Choose a connection protocol, Important isdn concepts, Isdn channel usage – Eicon Networks DIVA LAN ISDN User Manual
Page 20: Important isdn concepts isdn channel usage, Ep 3. choose a connection protocol, Isdn channels, Isdn access interfaces
Chapter Two: Getting Started
3. Choose a connection protocol
20
3. Choose a connection protocol
The usage of the ISDN link is governed by the type of connection protocol you choose. The connection
protocol defines the rules by which ISDN channels are enabled and disabled. The type of protocol you choose
to use depends on the type of connections you plan to make.
Important ISDN concepts
Before you can decide on a connection protocol, you must become familiar with the following ISDN concepts.
ISDN channels
ISDN lines are defined in terms of channels, with each channel supporting a specific type of communication.
The DIVA LAN ISDN Modem supports two ISDN channel types:
• D-channel: The Device channel is used to control the setup of ISDN connections on the other channels.
They can also be used to transmit packet data traffic. The D-channel has a transmission speed of 16 kbps.
• B-channel: Bearer channels are used to carry data or voice traffic. They have a transmission speed of 56
or 64 kbps.
ISDN access interfaces
An access interface is the physical connection between you and an ISDN network. It defines the number of D-
and B-channels that are available to you and the total transmission speed of the connection. The DIVA LAN
ISDN Modem supports a single Basic Rate Interface (BRI), which is comprised of one D-channel (16 kbps)
and two B-channels (64 kbps) for a total user bit rate of 144 kbps.
Each ISDN B-channel can have its own telephone number. Although in some cases you will only get one
number for both channels unless you order supplementary services.
ISDN channel usage
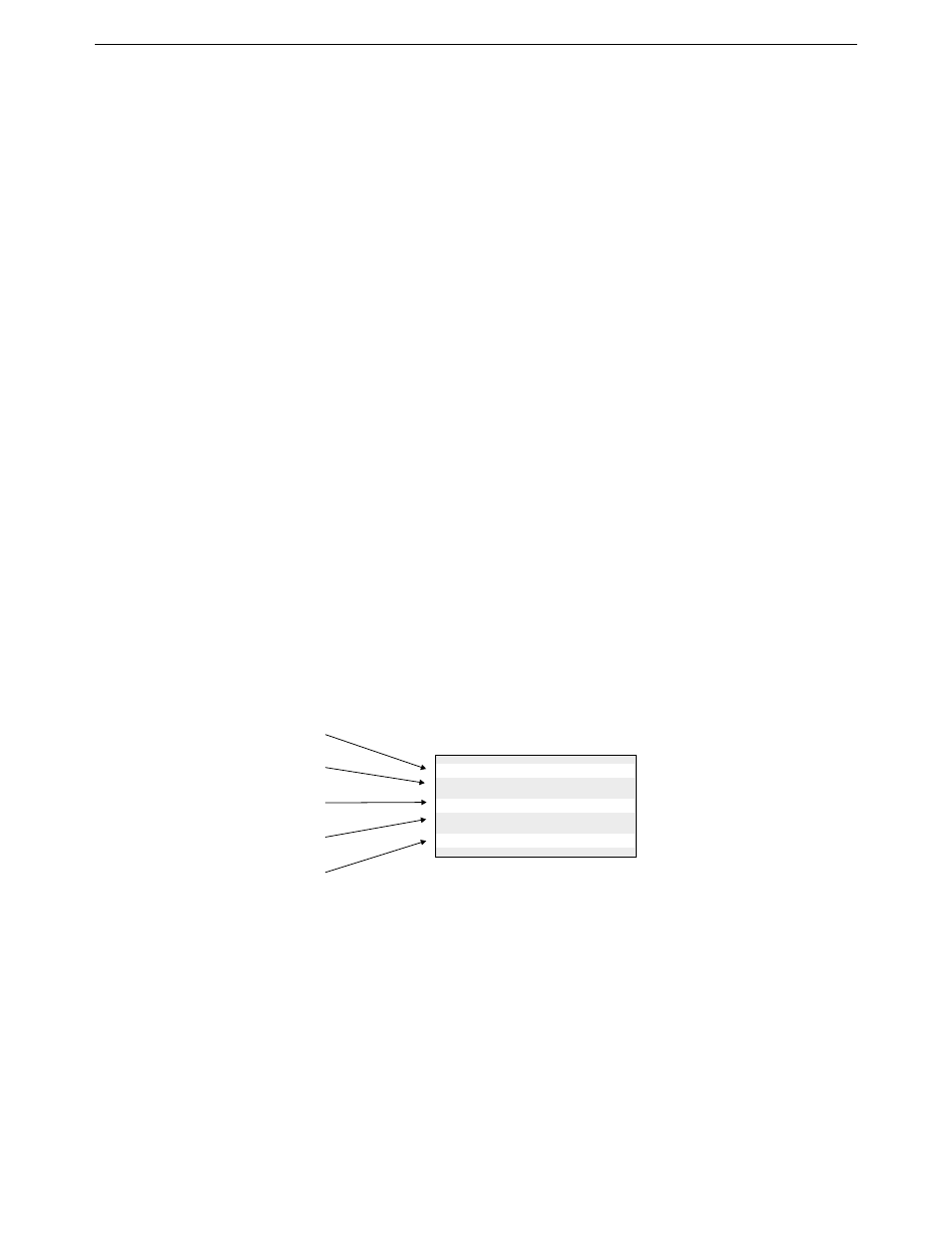
The following diagram shows all the potential connections a DIVA LAN ISDN Modem could make, if it was
configured to support an Internet connection, a corporate network connection, incoming data calls, and analog
calls on both PHONE ports.
All connections, both data and voice, are carried on the B-channels. (AO/DI enables you to also use the
D-channel for data connections, but this exception will be discussed later.) The DIVA LAN ISDN Modem
dynamically assigns B-channels on-demand. Therefore, there is no guarantee which B-channel a specific
connection will receive. The same is true for your ISDN phone numbers and your SPIDs. Your first phone
number does not necessarily map to ISDN channel B1.
Connections are mapped as follows:
• PHONE port 1 always uses the first ISDN phone number (and SPID).
• PHONE port 2 always uses the second ISDN phone number (and SPID).
• To help avoid conflicts, the DIVA LAN ISDN Modem always tries to establish data connections using
phone number 2 first, in an attempt to leave PHONE port 1 free. Of course, if phone number 2 is in use,
the data connection is established using phone number 1.
• When an analog or data connection is established, the first available ISDN B-channel is assigned to it.
ISDN BRI Line
Internet Connection
Corporate Network Connection
Incoming Data Call Connection
PHONE port #1
PHONE port #2
D-channel
1st B-channel
2nd B-channel
