Siemens MICROMASTER 420 User Manual
Page 141
Issue 07/04
3 Functions
MICROMASTER 420 Operating Instructions
6SE6400-5AA00-0BP0
141
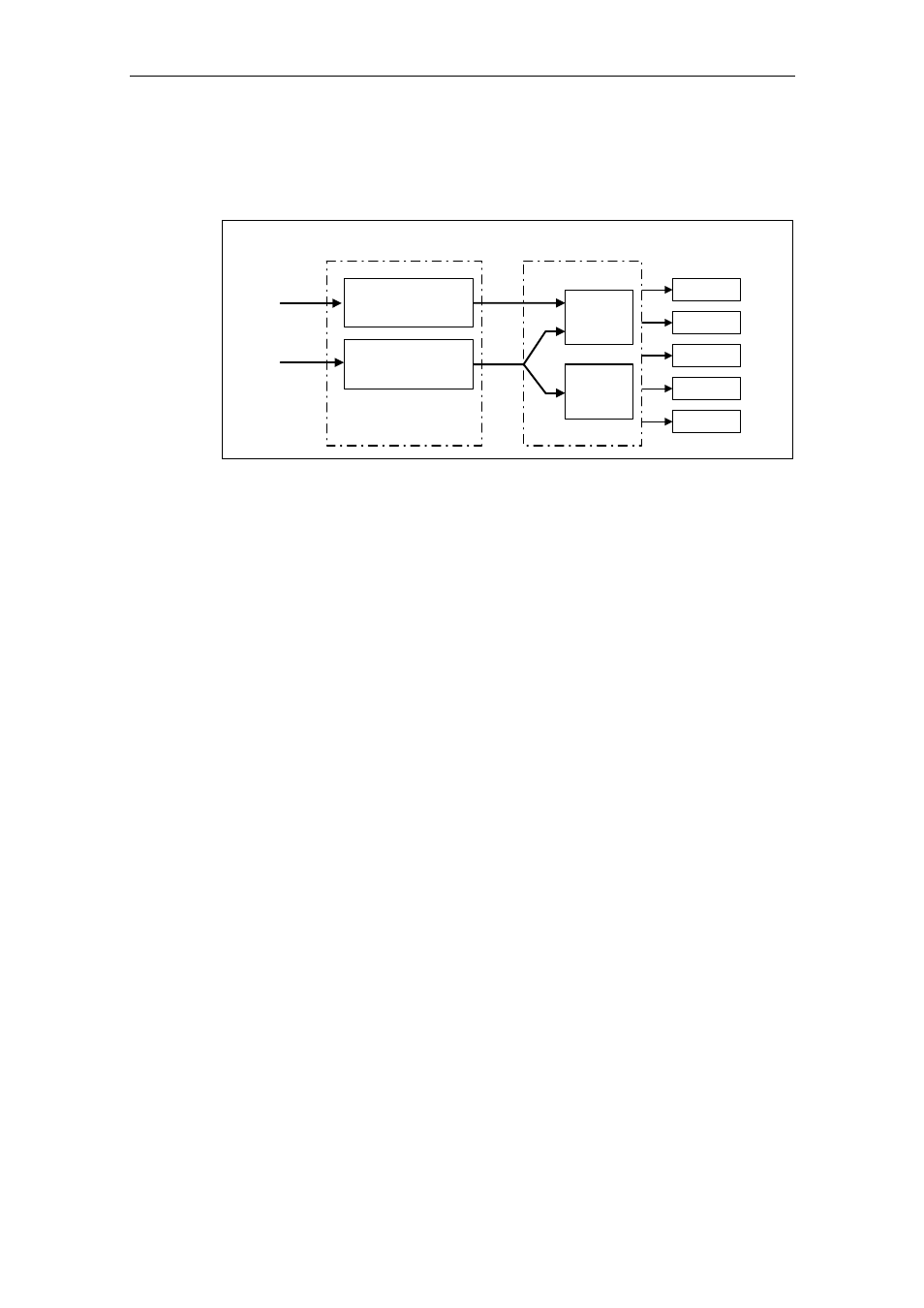
When an overload occurs regarding one of these monitoring functions, initially, a
warning is output. The warning threshold P0294 (i
2
t monitoring) and P0292
(heatsink temperature monitoring) can be parameterized relative to the shutdown
values.
f_pulse
control
i_max
control
A0504
A0505
A0506
F0004
F0005
Inverter overload reaction
P0290
r0036
r0037
Heat sink
temperature
P0292
i
2
t
P0294
Inverter monitoring
Fig. 3-60
Overload response of the drive inverter (P0290)
Example
The warning threshold P0292 for the temperature monitoring (heatsink
temperature) is set to 15 °C in the factory. This means that warning A0504 is
output 15 °C below the shutdown threshold.
At the same time that the warning is output, the parameterized responses are
initiated via P0290. Possible responses include:
Reducing the pulse frequency (P0290 = 2, 3)
This is an extremely effective method to reduce losses in the power module, as
the switching losses represent a very high proportion of the overall losses. In
many applications, a temporary reduction of the pulse frequency can be
tolerated in favor of maintaining the process.
Disadvantage
The current ripple is increased when the pulse frequency is reduced. This can
result in an increase of the torque ripple at the motor shaft (for low moments of
inertia) and an increase in the noise level.
Reducing the output frequency (P0290 = 0,2)
This is advantageous if it is not desirable to reduce the pulse frequency or if the
pulse frequency is already set to the lowest level. Further, the load should have
a characteristic similar to that of a fan, i.e. a square-law torque characteristic for
decreasing speed. When the output frequency is reduced, this significantly
reduces the drive inverter output current and in turn reduces the losses in the
power module.
