Structure types, Structure types –6 – Altera FIR Compiler User Manual
Page 48
4–6
Chapter 4: Functional Description
FIR Compiler
© May 2011
Altera Corporation
If you select multiple-set coefficients, the filter can update one coefficient set while
another set is being used for a calculation.
Structure Types
The FIR Compiler wizard generates multicycle variable, parallel, serial, multibit
serial, and multichannel structures. All of these structures support coefficient
reloading.
For information about reordering the coefficients before reloading them, refer to
“Coefficient Reloading and Reordering” on page 4–4
Multicycle Variable Structures
Multicycle variable (MCV) filters are optimized for high throughput. In a multicycle
variable structure, the designer specifies that the filter uses 1 to 1,024 clock cycles to
compute a result (for any filter that fits into a single device).
For Stratix, Stratix II, Stratix III, or Stratix IV devices, if you select the multicycle
variable structure, selecting DSP Blocks in the Multiplier list box allows the FIR
Compiler to use embedded DSP blocks for multipliers. This implementation results in
a smaller and faster design.
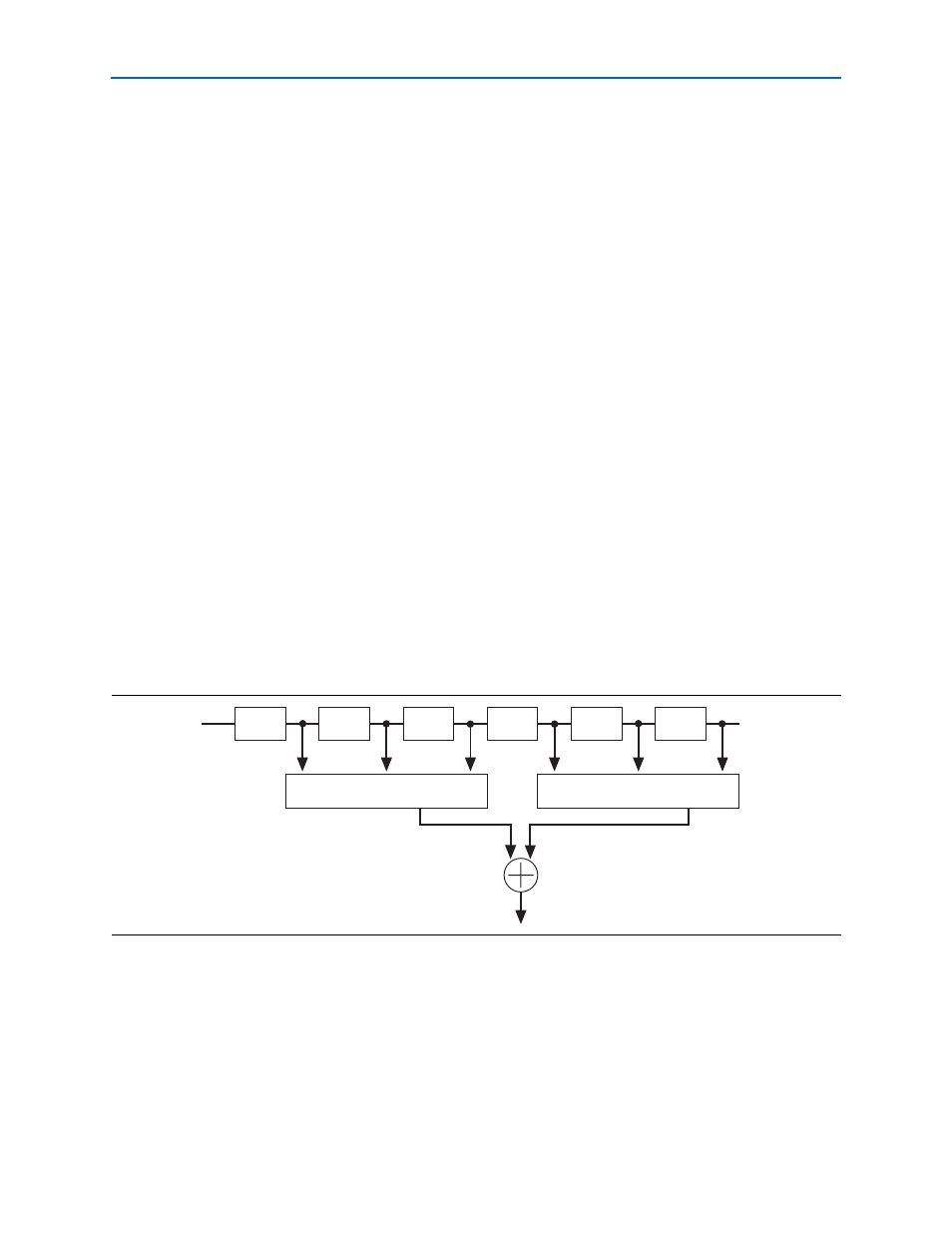
Parallel Structures
A parallel structure calculates the filter output in a single clock cycle. Parallel filters
provide the highest performance and consume the largest area. Pipelining a parallel
filter allows you to generate filters that run between 120 and 300 MHz at the cost of
pipeline latency.
shows the parallel filter block diagram.
Figure 4–3. Parallel Filter Block Diagram
yout
Array Multiplier
Array Multiplier
xin
xout
D Q
D Q
D Q
D Q
D Q
D Q
