Sampling methods – EXFO PSO-200 Optical Modulation Analyzer User Manual
Page 248
Coherent Detection and Sampling Methods
240
PSO-200
Sampling Methods
Thus, the detected signals correspond to the I and Q axes in the signal
space. The equation above is valid for co-polarized signal and LO. In order
for the coherent receiver to be polarization independent, a second
(identical) branch handles the orthogonal state of polarization (SOP). In
order to retrieve E
s
(t) and
s
(t), the IF must be tracked and removed from
the measured signal, which is carried out with advanced signal processing.
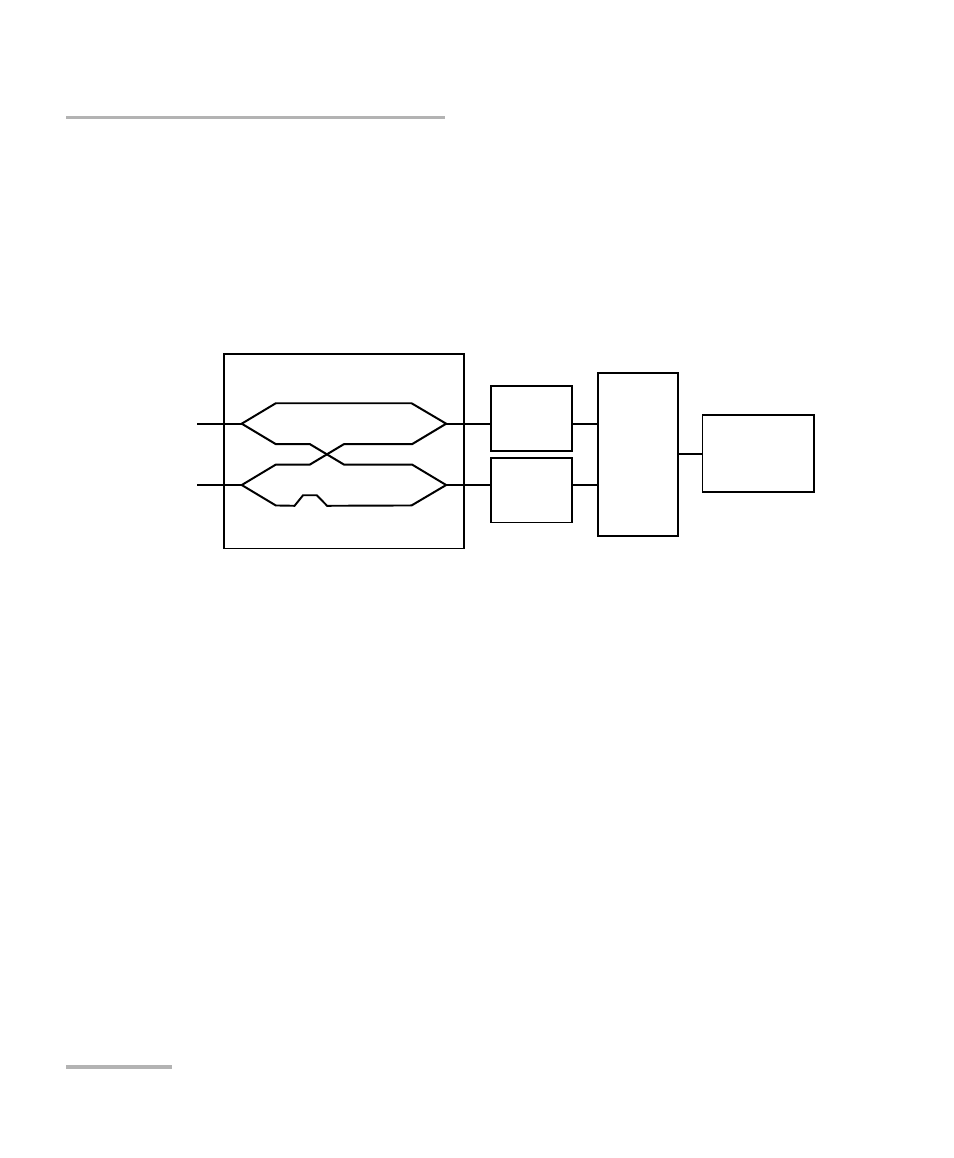
The diagram below shows a coherent receiver for a single SOP:
Sampling Methods
Digital sampling is used to visualize time-varying signals. The basic
principle is that a snapshot of the signal is acquired by a sampling gate. The
gate opens for a small fraction of a second and the signal is quantized by
analog-to-digital conversion (ADC).
In general, electronic sampling gates are used. However, for optical
measurements, it is preferable to implement optical sampling gates. The
benefit is that the sampling bandwidth can be significantly increased;
optical sampling systems with >500 GHz bandwidth exist.
Optical sampling gates can be implemented by exploiting nonlinearities in
optical fibers or crystals to create an ultra-high-speed optical switch, or, as
an alternative, via linear optical sampling. The latter method is unique in
that it obtains the optical field in the sampling process itself.
Digital sampling can be implemented as real-time sampling or
equivalent-time sampling. The PSO-200 uses the latter.
Signal
Processing
LO input
/2
ADC
Balanced
detector
90
o
Optical hybrid
Signal input
Balanced
detector
