Mldv2 enhancements, Enhancements in control capability of hosts – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 146
136
1.
The host sends an MLD done message (with the destination of FF02::2) to all IPv6 multicast routers
on the local subnet.
2.
After receiving the MLD done message, the querier sends a configurable number of
multicast-address-specific queries to the group that the host is leaving. The IPv6 multicast addresses
queried include both the destination address field and the group address field of the message.
3.
One of the remaining members (if any on the subnet) of the group sends a report within the time
of the maximum response delay advertised in the query messages.
4.
If the querier receives a report for the group within the maximum response delay time, it maintains
the memberships of the IPv6 multicast group. Otherwise, the querier assumes that no hosts on the
subnet are interested in IPv6 multicast traffic addressed to that group and stops maintaining the
memberships of the group.
MLDv2 enhancements
MLDv2 is based on and backwards-compatible with MLDv1. MLDv2 provides hosts with enhanced
control capabilities and enhances the MLD state.
Enhancements in control capability of hosts
MLDv2 has introduced IPv6 multicast source filtering modes (Include and Exclude). These modes allow
a host to join a designated IPv6 multicast group and to choose whether to receive or reject multicast data
from designated IPv6 multicast sources. When a host joins an IPv6 multicast group, one of the following
occurs:
•
If the host expects IPv6 multicast data from specific IPv6 multicast sources like S1, S2, …, it sends a
report with Filter-Mode denoted as "Include Sources (S1, S2, …)."
•
If the host does not expect IPv6 multicast data from specific IPv6 multicast sources like S1, S2, …,
it sends a report with Filter-Mode denoted as "Exclude Sources (S1, S2, …)."
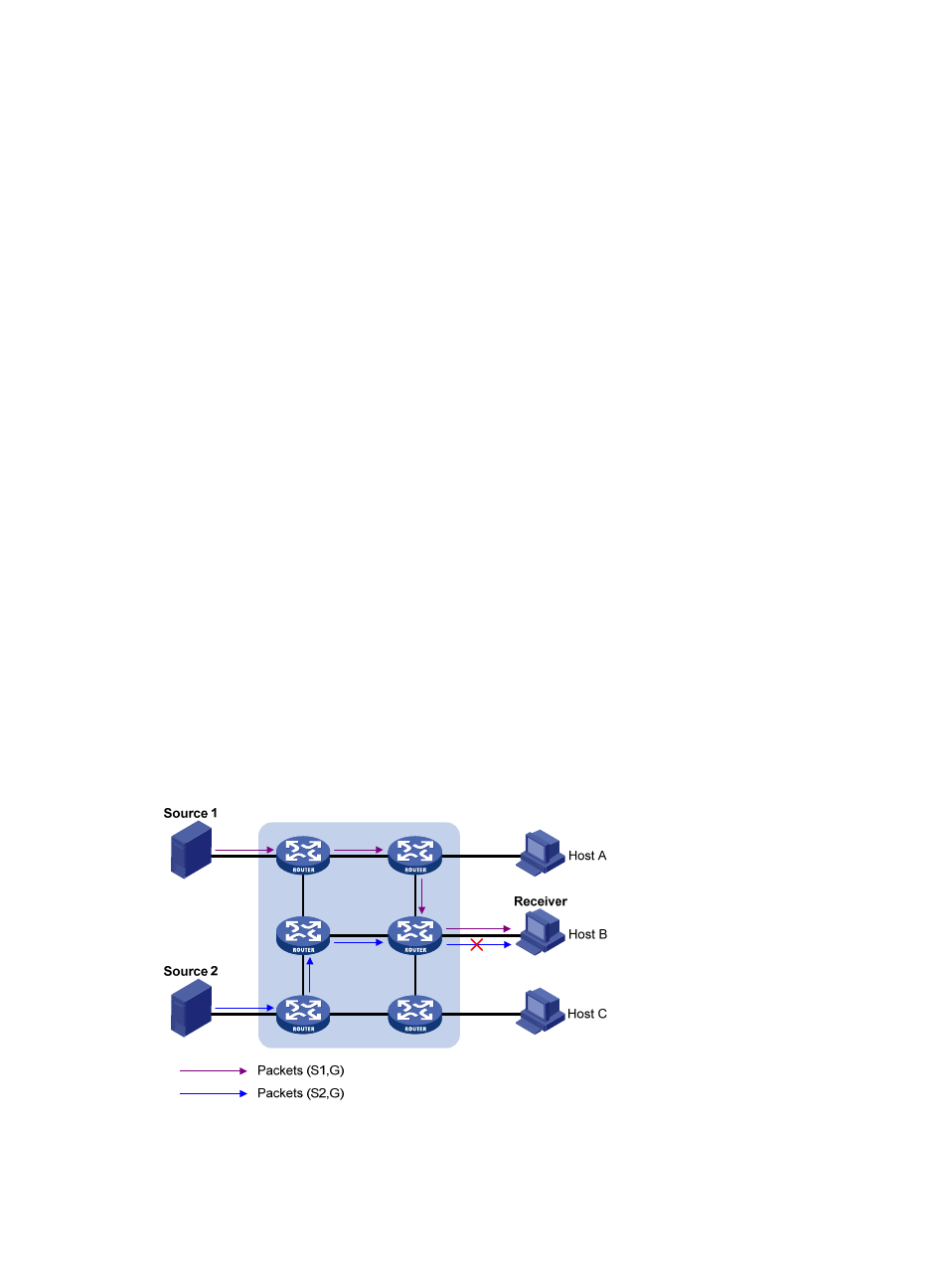
As shown in
, the network has two IPv6 multicast sources, Source 1 (S1) and Source 2 (S2). Both
of them can send IPv6 multicast data to IPv6 multicast group G. Host B is interested only in the IPv6
multicast data that Source 1 sends to G but not in the data from Source 2.
Figure 42 Flow paths of multicast-address-and-source-specific multicast traffic
In MLDv1, Host B cannot select IPv6 multicast sources when it joins IPv6 multicast group G, and IPv6
multicast streams from both Source 1 and Source 2 flow to Host B whether it needs them or not.
- H3C S9800 Series Switches H3C S5560 Series Switches H3C S5130 Series Switches H3C S5120 Series Switches H3C S12500 Series Switches H3C SR8800 H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module
