Rockwell Automation 20-COMM-K CANopen Adapter User Manual
Page 44
5-2
Using I/O Messaging
20-COMM-K CANopen Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM012B-EN-P
PDO Transmission Types
The transmission type (or data exchange type) parameter of a PDO specifies
the transmission mode and the triggering mode.
The transmission modes are:
•
Synchronous transmission
•
Asynchronous transmission
The adapter supports three PDO triggering modes:
•
COS (Change of State)
•
Cyclic
•
Remote Transmission Request (RTR)
The triggering mode is only relevant for TPDOs. For RPDOs, only the
transmission mode is important. To configure the PDOs, the adapter
parameters have to be adjusted and other settings made using a CANopen
configuration tool (for example, IXXAT CANopen Configuration Studio).
PDO Transmission Modes
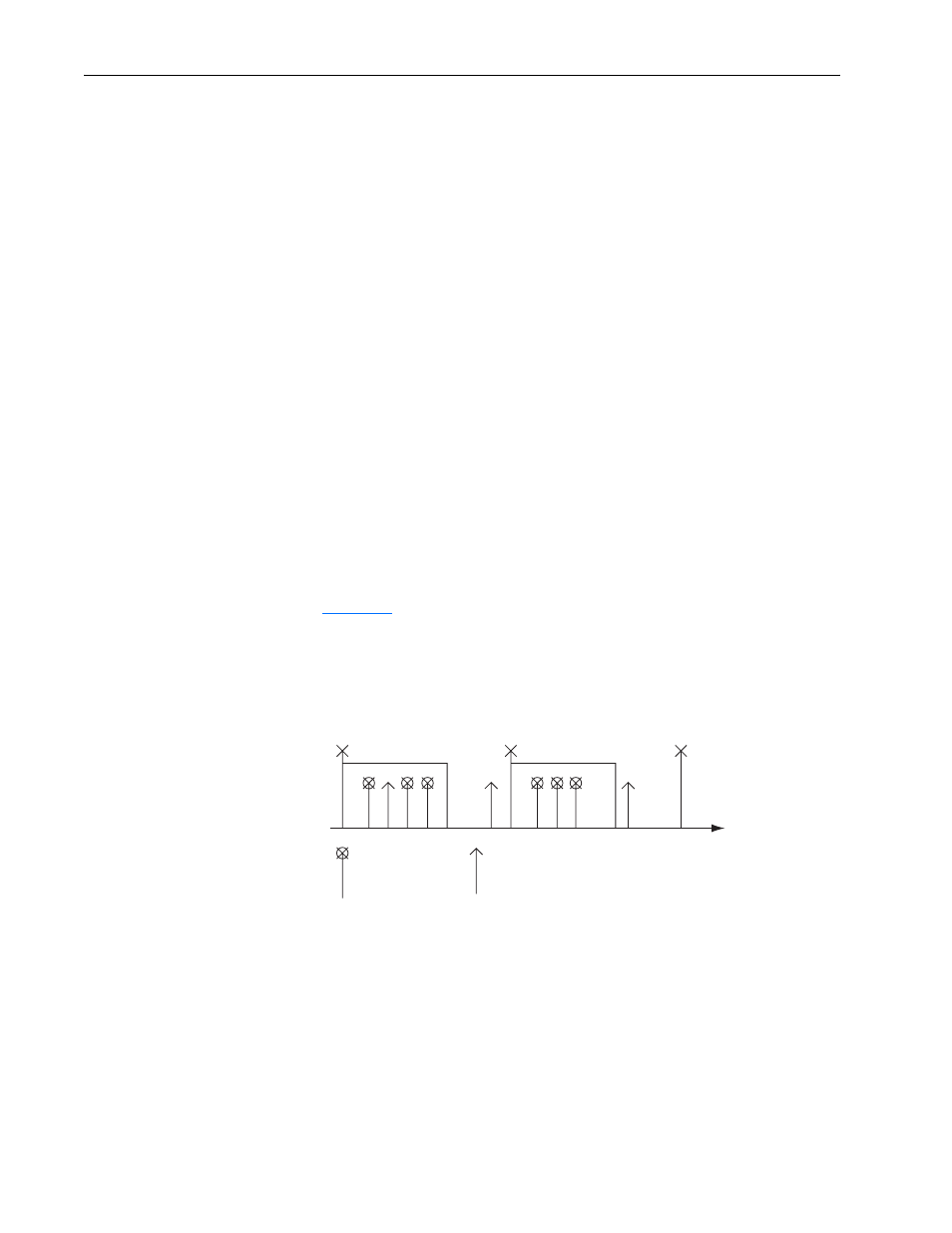
To synchronize devices, a synchronization object (SYNC object) is
transmitted periodically by a synchronization application (SYNC Master).
shows the principle of synchronous and asynchronous
transmission. The time between two SYNC objects is the Communication
Cycle Period.
Figure 5.1
Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission
Synchronous TPDO: The data for Synchronous TPDOs are sampled at the
moment the SYNC object is received. For COS and cyclic transmission, the
TPDOs are sent immediately after sampling (therefore, after the SYNC
object). For RTR transmission, the TPDOs are sent after the receipt of the
request message.
Asynchronous TPDO: Asynchronous TPDOs are transmitted without any
correlation to a SYNC. The data for asynchronous TPDOs are sampled
continuously.
Sync
Object
= Synchronous
PDOs
= Asynchronous
PDOs
Sync
Object
Sync
Object
Time
