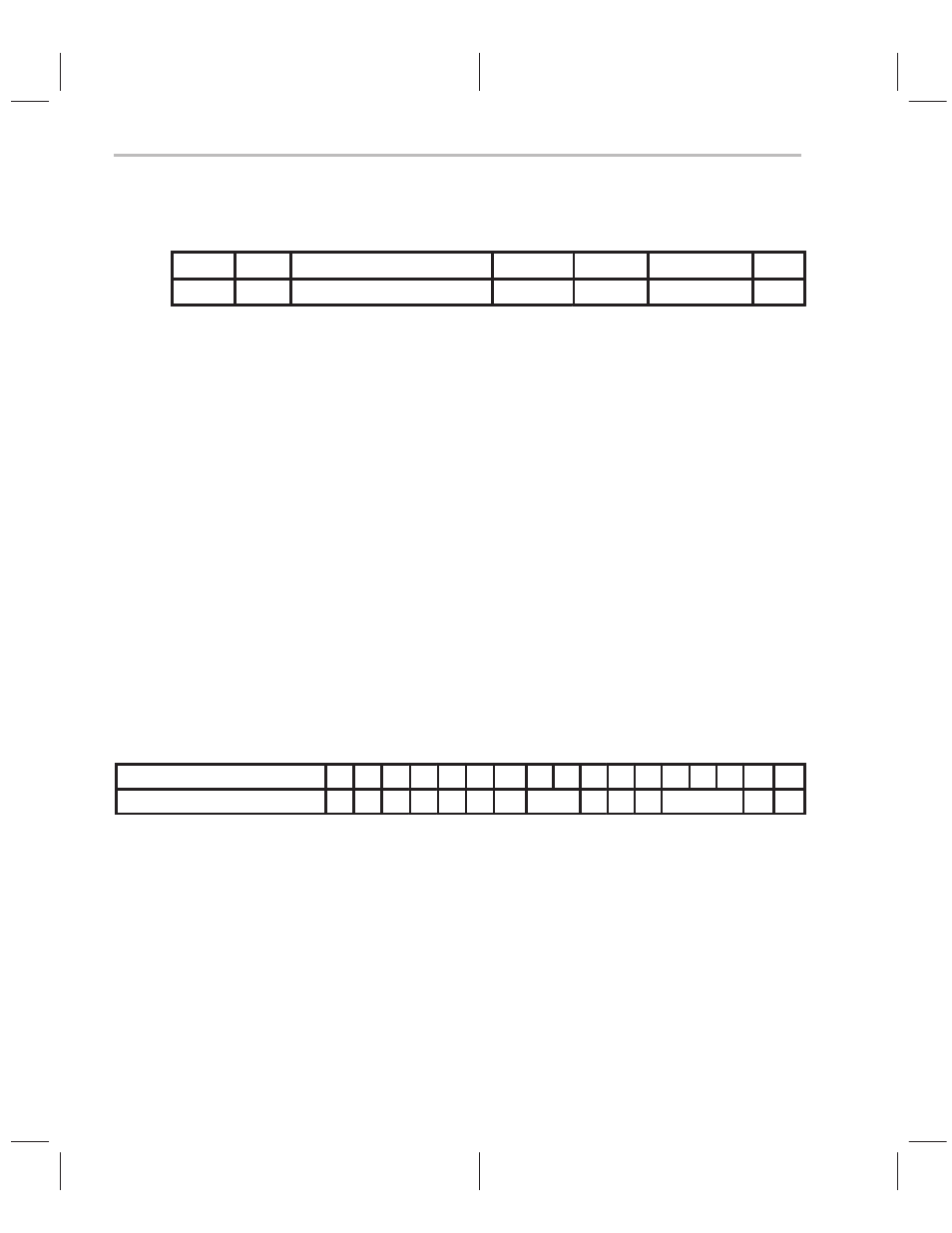
Opcode
Instructions
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
FIR A
n, *Rx
1
1
1
0
1
0
0
A
n
0
1
0
R
x
1
1
Description
Finite impulse response (FIR) filter. Execute finite impulse response filter taps
using coefficients from data memory and samples from data memory. The
instruction specifies two registers, R
x and R(x+1) which sequentially address
coefficients and the sample buffer in the two instruction FIR tap sequence.
This instruction must be used with RPT instruction. When used with the repeat
counter it will execute a 16
×
16 multiplication between two indirect addressed
data memory buffers, 32-bit accumulation, and circular buffer operation.
Executes in 2 instruction cycles.
Selected register R
x must be even. This instruction also uses R(x+1). See
section 4.11 for more detail on the setup of coefficients and sample data.
During FIR execution, interrupt is queued.
