Kontron NSN2U IP Network Server User Manual
Page 29
28
platform is {A1, B1, D1, E1}. {A1, B1} must be identical and {D1, E1} must be
identical. However, DIMMs do not need to be identical across sockets.
In this configuration, DIMMs {A1, B1} and {D1, E1} operate as (primary copy, secondary
copy) pairs independent from each other. Therefore, the optimal number of DDR3 DIMMs
for channel mirroring is a multiple of four, arranged as mentioned above. The BIOS
disables all non-identical DDR3 DIMMs or pairs of DDR3 DIMMs across the channels to
achieve symmetry and balance between the channels.
Mirroring DIMM Population Rules Variance Across Nodes
Memory mirroring in Intel
®
Xeon
®
Processor 5500 Series-based platforms is channel
mirroring. Mirroring is not done across sockets, so each socket may have a different
memory configuration. Channel mirroring in socket 1 and socket 2 is mutually
independent. As a result, if channel A and channel B DIMMs are populated identically
and channel D and channel E DIMMs are identically populated, then mirroring is
possible even if the DIMMs in each socket are not identical with the DIMMs in the
other socket, i.e., for channel A and channel D.
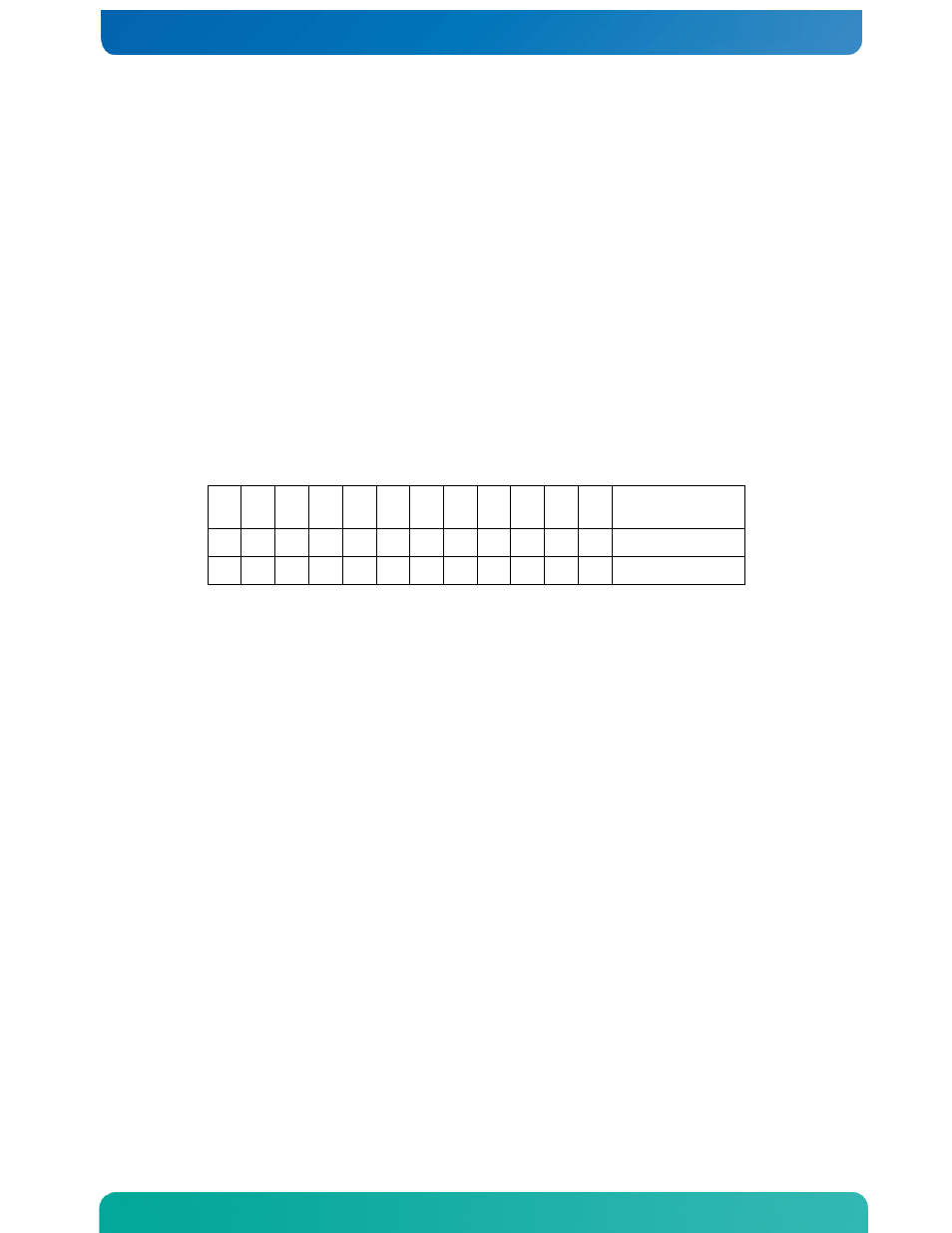
For example, if the system is populated with six DIMMS {A1, B1, A2, B2, D1, E1},
channel mirroring is possible. Both socket populations shown in the following table
are valid.
Table 4. Mirroring DIMM Population Rules Variance across Nodes
A1 A2 B1 B2 C1 C2 D1 D2 E1 E2 F1 F2
Mirroring
Possible?
P
P
P
P
YES
P
P
P
P
P
P
YES
Memory Upgrade Rules
Upgrading the system memory requires careful positioning of the DDR3 DIMMs based on
the following factors:
•
Current RAS mode of operation
•
Existing DDR3 DIMM population
•
DDR3 DIMM characteristics
•
Optimization techniques used by the Intel® Xeon® Processor 5500 Series to maximize
memory bandwidth
In the Channel Independent mode, all DDR3 channels operate independently. Slot to slot
DIMM matching is not required across channels, that is, A1 and B1 do not have to match
with each other in terms of size, organization, and timing. DIMMs within a channel can
be of different size and organization but they operate in the maximum common
frequency. The Channel Independent mode can also be used to support a single DIMM
configuration in channel A and in the single channel mode.
The following general rules must be observed when selecting and configuring memory to
obtain the best performance from the system:
•
Mixing RDIMMs and UDIMMs is not supported.
•
When CPU socket 1 is empty, any DIMM memory in channel A through channel C is
unavailable.
•
When CPU socket 2 is empty, any DIMM memory in channel D through channel F is
unavailable.
•
If both processor sockets are populated but channel A through channel C are empty,
the platform can still function with remote memory in channel D through channel F.
However, platform performance suffers latency with remote memory.
