Tos switching, Tos background, Tos background . . . . . . . . . . . . . . b-18 – Comtech EF Data CDD-56X Series Vipersat User Manual
Page 118: Figure b-8 tos field location within the ip header
ToS Switching
MN/22137, rev 1
B-18
Vipersat CDD-56X Series User Guide
ToS Switching
ToS Background
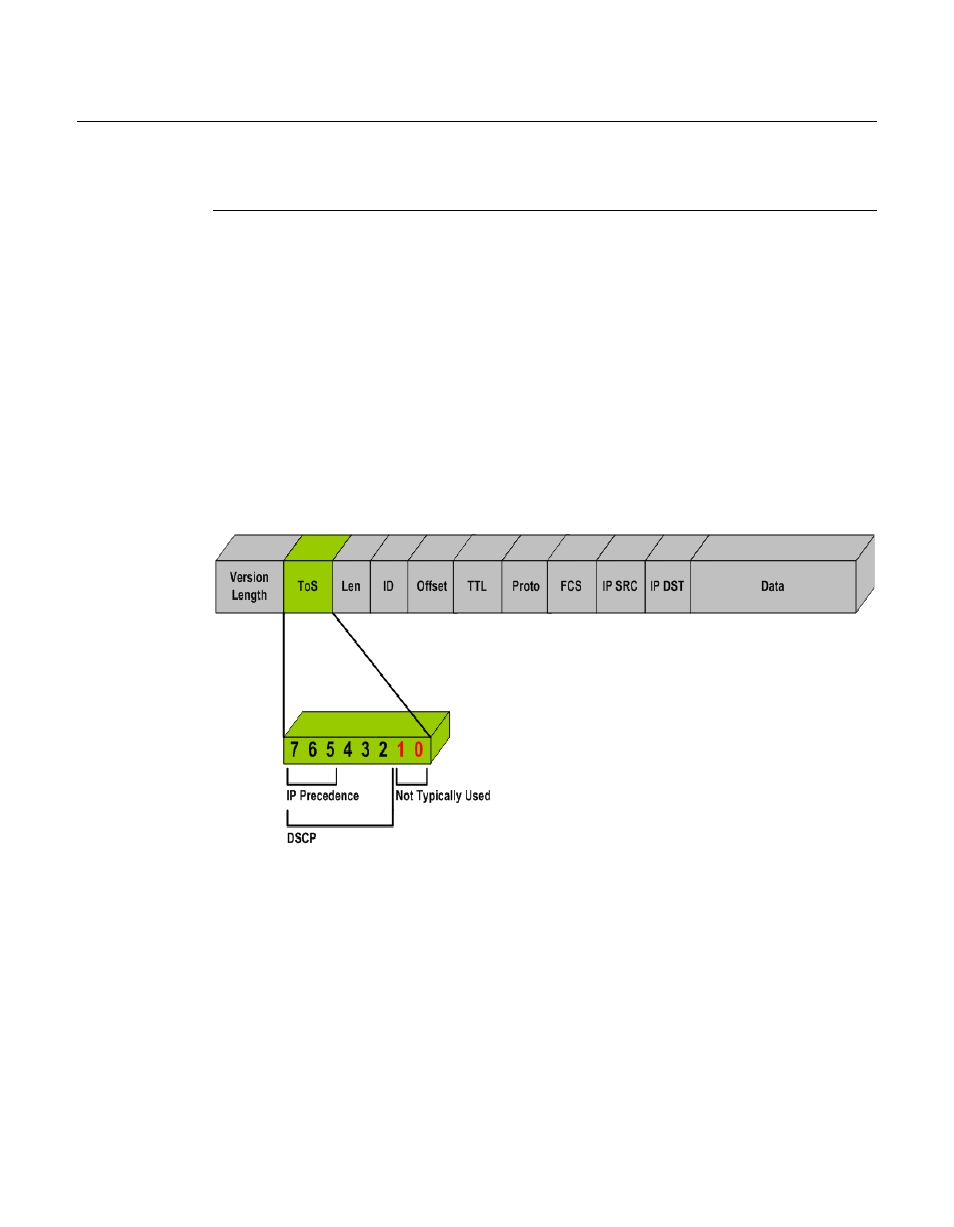
The Type of Service (ToS) byte is an 8-bit field contained within the IP header
portion of an IPv4 packet. This field provides a means of marking packets for
traffic identification and classification purposes. Devices within the network
can utilize the ToS value to classify traffic and apply per hop queuing and Qual-
ity of Service (QoS) for different types of traffic.
The first 3 bits of the ToS byte are referred to as IP precedence bits. The IP
precedence bits and the next 3 bits combined are known as the Differentiated
Services Code Point bits (DSCP). The 6 bits of DSCP allow for 63 discrete traf-
fic identifiers. The DSCP field is the portion of the ToS byte that can be
detected by the SLM-5650A modems and can be used for dSCPC switching
within a Vipersat network. Figure B-8 provides a graphical representation of the
ToS field within an IPv4 packet.
Figure B-8 ToS Field Location within the IP Header
The process of marking a packet with a ToS value is typically done in one of
two places, either by the application device itself (e.g., VoIP phone), or by the
packet marking capabilities of a network device such as a router.
Encrypted networks often pose additional limitations for prioritizing and classi-
fying traffic. When encryption is applied to an IP packet, a majority of the infor-
mation is no longer available for classification. Application layer protocols can
no longer be detected by routers for classification purposes. In many encrypted
environments the IP header, which includes the ToS value, typically remains in
