Basic pixel-mapping, Overview – PRG Mbox Studio Manual 3.8 User Manual
Page 86
78
MBOX
®
STUDIO USER MANUAL
BASIC PIXEL-MAPPING
Note: The Mbox Studio pixel-mapping has a limit of 6144 patched pixels. These pixels can be spread across as
many output Art-Net universes as desired.
Overview
The Mbox software allows mapping of certain functions of Color Kinetics KiNET or Art-Net-controlled fixtures (RGB,
Intensity, CMY, etc.) to each of the pixels in the composite video image. Pixel-mapping data is generated from the
screen image and is output from an available Ethernet port of the Mac computer. It may be necessary to use an Art-
Net to DMX512 converter to change the data into a more suitable protocol if the device intended to be controlled
cannot receive Art-Net directly. KiNET devices will receive that protocol directly over Ethernet. When pixel-mapping,
Mbox retains the normal video output so a video signal can still be sent to a display device. Mbox also provides the
ability to previsualize the pixel-mapping setup on the video monitor.
Using Pixel-Mapping with Different Modes:
+
While in Single Output mode, the entire screen can be mapped.
+
While in Panoramic Wide and Panoramic Dual modes, the entire width of the two screens can be mapped.
+
While in Dual Independent mode, only first screen (Output 1) can be mapped.
When pixel-mapping, it is advisable to use a
second Ethernet port on the Mac to output
the pixel-mapping data. If the Art-Net input
and the pixel-mapping output share a single
Ethernet port, the volume of network traffic
generated by complex pixel-mapping
configurations will affect the reception of Art-
Net control data. If you want to use two
different ports for Art-Net input and pixel-
mapping Art-Net output you will need to set
up the Ethernet ports of your computer
properly. Some knowledge of IP addressing
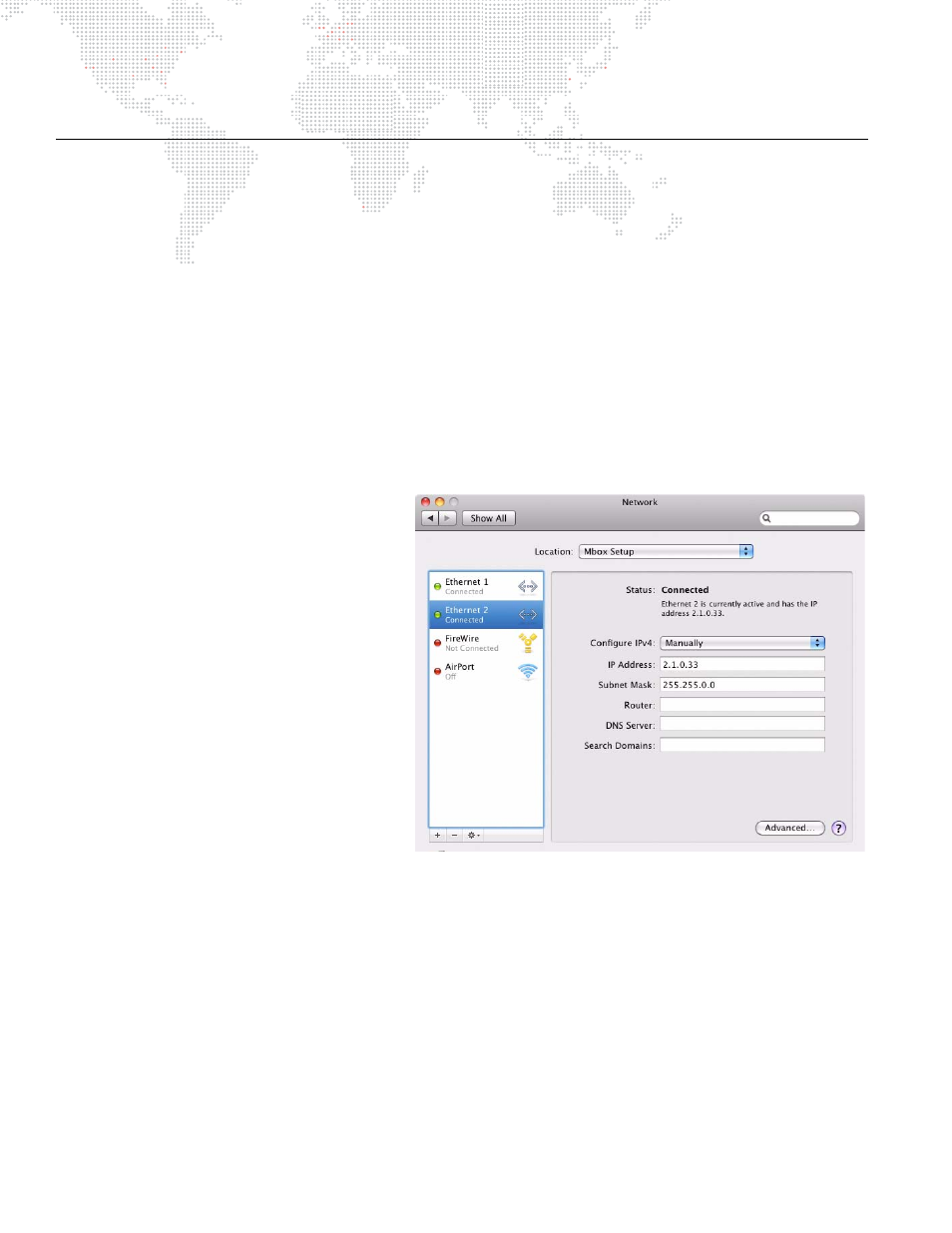
and subnetting practices is required..
Network settings can be changed from the
Mac’s Network preferences window.
The following guidelines assume that your
computer's first Ethernet port is set to receive
Art-Net to control Mbox and you are using a
second Ethernet port to output pixel-mapping
data.
+
Art-Net is typically sent to the broadcast destination IP address for the local network being used. For Art-Net this
destination address is usually 2.255.255.255. Art-Net can also be unicast (sent to one specific IP address). Mbox
Art-Net output can automatically be unicast to ArtPOLL compliant devices.
+
KiNET devices have user-configurable IP addresses, therefore, the computer's Ethernet port will need to be set
up accordingly to use the same subnet. Destination IP addresses for KiNET are always unicast.
+
If your computer uses an overlapping or ambiguous IP/subnet scheme for the two Ethernet ports, then your pixel-
mapping output may not be routed from the correct Ethernet port on your computer resulting in a lack of function.
You must ensure that the two ports have settings that allow Mbox to send the data from the correct port.
+
You must also coordinate the IP/subnet of the pixel-mapping output port with the destination IP address(es) in the
Mbox Pix Map Destination Settings (see
).
