Multicast packet forwarding mechanism, Multicast protocols – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 21
11
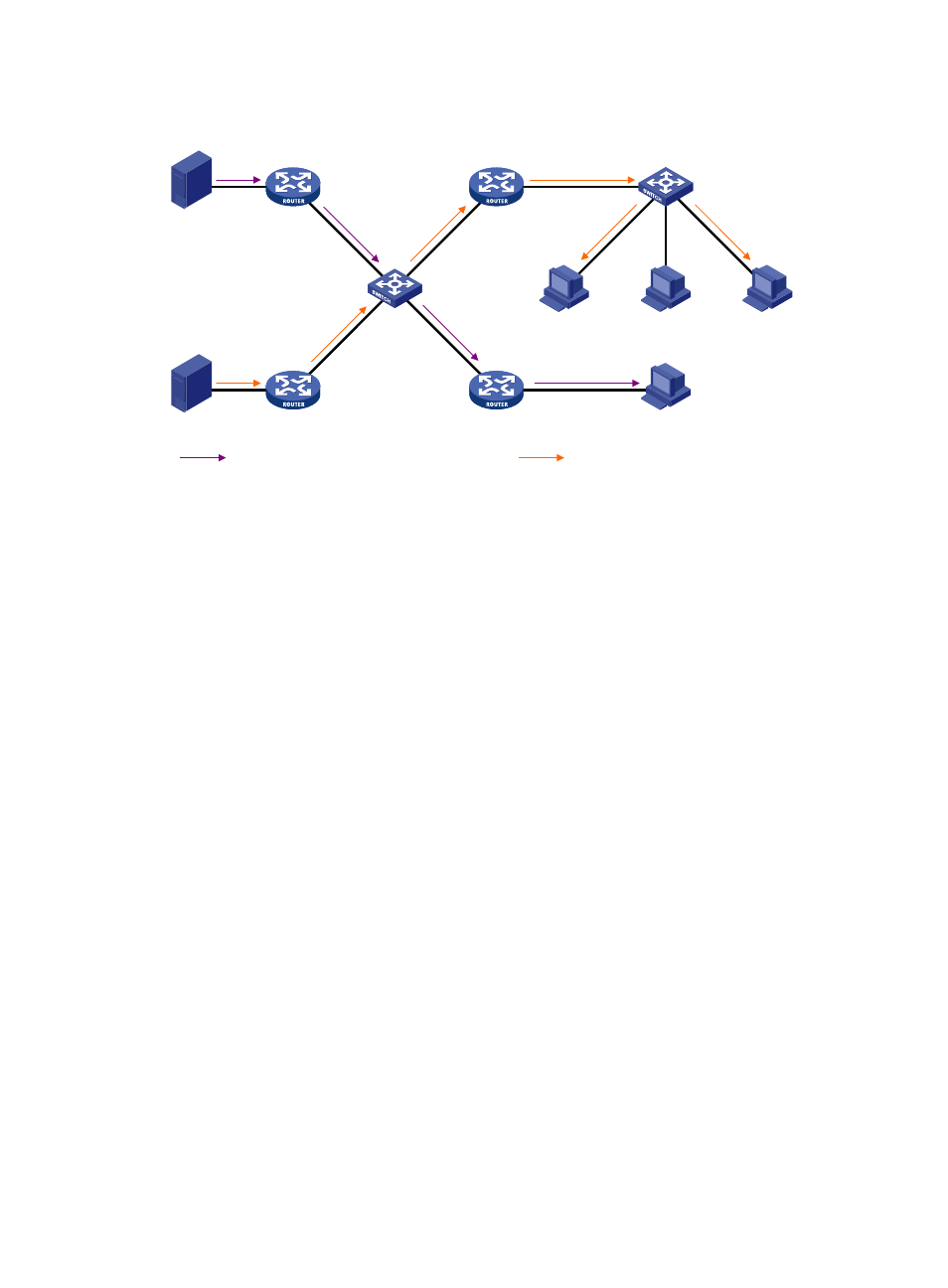
Figure 9 Positions of Layer 2 multicast protocols
•
IGMP snooping and MLD snooping:
IGMP snooping and MLD snooping run on Layer 2 devices as multicast constraining mechanisms
to improve multicast forwarding efficiency. They generate Layer 2 multicast forwarding tables by
listening to IGMP or MLD messages exchanged between the hosts and Layer 3 multicast devices,
and manage and control multicast data forwarding on demand in Layer 2 networks.
•
PIM snooping and IPv6 PIM snooping:
PIM snooping and IPv6 PIM snooping run on Layer 2 devices. They work with IGMP snooping or
MLD snooping to analyze received PIM messages, and add the ports that are interested in specific
multicast data to a PIM snooping routing entry or IPv6 PIM snooping routing entry. In this way,
multicast data can be forwarded to only the ports that are interested in the data.
•
Multicast VLAN and IPv6 multicast VLAN:
In the traditional multicast-on-demand mode, when users in different VLANs on a Layer 2 device
need multicast information, the upstream Layer 3 device must forward a separate copy of the
multicast data to each VLAN of the Layer 2 device. When the multicast VLAN or IPv6 multicast
VLAN feature is enabled on the Layer 2 device, the Layer 3 multicast device sends only one copy
of multicast to the multicast VLAN or IPv6 multicast VLAN on the Layer 2 device. This method
avoids waste of network bandwidth and extra burden on the Layer 3 device.
Multicast packet forwarding mechanism
In a multicast model, a multicast source sends information to the host group identified by the multicast
group address in the destination address field of IP multicast packets. To deliver multicast packets to
receivers located at different positions of the network, multicast routers on the forwarding paths usually
need to forward multicast packets that an incoming interface receives to multiple outgoing interfaces.
Compared to a unicast model, a multicast model is more complex in the following aspects:
•
To ensure multicast packet transmission in the network, unicast routing tables, routing tables for
multicast (for example, the MBGP routing table), and static multicast routes must be used as
guidance for multicast forwarding.
•
To process the same multicast information from different peers received on different interfaces of the
same device, every multicast packet undergoes a reverse path forwarding (RPF) check on the
IPv4/IPv6 multicast packets (S1, G1)
IPv4/IPv6 multicast packets (S2, G2)
Source 1
Source 2
Receiver
IGMP Snooping
/MLD Snooping
Receiver
Receiver
Multicast VLAN
/IPv6 Multicast VLAN
PIM Snooping
/IPv6 PIM Snooping
- H3C S9800 Series Switches H3C S5560 Series Switches H3C S5130 Series Switches H3C S5120 Series Switches H3C S12500 Series Switches H3C SR8800 H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module
