Typical rrpp networking, Single ring, Tangent rings – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 79
7-8
master node before the Fast-Fail timer expires, the entire ring is in Health state; otherwise,
the ring transits into Disconnect state.
z
The edge node sends Fast-Edge-Hello packets out its common ports at the interval
specified by the timer resolution. If the assistant-edge node fails to receive the
Fast-Edge-Hello packets within three times the timer resolution, the SRPTs transit to
Disconnect state.
As shown in
, with fast detection enabled for RRPP domain 1, Device A, the master
node of Ring 1, sends out Fast-Hello packets periodically and determines the ring status
according to whether Fast-Hello packets are received before the Fast-Fail timer expires, thus
implementing link status fast detection.
z
The timer resolution refers to the shortest-period timer provided on an RRPP node.
z
To implement fast detection on an RRPP ring, enable fast detection on the master node,
edge node, and assistant-edge node of the RRPP ring.
Typical RRPP Networking
Here are several typical networking applications.
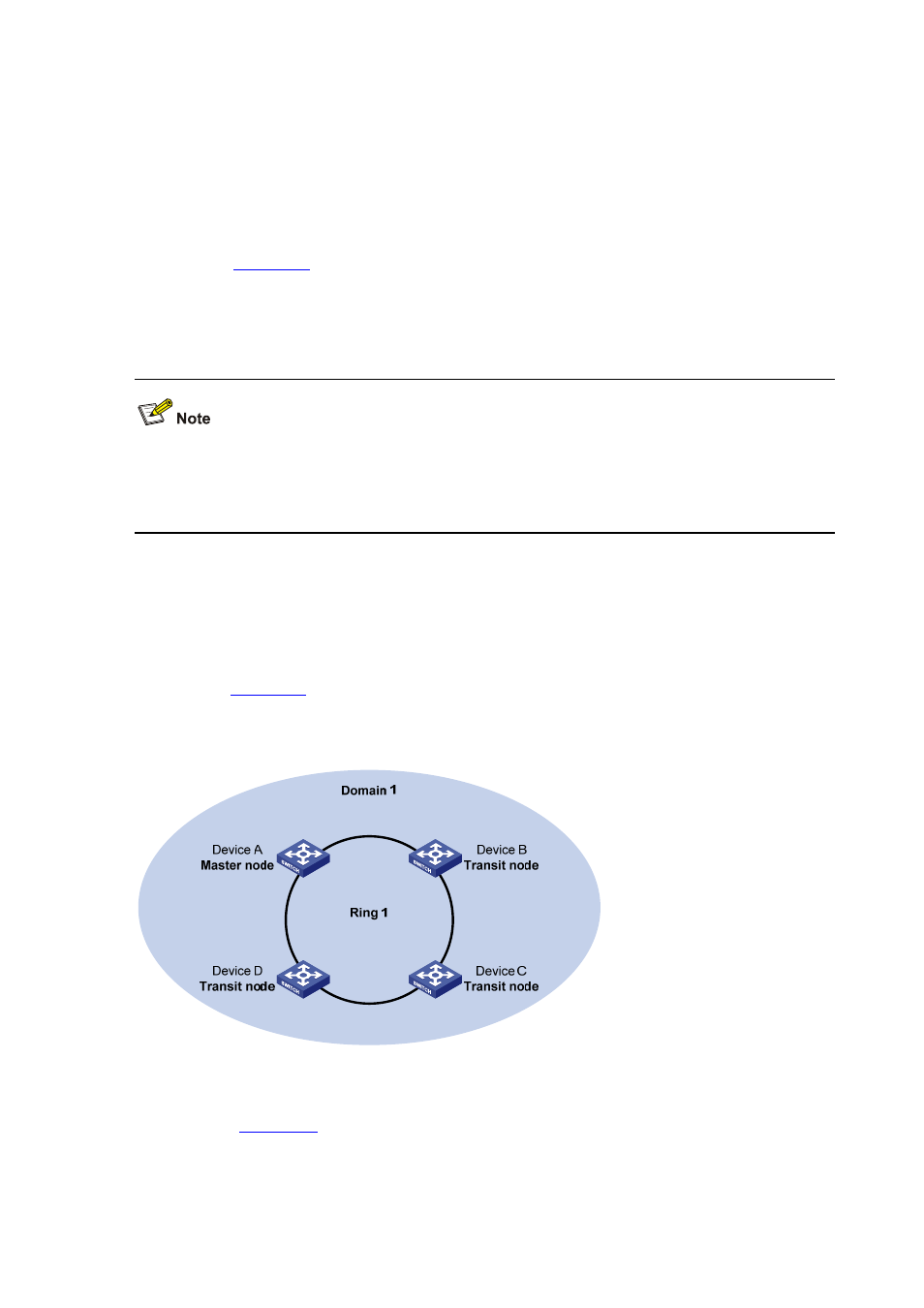
Single ring
As shown in
, there is only a single ring in the network topology. In this case, you only
need to define an RRPP domain.
Figure 7-2 Schematic diagram for a single-ring network
Tangent rings
As shown in
, there are two or more rings in the network topology and only one
common node between rings. In this case, you need to define an RRPP domain for each ring.
