Rpf check implementation in ipv6 multicast – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 139
129
RPF check implementation in IPv6 multicast
Implementing an RPF check on each received IPv6 multicast packet would heavily burden the router. The
IPv6 multicast forwarding table is the solution to this issue. When the router creates an IPv6 multicast
routing entry and an IPv6 multicast forwarding entry for an IPv6 multicast packet, it sets the RPF interface
of the packet as the incoming interface of the forwarding entry. After the router receives an IPv6 multicast
packet on an interface, it searches its IPv6 multicast forwarding table:
•
If no forwarding entry matches the packet, the packet undergoes an RPF check. The router creates
an IPv6 multicast routing entry with the RPF interface as the incoming interface and adds the entry
to the IPv6 multicast forwarding table.
{
If the receiving interface is the RPF interface, the RPF check succeeds and the router forwards the
packet out of all outgoing interfaces.
{
If the receiving interface is not the RPF interface, the RPF check fails and the router discards the
packet.
•
If a forwarding entry matches the packet, and the receiving interface is the incoming interface of the
forwarding entry, the router forwards the packet out of all outgoing interfaces.
•
If a forwarding entry matches the packet, but the receiving interface is not the incoming interface of
the forwarding entry, the IPv6 multicast packet undergoes an RPF check.
{
If the RPF interface is the incoming interface, it means that the forwarding entry is correct but the
packet traveled along a wrong path. The router discards the packet.
{
If the RPF interface is not the incoming interface, it means that the forwarding entry has expired,
and the router replaces the incoming interface with the RPF interface. If the receiving interface
is the RPF interface, the router forwards the packet out of all outgoing interfaces. Otherwise, it
discards the packet.
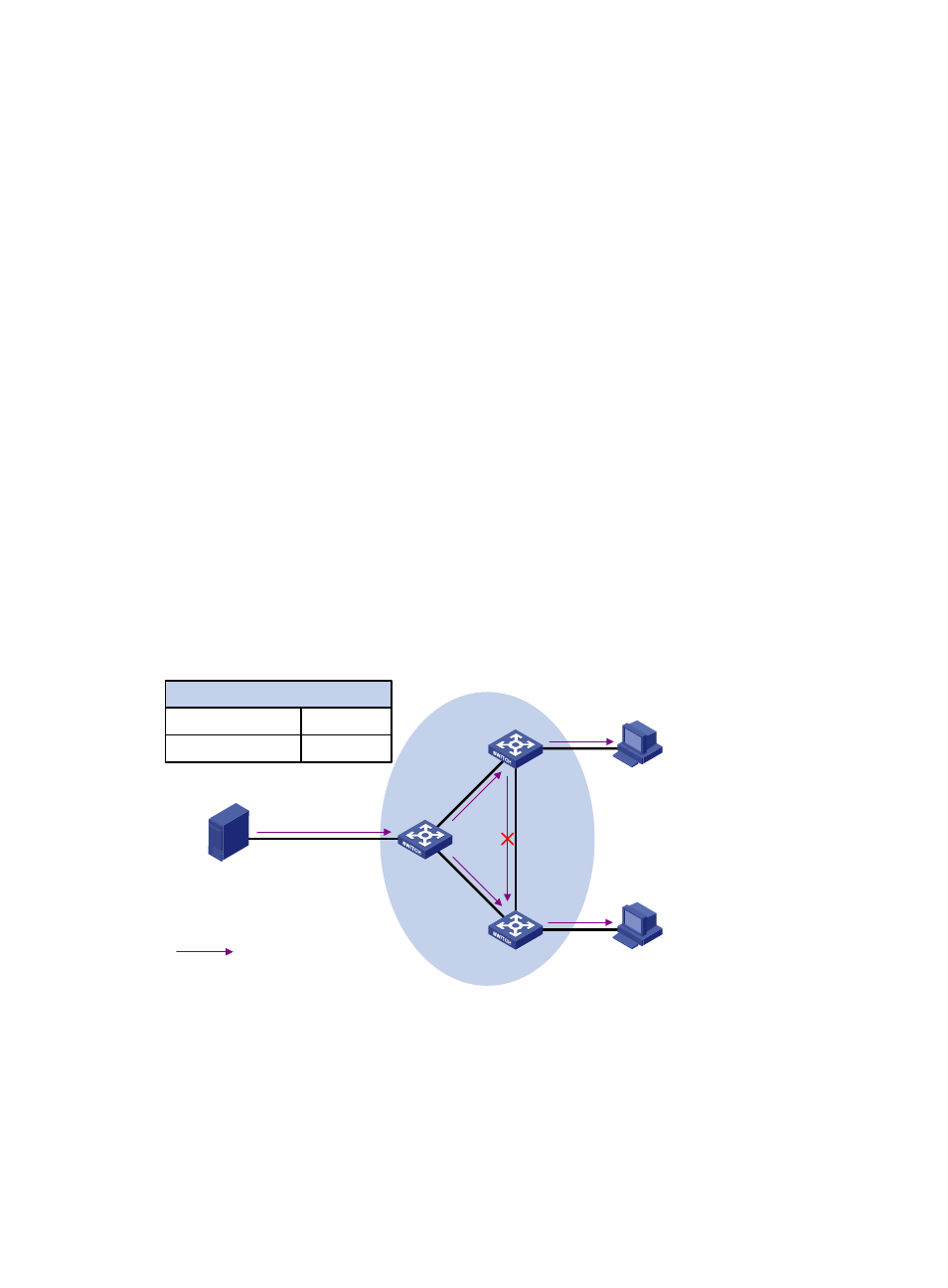
Figure 40 RPF check process
As shown in
, assume that IPv6 unicast routes are available in the network, and IPv6 multicast
packets travel along the SPT from the multicast source to the receivers. The IPv6 multicast forwarding table
on Switch C contains the (S, G) entry, with VLAN-interface 20 as the RPF interface.
•
When VLAN-interface 20 of Switch C receives an IPv6 multicast packet, because the interface is the
incoming interface of the (S, G) entry, the router forwards the packet out of all outgoing interfaces.
•
When VLAN-interface 10 of Switch C receives an IPv6 multicast packet, because the interface is not
the incoming interface of the (S, G) entry, the router performs an RPF check on the packet. The router
Receiver
Receiver
Source
2000::101/16
Switch A
Switch B
Switch C
Vlan-int20
Vlan-int10
Vlan-int10
IPv6 Multicast packets
Destination/Prefix
IPv6 Routing Table on Switch C
2000::/16
Interface
Vlan-int20
- H3C S9800 Series Switches H3C S5560 Series Switches H3C S5130 Series Switches H3C S5120 Series Switches H3C S12500 Series Switches H3C SR8800 H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module
