Managing memory, In figure 8, These – Echelon FTXL User Manual
Page 58
46
Creating a Model File
Device B
(reader)
1
2
3
4
ACKD Message or
Request
Challenge
Reply to challenge
ACK or Response
Device A
(Writer)
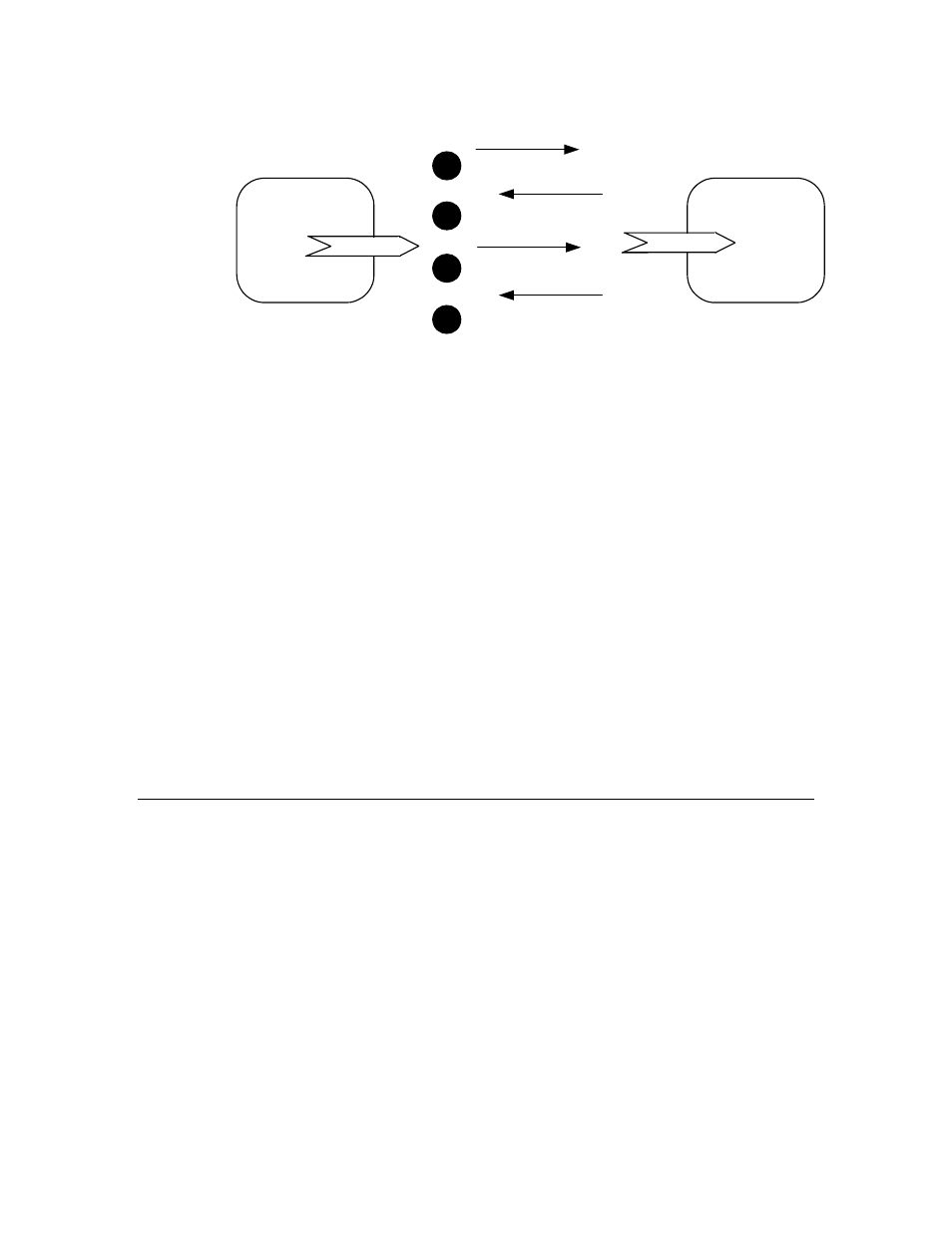
Figure 8. Authentication Process
If Device A attempts to update an output network variable that is connected to
multiple readers, each receiver device generates a different 64-bit random
number and sends it in a challenge packet to Device A. Device A must then
transform each of these numbers and send a reply to each receiver device.
The principal strength of authentication is that it cannot be defeated by simple
record and playback of commands that implement the desired functions (for
example, unlocking the lock). Authentication does not require that the specific
messages and commands be secret, because they are sent unencrypted over the
network, and anyone who is determined can read those messages.
It is good practice to connect a device directly to a network management tool
when initially installing its authentication key. This direct connection prevents
the key from being sent over the network, where it might be detected by an
intruder. After a device has its authentication key, a network management tool
can modify the key, over the network, by sending an increment to be added to the
existing key.
You can update the device’s address without having to update the key, and you
can perform authentication even if the devices’ domains do not match. Thus, an
FTXL device can set its key during device manufacturing, and you can then use a
network management tool to update the key securely over the network.
Managing Memory
The LonTalk Interface Developer Neuron C compiler generates four tables that
affect memory usage. The FTXL LonTalk protocol stack and network
management tools use these tables to define the network configuration for a
device. The LonTalk Interface Developer utility allocates space for the following
tables:
• The address table
• The alias table
• The domain table
• The network variable configuration table
See the
LonTalk Control Network Protocol Specification
, EIA/CEA 709.1-B-2002,
for more information about these tables. This document is available from the
IHS Standards Store:
