Kontron NSN2U IP Network Server User Manual
Page 27
26
Memory Map and Population Rules
The nomenclature for DIMM sockets implemented on the Intel® Server Board T5520UR is
shown in Table X.
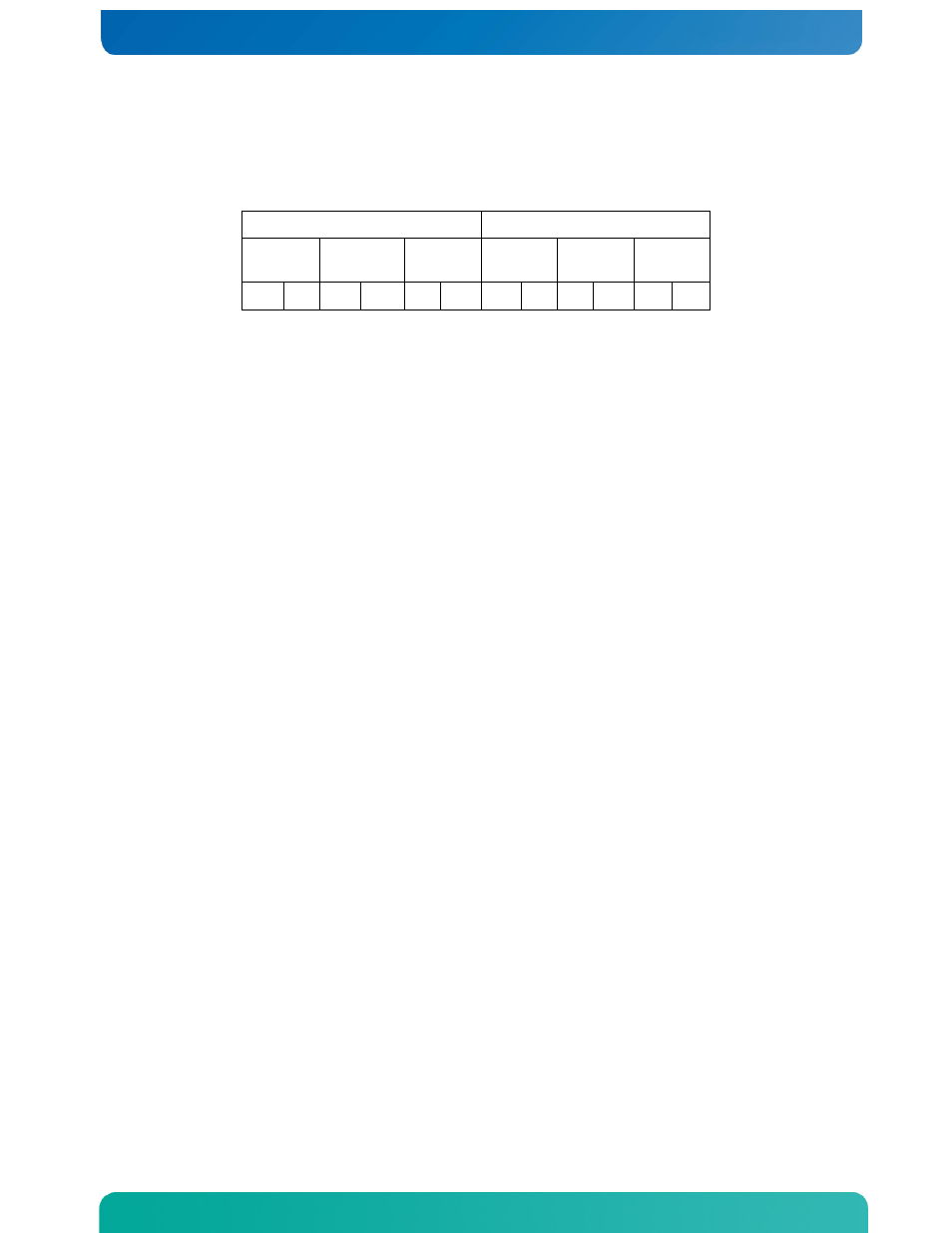
Table 2. Memory Map
Processor Socket 1
Processor Socket 2
Channel
A
Channel
B
Channel
C
Channel
D
Channel
E
Channel
F
A1 A2 B1 B2 C1 C2 D1 D2 E1 E2 F1 F2
Memory Population Rules
The T5520UR server board memory is implemented according to the following rules
•
DIMMs are organized into physical slots on DDR3 memory channels that belong to
processor sockets.
•
The memory channels from processor socket 1 are identified as Channel A, B, and C.
The memory channels from processor socket 2 are identified as Channel D, E, and F.
•
The silk screened DIMM slot identifiers on the board provide information about the
channel and the processor to which they belong.
For example, DIMM_A1 is the first slot on Channel A on processor 1; DIMM_D1 is the
first DIMM socket on Channel D on processor 2.
•
The memory slots associated with a given processor are unavailable if the given
processor socket is not populated.
•
A processor can be installed without populating the associated memory slots,
provided the other processor is installed with associated memory. In this case, the
memory is shared by the processors. However, the platform suffers performance
degradation and latency because of the remote memory accesses.
•
Processor sockets are self-contained and autonomous. However, all memory subsystem
support (i.e., Memory RAS, Error Management, etc.) in the BIOS setup are applied
commonly across processor sockets.
Memory RAS
The server board supports the following memory RAS features:
•
Channel Independent Mode
•
Channel Mirroring Mode
The memory RAS offered by the Intel® Xeon® Processor 5500 Series is done at the
channel level, i.e., during mirroring, channel B mirrors channel A. All DIMM matching
requirements are on a slot- to-slot basis on adjacent channels. For example, to enable
mirroring, corresponding slots on channel A and channel B must have DIMMS of identical
parameters. But DIMMs on adjacent slots on the same channel do not need identical
parameters.
If one socket fails the population requirements for RAS, the BIOS sets all six
channels to the Channel Independent mode. One exception to this rule is when all DIMM
slots for a socket are empty, for example, when only sockets A1, B1, C1 are populated,
mirroring is possible on the platform.
The memory slots of DDR3 channels from the Intel
®
Xeon
®
Processor 5500 Series should be
populated in a “farthest first” fashion. This holds true even in the Channel
Independent mode. This means, for example, that A2 cannot be populated/used if A1 is
empty.
