28 (2) electronic gear ratio setting examples – Yaskawa Sigma-5 Large Capacity Users Manual: Design and Maintenance-Rotary Motors-Mechatrolink-III Communication Reference User Manual
Page 124
4 Operation
4.4.3 Electronic Gear
4-28
(2) Electronic Gear Ratio Setting Examples
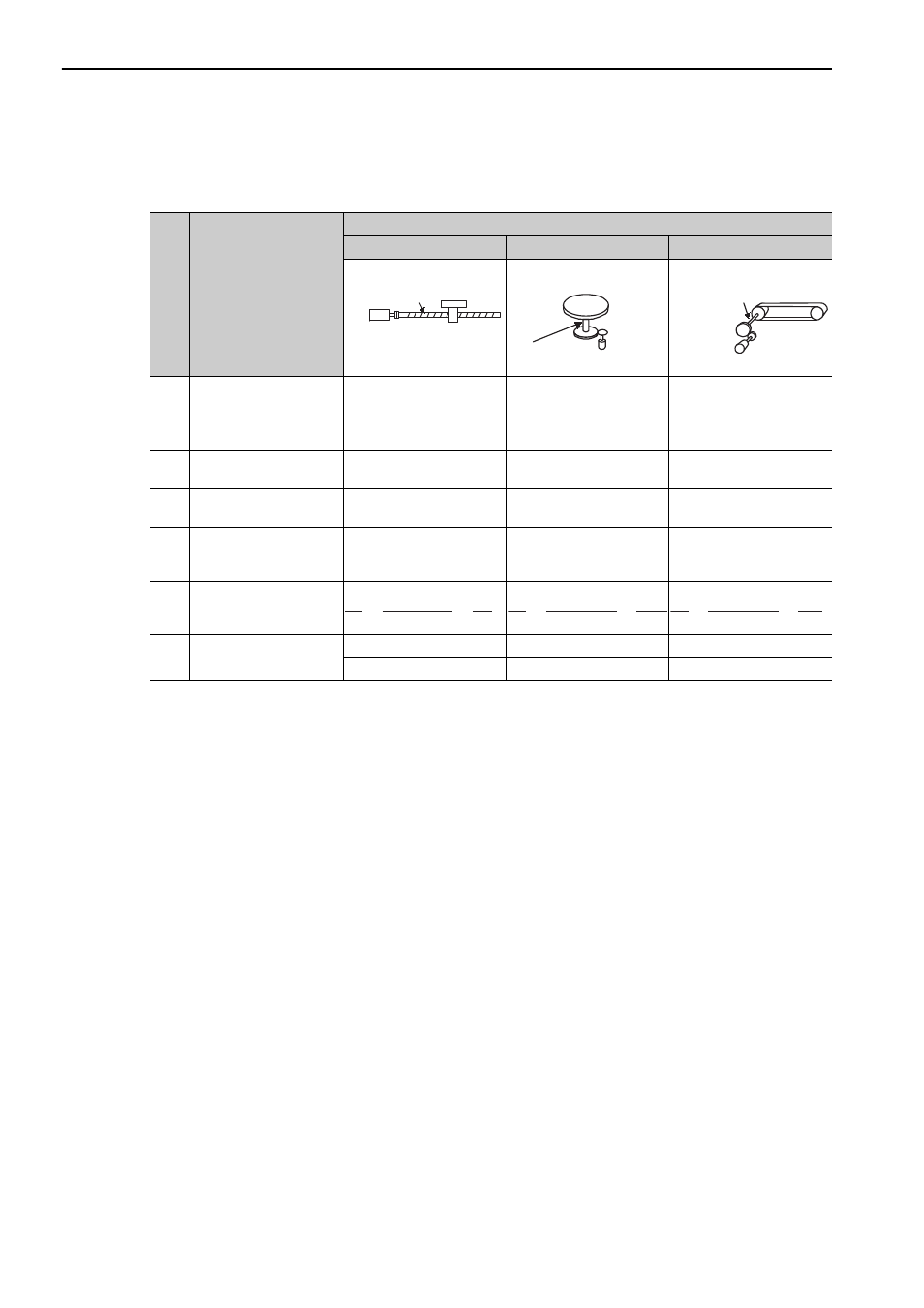
The following examples show electronic gear ratio settings for different load configurations.
Step
Operation
Load Configuration
Ball Screw
Disc Table
Belt and Pulley
1
Check machine specifica-
tions.
Ball screw pitch: 6 mm
Gear ratio: 1/1
Rotation angle per revolu-
tion: 360
°
Gear ratio: 1/100
Pulley diameter: 100 mm
(pulley circumference: 314
mm)
• Gear ratio: 1/50
2
Check the encoder reso-
lution.
1048576 (20-bit)
1048576 (20-bit)
1048576 (20-bit)
3
Determine the reference
unit used.
Reference unit: 0.001 mm
(1
μm)
Reference unit: 0.01
°
Reference unit: 0.005 mm
(5
μm)
4
Calculate the travel dis-
tance per load shaft revo-
lution. (Reference unit)
6 mm/0.001 mm = 6000
360
°/0.01° = 36000
314 mm/0.005 mm =
62800
5
Calculate the electronic
gear ratio.
6
Set parameters.
Pn20E: 1048576
Pn20E: 104857600
Pn20E: 52428800
Pn210: 6000
Pn210: 36000
Pn210: 62800
Ball screw
pitch: 6 mm
20-bit encoder
Load shaft
Reference unit: 0.001 mm
20-bit encoder
Load shaft
Reference unit: 0.01
°
Gear ratio:
1/100
Load shaft
Gear ratio
1/50
Reference unit: 0.005 mm
Pulley diameter:
100 mm
20-bit encoder
1048576
6000
1
1
=
B
A
B
A
1048576
36000
100
1
=
B
A
1048576
62800
50
1
=
