Figure 2-3. remote sensing, 6 series operation, 7 parallel/redundant operation – KEPCO KLP Series (older -1200 models) Operator Manual User Manual
Page 36: Series operation -10, Parallel/redundant operation -10, Remote sensing -10, E 2-3
2-10
KLP-HV 073008
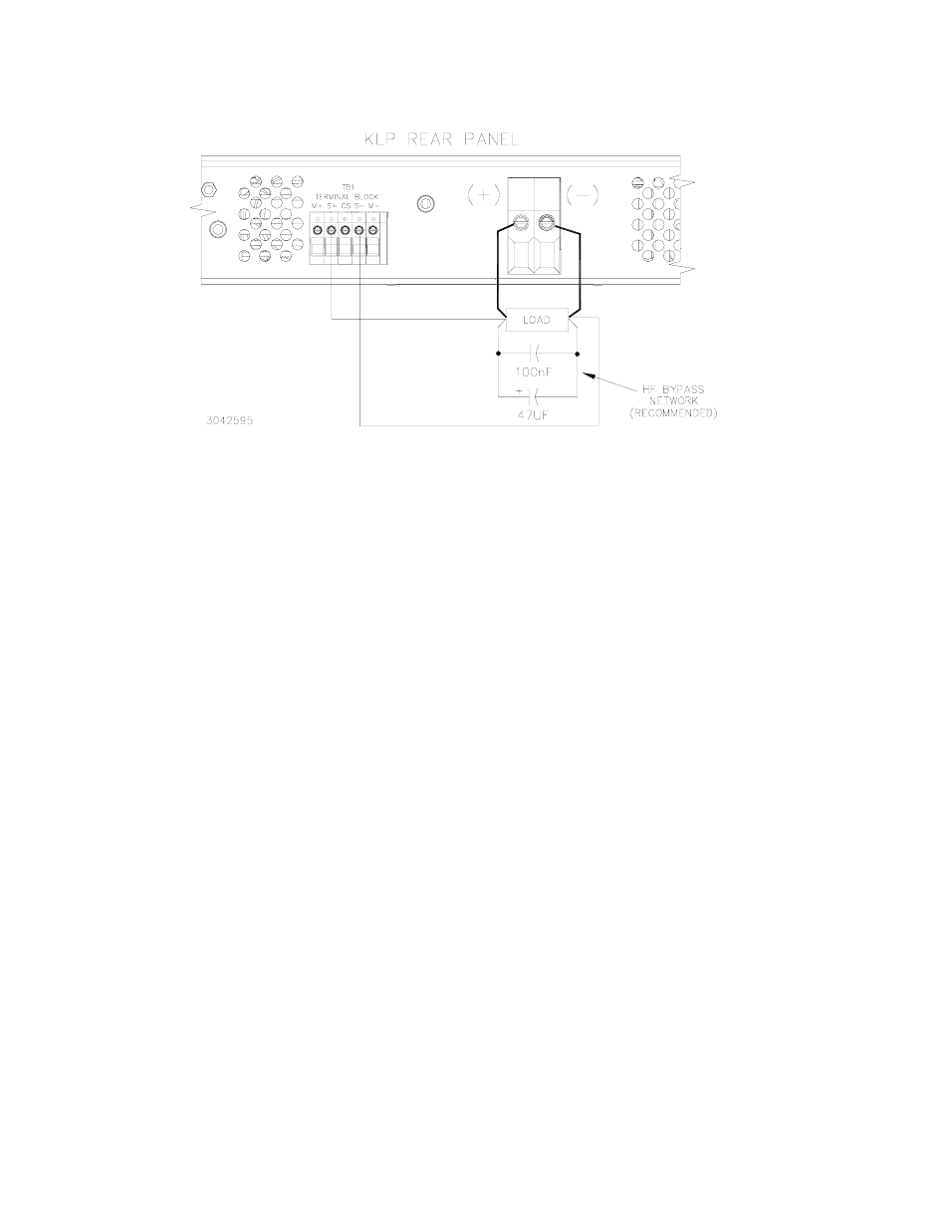
FIGURE 2-3. REMOTE SENSING
2.7.6
SERIES OPERATION
Units may be connected in series to obtain higher output voltages. Each power supply in the
series may be protected by a clamping diode connected in its non-conducting direction in paral-
lel with the output. This diode protects the power supply outputs against secondary effects in the
event of a load short. (Note that this is NOT the same as the blocking diode used for parallel/
redundant operation.) Selection of the clamping diode is entirely dependent upon output volt-
age/current parameters. The clamping diode must be rated for the maximum voltage and cur-
rent of the series connection. Several clamping diodes in parallel may be required to meet the
total current rating. The user must also respect the ±600V d-c maximum isolation from output to
chassis when determining the maximum series voltage. Figure 2-4 shows a series connection of
two KLP power supplies using remote sensing. Kepco strongly recommends that series applica-
tions employ master/slave control as described in PAR’s. 2.7.8 and 3.2.10.
2.7.7
PARALLEL/REDUNDANT OPERATION
Identical KLP power supply models may be connected in parallel in order to provided increased
output current to a common load (see Figure 2-5). This permits the user to obtain significantly
higher load ratings than for a single KLP power supply. The number of power supplies required
is determined by dividing the required load current by the current rating of the applicable KLP
model, and rounding up to the next whole number when necessary. KLP power supplies utilize
active current sharing circuitry to distribute the load current equally among the paralleled units.
Redundant operation is achieved by paralleling one or more power supplies than the minimum
number required to support the load; in this way, system operation is not compromised by the
failure of a single power supply. Any number of KLP power supplies (N+M) can be wired for
redundant operation as long as (N) power supplies can support the load, M representing the
total number of failed power supplies. When operating KLP power supplies in any parallel con-
figuration, load sharing must be implemented among the paralleled modules. Kepco strongly
recommends that parallel/redundant applications employ master/slave control as described in
PAR’s. 2.7.8 and 3.2.10.
